Inflammation of the eyelids, known as blepharitis, can be addressed through various therapeutic avenues. Some individuals explore the potential of plant-derived remedies to alleviate the discomfort and manage the symptoms associated with this condition. Such approaches aim to reduce inflammation, soothe irritation, and promote overall eyelid hygiene using natural compounds. For instance, tea tree oil, chamomile, and eyebright are sometimes cited for their potential anti-inflammatory and antibacterial properties in the context of eyelid care.
The appeal of utilizing botanical elements stems from a desire for gentler, alternative methods of managing chronic conditions. Throughout history, various cultures have incorporated plants into their healthcare practices, and the exploration of their application for conditions such as blepharitis reflects a continuation of this tradition. Proponents suggest that natural substances may offer a complementary approach to conventional treatments, potentially minimizing reliance on synthetic medications. Careful selection and proper application are critical considerations.
This article will delve into specific botanical substances commonly considered for managing blepharitis, examining the available evidence supporting their use. The discussion will also cover potential risks and side effects associated with these treatments, emphasizing the importance of consulting with healthcare professionals before incorporating them into a treatment plan. Furthermore, the text will explore appropriate application methods and emphasize the role of complementary hygiene practices for optimizing outcomes.
Guidance on Botanical Approaches
The following recommendations aim to provide informed guidance regarding the adjunctive use of botanical substances in the management of blepharitis. These tips are not intended as a replacement for professional medical advice.
Tip 1: Prioritize Consultation. Before incorporating any plant-based remedy, consult with a qualified ophthalmologist or healthcare provider. This step is crucial to ensure the chosen treatment is appropriate for the individual’s specific condition and will not interfere with existing medications or underlying health concerns.
Tip 2: Emphasize Eyelid Hygiene. Regardless of the chosen therapeutic path, diligent eyelid hygiene remains paramount. This includes warm compresses to loosen debris, followed by gentle scrubbing of the eyelid margin with a diluted, pH-balanced cleanser.
Tip 3: Exercise Caution with Tea Tree Oil. Tea tree oil is sometimes cited for its anti-inflammatory properties. However, it must be used with extreme caution and properly diluted to avoid causing further irritation. Preparations specifically designed for ocular use are preferable.
Tip 4: Consider Chamomile Compresses. Chamomile infusions, applied as warm compresses, may offer soothing relief. Ensure the chamomile is of high quality and free from contaminants. Discontinue use if irritation occurs.
Tip 5: Understand Potential Allergies. Plant-derived substances can trigger allergic reactions. Perform a patch test on a small area of skin before applying any new substance to the eyelids.
Tip 6: Choose Reputable Sources. When selecting botanical preparations, prioritize products from reputable manufacturers that adhere to quality control standards. This helps minimize the risk of contamination or adulteration.
Tip 7: Monitor for Adverse Reactions. Closely monitor for any adverse reactions, such as increased redness, swelling, itching, or burning. Discontinue use immediately if any of these symptoms develop.
The careful and informed application of these suggestions may contribute to improved symptom management. However, remember that botanical interventions are often most effective as part of a comprehensive treatment strategy prescribed by a medical professional.
Subsequent sections of this document will address specific substances and their documented effects, while maintaining a focus on evidence-based insights.
1. Source
The origin of plant-derived substances employed in approaches to manage blepharitis is a critical determinant of treatment safety and potential efficacy. The source encompasses several factors, including the geographical location of cultivation, the farming practices employed, and the methods used for extraction and processing. Contamination with pesticides, heavy metals, or other adulterants can compromise the quality of the final product, potentially exacerbating eyelid inflammation or causing unforeseen adverse reactions. For example, herbal remedies sourced from regions with lax environmental regulations may contain elevated levels of pollutants, negating any potential therapeutic benefit and posing a risk to the user’s health. Precise botanical identification is also vital to ensure the correct species is used and to avert the risk of mistakenly using a related, but potentially harmful, plant.
The significance of the source extends to the extraction process. Different extraction methods can yield varying concentrations of active compounds and may also introduce impurities. For instance, solvent-based extraction, if not performed meticulously, may leave residual solvents in the final product. In contrast, supercritical fluid extraction, while often more expensive, is regarded as a cleaner method. Certified organic sourcing provides assurance that the plants have been grown without synthetic pesticides or herbicides, minimizing the risk of exposure to these chemicals. An example is organic chamomile, which is preferable to non-organic varieties due to the absence of potentially irritating pesticide residues, particularly when used in a compress applied directly to the eyelids. The absence of quality control at the production source has the potential to lead to a therapeutic process that is rendered harmful.
In summary, the selection of a botanical source for blepharitis treatment is an important aspect of informed decision-making. Prioritizing reputable suppliers who adhere to stringent quality control standards, employing certified organic practices where feasible, and ensuring accurate botanical identification are vital steps. Verification of the source helps to minimize the risk of contamination and maximize the likelihood of a beneficial outcome, aligning with a responsible approach to natural therapies. The origin of a product is crucial and should not be understated.
2. Dilution
Dilution is a critical parameter in the context of plant-derived treatments for blepharitis. The potency of many botanical substances necessitates precise dilution to mitigate the risk of irritation or adverse reactions on the delicate eyelid tissue. Direct application of concentrated herbal extracts can trigger significant inflammation, counteracting the intended therapeutic effect and potentially exacerbating the condition. For instance, tea tree oil, often cited for its anti-inflammatory properties, contains potent terpinen-4-ol, a compound that can cause severe irritation if applied undiluted. The appropriate dilution factor depends on the specific substance, its concentration, and the individual’s sensitivity.
The practical significance of dilution is evident in the application protocols for common botanical remedies. Tea tree oil, for example, typically requires dilution to concentrations ranging from 1% to 5% in a carrier oil, such as coconut or olive oil, before being applied to the eyelid margin. Similarly, chamomile infusions, used as warm compresses, must be prepared with a specific water-to-herb ratio to ensure the final solution is gentle and non-irritating. The failure to adhere to proper dilution guidelines can result in contact dermatitis, characterized by redness, swelling, and itching, thereby negating any potential benefits. Moreover, variability in product formulations underscores the necessity of carefully following the manufacturer’s instructions regarding dilution.
In summary, the careful control of concentration through proper dilution is an indispensable element of blepharitis management using botanical substances. It is essential to recognize that “natural” does not equate to “harmless,” and that even substances with potential therapeutic benefits can cause harm if applied inappropriately. Emphasizing proper dilution techniques, alongside thorough monitoring for adverse reactions, is integral to ensuring the safe and effective application of herbal remedies for blepharitis. Prior adherence to dilution best practices minimizes risk and optimizes the potential for benefit.
3. Application
The method of application is a pivotal determinant in the safety and effectiveness of plant-derived therapies for blepharitis. Improper application can render an otherwise beneficial substance ineffective or even harmful. The eyelid margin, being a delicate and sensitive area, requires careful and precise techniques to avoid irritation or damage. Furthermore, the specific method of application can influence the extent to which the active compounds are absorbed and exert their therapeutic effects. For instance, the use of a cotton swab versus a warm compress results in varying degrees of contact time and substance penetration, thereby influencing the therapeutic outcome. Ineffective or inappropriate implementation of blepharitis herbal treatment risks nullifying the benefits of the treatment regimen.
Practical considerations regarding application methods include the concentration of the solution, the temperature, and the duration of exposure. Applying a solution that is too concentrated can lead to inflammation, while applying a solution that is too cold may not provide adequate relief. Extending the duration of exposure beyond recommended guidelines can increase the risk of irritation, whereas insufficient exposure may not allow sufficient time for the active compounds to exert their effects. Therefore, adhering to recommended application protocols is imperative for maximizing therapeutic benefits and minimizing potential adverse effects. One example would be the application of warm chamomile compresses, the proper warmth, moisture, and duration can allow for a soothing feeling without over-exposure to the skin.
In summary, the application component of botanical treatments for blepharitis is not merely a procedural step but an integral determinant of treatment success. Precise attention to detail, adherence to established protocols, and careful consideration of the individual’s sensitivity are essential for achieving optimal outcomes. Ignoring or downplaying the importance of proper application can compromise the safety and effectiveness of otherwise promising botanical interventions. Application is a key to effective implementation and should be carefully considered.
4. Hygiene
Meticulous hygiene practices form an indispensable cornerstone in the management of blepharitis, irrespective of whether plant-derived remedies are incorporated into the treatment regimen. Adequate hygiene serves to minimize bacterial load, remove irritating debris, and optimize the environment for healing. Inadequate hygiene compromises the efficacy of any chosen therapeutic intervention, including botanical approaches, and can exacerbate the underlying condition.
- Eyelid Cleansing
Regular and thorough cleansing of the eyelid margin removes accumulated debris, such as dead skin cells, oils, and bacteria, which contribute to inflammation. This practice typically involves using a diluted, pH-balanced cleanser specifically formulated for ocular use. Failure to cleanse the eyelids adequately can result in a build-up of irritants, negating the potential benefits of botanical anti-inflammatory agents.
- Warm Compresses
The application of warm compresses helps to soften and loosen encrusted debris along the eyelid margin, facilitating its removal during cleansing. Warm compresses also stimulate the flow of meibum from the meibomian glands, which contributes to a healthy tear film. Without proper warm compress application, the meibomian glands may remain blocked, contributing to evaporative dry eye and exacerbating blepharitis symptoms, regardless of herbal treatments.
- Hand Washing
Thorough hand washing before touching the eyelids is crucial to prevent the introduction of additional bacteria and contaminants. The hands are a common vector for transmitting microorganisms, and neglecting hand hygiene can undo the benefits of any topical treatment, including botanical remedies. Consistent hand washing is a fundamental aspect of infection control and is paramount in managing blepharitis.
- Avoiding Irritants
Minimizing exposure to environmental irritants, such as smoke, dust, and allergens, can help to reduce inflammation and prevent exacerbations of blepharitis. These irritants can trigger an inflammatory response in the eyelids, counteracting the effects of botanical anti-inflammatory agents. Avoiding these triggers complements any chosen therapeutic approach, including the use of plant-derived substances.
These facets collectively highlight that hygiene is not merely an adjunctive measure but an essential prerequisite for successful blepharitis management. While plant-derived remedies may offer symptomatic relief or address underlying inflammatory processes, their efficacy is contingent upon maintaining rigorous hygiene practices. A comprehensive approach integrates both hygiene and targeted therapies to achieve optimal outcomes. For example, using tea tree oil to combat demodex mites without first removing eyelid debris through proper cleaning will likely prove less effective.
5. Inflammation
Inflammation is a central pathological feature of blepharitis, characterized by swelling, redness, and irritation of the eyelids. Plant-derived treatments often target the inflammatory pathways involved in this condition, aiming to alleviate symptoms and promote tissue healing. The effectiveness of botanical interventions is predicated on their ability to modulate these inflammatory processes.
- Cytokine Modulation
Inflammation in blepharitis is driven by the release of pro-inflammatory cytokines, such as TNF- and IL-1. Certain herbal extracts are thought to exert their effects by inhibiting the production or activity of these cytokines, thereby reducing inflammation. For example, chamomile contains compounds that may suppress cytokine release, contributing to its soothing properties. By reducing cytokine action, botanical treatments can provide relief from inflammation.
- Antioxidant Activity
Oxidative stress contributes to inflammation in blepharitis. Free radicals damage cells and trigger inflammatory cascades. Some botanical substances possess antioxidant properties, scavenging free radicals and protecting cells from oxidative damage. Green tea, for instance, contains polyphenols with demonstrated antioxidant activity. The reduction of oxidative stress through antioxidant mechanisms may play a role in mitigating inflammation.
- Mast Cell Stabilization
Mast cells release histamine and other mediators that contribute to inflammation and itching in allergic forms of blepharitis. Certain botanical compounds are believed to stabilize mast cells, preventing the release of these mediators and reducing inflammatory responses. Quercetin, found in various plants, has been investigated for its mast cell-stabilizing properties. The modulation of mast cell activity may alleviate inflammatory symptoms, especially itching.
- Inhibition of Inflammatory Enzymes
Enzymes such as cyclooxygenase (COX) and lipoxygenase (LOX) play key roles in the synthesis of pro-inflammatory mediators. Some herbal extracts contain compounds that inhibit these enzymes, reducing the production of inflammatory molecules. Ginger, for example, contains gingerol, which has been shown to inhibit COX and LOX. By targeting these enzymes, botanical treatments can reduce the inflammatory response.
The multifaceted approach of botanical treatments in addressing inflammation highlights their potential role in managing blepharitis. However, it is essential to recognize that the efficacy of these treatments can vary depending on the specific botanical substance, the severity of inflammation, and individual patient factors. A comprehensive strategy, incorporating conventional treatments and appropriate hygiene practices, often yields optimal outcomes. The interplay between conventional and botanical treatment of inflammation related to blepharitis creates more options for the end-user.
6. Allergies
Allergic reactions constitute a significant concern in the context of botanical interventions for blepharitis. The introduction of plant-derived substances to the delicate periocular region carries an inherent risk of eliciting hypersensitivity responses in susceptible individuals. These reactions can manifest as contact dermatitis, characterized by erythema, edema, pruritus, and scaling of the eyelids, potentially exacerbating the symptoms of blepharitis. Furthermore, systemic allergic reactions, although less common, pose a serious threat and necessitate prompt medical intervention. For instance, an individual with an undiagnosed allergy to chamomile might experience localized skin irritation or, in severe cases, anaphylaxis following the application of chamomile compresses to the eyelids. The potential for allergies thus represents a critical consideration in the implementation of approaches.
The importance of identifying and avoiding potential allergens cannot be overstated. Before initiating any treatment, a thorough allergy history should be obtained. Patch testing can be performed to assess an individual’s sensitivity to specific botanical substances. Moreover, cross-reactivity between different plant species should be considered. For example, individuals allergic to ragweed may also exhibit sensitivity to chamomile or echinacea. Vigilant monitoring for signs of allergic reactions is essential throughout the treatment course. Real-life examples underscore the significance of this precaution; reports of severe allergic reactions following the use of undiluted tea tree oil for blepharitis highlight the potential dangers. Therefore, awareness of allergenic potential and careful pre-screening are required.
In summary, the risk of allergic reactions constitutes a primary challenge in the deployment of botanical remedies for blepharitis. A comprehensive understanding of allergic mechanisms, meticulous pre-treatment screening, and ongoing monitoring are essential for ensuring patient safety. Failure to address this concern can lead to adverse outcomes and negate any potential therapeutic benefits. The integration of allergy awareness into all herbal treatment for blepharitis protocols is thus paramount. An integrative and all-inclusive approach is critical.
7. Consultation
The integration of plant-derived substances into blepharitis management necessitates prior consultation with a qualified healthcare professional. This consultation serves as a critical checkpoint to assess the suitability of botanical interventions for the individual’s specific condition, considering factors such as disease severity, concurrent medications, and underlying health status. The self-administration of herbal remedies without professional guidance carries the risk of adverse interactions, delayed diagnosis of alternative conditions, or exacerbation of existing symptoms. For example, an individual with undiagnosed meibomian gland dysfunction, masquerading as blepharitis, might find that botanical treatments targeting inflammation provide only temporary relief, while the underlying cause remains unaddressed. Professional consultation mitigates these risks by ensuring an accurate diagnosis and the selection of appropriate therapies.
Moreover, consultation allows for the assessment of potential contraindications and the development of a comprehensive treatment plan. Certain botanical substances may interact with prescription medications or be contraindicated in individuals with specific medical conditions. A healthcare professional can evaluate these risks and provide guidance on appropriate dosages and application techniques. For instance, individuals taking anticoagulant medications should exercise caution when using herbal remedies with potential blood-thinning effects, such as garlic or ginger. Similarly, pregnant or breastfeeding women should consult with their healthcare provider before using any plant-derived substance. Through consultation, the integration of plant-derived remedies is carefully monitored to avoid harm to the individual. A lack of consultation can lead to dangerous scenarios.
In summary, professional consultation is an indispensable component of incorporating botanical approaches into blepharitis management. It ensures accurate diagnosis, facilitates the selection of appropriate therapies, mitigates the risk of adverse interactions, and promotes patient safety. Neglecting this step can compromise the effectiveness of treatment and potentially lead to harm. Thus, seeking expert guidance prior to initiating any botanical regimen is essential for responsible and effective blepharitis care. The inclusion of consultation ensures all factors are taken into consideration before treatment begins.
Frequently Asked Questions
This section addresses common inquiries regarding plant-derived substances in the context of blepharitis management. The information presented is intended for educational purposes and should not be construed as medical advice.
Question 1: Are botanical substances a substitute for conventional blepharitis treatments?
No, botanical substances are not typically a substitute for conventional treatments such as eyelid hygiene, prescription medications, or lubricating eye drops. Instead, they are often considered as complementary or adjunctive therapies to be used in conjunction with established medical protocols.
Question 2: What specific botanical substances are commonly used for blepharitis?
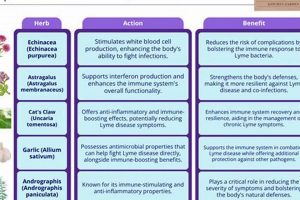
Certain substances, including tea tree oil, chamomile, eyebright, and green tea, are sometimes cited for their potential anti-inflammatory, antibacterial, or antioxidant properties. However, the evidence supporting their efficacy varies, and further research is often needed.
Question 3: How should tea tree oil be used to treat blepharitis?
Tea tree oil must be diluted significantly before application to the eyelids to avoid irritation. Typically, a concentration of 1% to 5% in a carrier oil, such as coconut or olive oil, is recommended. Preparations specifically formulated for ocular use are preferable.
Question 4: Are there any risks associated with botanical treatments for blepharitis?
Yes, potential risks include allergic reactions, skin irritation, and interactions with medications. It is crucial to perform a patch test before using any new botanical substance and to consult with a healthcare professional.
Question 5: How long does it take to see results from botanical blepharitis treatments?
The time to see results can vary depending on the individual, the severity of the condition, and the specific botanical substance used. Some individuals may experience improvement within a few days, while others may require several weeks or months of consistent treatment.
Question 6: Where can reputable botanical products for blepharitis be purchased?
Reputable products should be sourced from manufacturers that adhere to quality control standards and provide detailed information about the product’s ingredients and sourcing. Pharmacies, health food stores, and online retailers specializing in natural health products are potential sources.
The safe and effective use of botanical treatments for blepharitis requires informed decision-making, professional guidance, and careful monitoring for adverse reactions. Adherence to established medical protocols and meticulous hygiene practices is essential.
The subsequent section will explore the regulatory landscape surrounding botanical products and highlight the importance of consumer awareness.
Conclusion
The exploration of blepharitis herbal treatment reveals a complex landscape of potential benefits and inherent risks. This document has emphasized the critical importance of professional consultation, meticulous hygiene practices, appropriate application techniques, and vigilance regarding allergic reactions. Botanical interventions should not be considered a replacement for conventional medical care but rather a potential adjunct under strict professional supervision.
The responsible implementation of blepharitis herbal treatment necessitates a thorough understanding of the factors outlined herein. Further research is warranted to fully elucidate the efficacy and safety profiles of specific botanical substances. Individuals considering such approaches must prioritize informed decision-making and prioritize their health above all else.