Beverages crafted from infusions or decoctions of herbs, spices, or other plant materials, excluding true teas (Camellia sinensis), and intended to support the body’s defense mechanisms, constitute a category of wellness products. These preparations leverage phytochemicals and other bioactive compounds inherent in various botanicals to potentially enhance immune function.
The consumption of such botanical infusions has a long-standing history in traditional medicine systems across cultures. These practices recognized the potential of certain plants to provide protection against illness. Compounds within these plants, such as antioxidants and anti-inflammatory agents, are theorized to contribute to overall health and resilience against pathogens. Further research is needed to fully validate these traditional uses and mechanisms.
The following sections will explore specific herbal ingredients known for their potential immunomodulatory properties, methods of preparation, and considerations for responsible consumption. The discussion will focus on the scientific rationale behind the use of these botanicals in supporting a healthy immune response.
Optimizing Botanical Infusions for Immune Support
The following are guidelines for maximizing the potential benefits of utilizing botanical infusions to bolster the body’s defense systems. Proper preparation and informed selection are paramount.
Tip 1: Prioritize Ingredient Sourcing: Select organically cultivated herbs when available. This minimizes exposure to synthetic pesticides and herbicides, potentially enhancing the beneficial compounds within the plant material.
Tip 2: Optimize Infusion Time: Adhere to recommended steeping times for specific herbs. Over-steeping can result in bitter flavors and potentially release undesirable compounds, while under-steeping may limit the extraction of beneficial components.
Tip 3: Consider Water Temperature: Different herbs require varying water temperatures for optimal extraction. Delicate herbs generally benefit from lower temperatures, while tougher roots and barks may require boiling water.
Tip 4: Incorporate Synergistic Blends: Combine multiple herbs known for complementary properties. This approach can create a more comprehensive and potent blend than using single herbs alone. Consult with a qualified herbalist for guidance.
Tip 5: Maintain Consistent Consumption: Regular, moderate consumption is often more effective than infrequent, large doses. Incorporate botanical infusions into a daily routine to promote sustained immune support.
Tip 6: Store Herbs Properly: Keep dried herbs in airtight containers away from direct sunlight, heat, and moisture. This preserves their potency and prevents degradation of active compounds.
Tip 7: Filter the Infusion: Use a fine-mesh strainer or cheesecloth to remove plant debris before consumption. This improves palatability and prevents potential irritation of the digestive tract.
By adhering to these guidelines, individuals can potentially enhance the efficacy of botanical infusions and maximize their potential to contribute to a healthy immune response. Responsible and informed utilization is key.
The subsequent sections will address potential contraindications and interactions to consider when incorporating botanical infusions into a wellness regimen.
1. Botanical Composition
The efficacy of botanical infusions in supporting immune function is intrinsically linked to their specific botanical composition. The diversity of phytochemicals present within each herb contributes to a range of potential immunomodulatory effects. Understanding this composition is paramount for selecting appropriate botanicals.
- Presence of Polyphenols
Polyphenols, including flavonoids and phenolic acids, are abundant in many herbs used in infusions. These compounds exhibit antioxidant properties, neutralizing free radicals that can compromise immune cell function. Examples include quercetin in elderberry and catechins in green tea (though technically Camellia sinensis, it illustrates the principle). The concentration and type of polyphenols directly influence the infusion’s potential to mitigate oxidative stress on the immune system.
- Essential Oils and Terpenes
Certain herbs contain volatile essential oils and terpenes with documented antimicrobial and anti-inflammatory properties. These compounds can act directly against pathogens and modulate the inflammatory response, preventing excessive inflammation that can suppress immune function. For instance, thyme contains thymol, an antiseptic compound, while chamomile contains bisabolol, known for its anti-inflammatory effects. The specific profile of essential oils determines the infusion’s ability to combat infection and regulate inflammation.
- Presence of Polysaccharides
Polysaccharides, complex carbohydrates found in herbs such as Astragalus and medicinal mushrooms, can stimulate immune cell activity, enhancing the body’s innate defense mechanisms. These compounds interact with immune cell receptors, promoting the production of cytokines and other signaling molecules that activate the immune system. The type and structure of polysaccharides influence their immunomodulatory potential, with some exhibiting more potent effects than others.
- Alkaloid Content (Considerations)
While alkaloids can possess potent medicinal properties, their presence in herbal infusions requires careful consideration due to potential toxicity or interactions. Some alkaloids may have immunostimulatory effects, but others can be immunosuppressive or have adverse side effects. It is crucial to select herbs with low or safe alkaloid levels and to consult with a qualified herbalist before using infusions containing significant alkaloid content. Proper identification and preparation are essential to mitigate potential risks.
In summary, the specific combination of polyphenols, essential oils, polysaccharides, and, cautiously, alkaloids within a botanical infusion dictates its potential impact on the immune system. A thorough understanding of the phytochemical profile of each herb is essential for formulating effective and safe blends aimed at supporting immune function. The interactions between these compounds, and their individual mechanisms of action, contribute to the overall therapeutic potential of these botanical preparations.
2. Antimicrobial Properties
The presence of antimicrobial properties within certain herbal infusions directly contributes to their potential to support immune function. Pathogenic microorganisms, including bacteria, viruses, and fungi, pose a constant challenge to the immune system. Botanical compounds with antimicrobial activity can directly inhibit the growth or viability of these pathogens, thereby reducing the burden on the immune system and allowing it to focus on other threats. This constitutes a key mechanism by which herbal infusions may contribute to enhanced immunity.
Numerous herbs traditionally used to support immunity contain well-documented antimicrobial compounds. For instance, thyme contains thymol and carvacrol, both of which exhibit potent antibacterial and antifungal activity. Similarly, garlic, often incorporated into herbal preparations, contains allicin, a compound known for its broad-spectrum antimicrobial effects. Echinacea species possess echinacein, which has demonstrated antiviral properties. The inclusion of such herbs in infusions can provide a first line of defense against invading pathogens, supplementing the body’s natural immune responses. It is crucial to acknowledge that the in vivo efficacy and bioavailability of these compounds may vary and require further investigation to confirm their effectiveness in humans.
The utilization of botanical infusions with antimicrobial properties as a component of a holistic approach to immune support presents a rational strategy. By reducing the pathogenic load within the body, these infusions can potentially alleviate the strain on the immune system, allowing it to function more efficiently. However, it is imperative to recognize that these infusions are not substitutes for conventional medical treatments in cases of established infections. Furthermore, indiscriminate use of antimicrobial herbs could contribute to the development of antimicrobial resistance. Responsible and informed consumption, guided by qualified healthcare professionals, is essential to ensure the safe and effective integration of these botanicals into a comprehensive immune support plan.
3. Anti-inflammatory Actions
Chronic inflammation is implicated in the pathogenesis of numerous diseases and can significantly compromise immune function. An overactive inflammatory response diverts resources away from combating pathogens, potentially weakening the body’s defenses. Botanical infusions containing anti-inflammatory compounds may modulate this inflammatory cascade, promoting a balanced immune response. This modulation is crucial for effective immunity, as it allows the body to respond appropriately to threats without causing excessive tissue damage. The inclusion of herbs with anti-inflammatory actions is therefore a rational strategy in formulations designed to support immune health.
Herbs such as ginger (Zingiber officinale), turmeric (Curcuma longa), and chamomile (Matricaria chamomilla) are renowned for their anti-inflammatory properties. Ginger contains gingerols, which inhibit the production of pro-inflammatory cytokines. Turmeric’s active compound, curcumin, similarly suppresses inflammatory pathways. Chamomile contains apigenin, an antioxidant with anti-inflammatory effects. The consumption of infusions containing these herbs may help to reduce systemic inflammation, freeing up immune resources for pathogen defense. For example, individuals experiencing chronic low-grade inflammation due to lifestyle factors might benefit from incorporating ginger or turmeric infusions into their daily routine. It’s worth noting that the bioavailability of some compounds, such as curcumin, is limited and may require co-administration with enhancers like piperine (found in black pepper) for optimal absorption.
In summary, the anti-inflammatory actions of certain botanical infusions play a significant role in supporting a healthy immune system. By mitigating chronic inflammation, these infusions help to optimize immune function and enhance the body’s ability to respond effectively to infections and other threats. While promising, further research is warranted to fully elucidate the mechanisms and clinical benefits of these botanical interventions. Individuals considering incorporating anti-inflammatory herbal infusions into their health regimen should consult with a qualified healthcare professional or herbalist, particularly if they have pre-existing medical conditions or are taking other medications.
4. Antioxidant Content
The antioxidant content of herbal infusions is a critical factor contributing to their potential to support immune function. Oxidative stress, caused by an imbalance between free radical production and antioxidant defenses, can damage cells and impair immune responses. Herbal infusions rich in antioxidants can help neutralize free radicals, protecting immune cells and promoting optimal immune function.
- Protection of Immune Cells
Antioxidants safeguard immune cells from oxidative damage, ensuring their functionality. Free radicals can damage cell membranes, proteins, and DNA within immune cells, reducing their ability to effectively respond to pathogens. For example, vitamin C, a potent antioxidant found in rosehip infusions, protects lymphocytes (white blood cells) from oxidative stress, enhancing their ability to proliferate and produce antibodies. The direct protection of immune cells by antioxidants is a key mechanism by which herbal infusions may contribute to improved immunity.
- Modulation of Inflammatory Responses
Antioxidants can influence inflammatory pathways, reducing chronic inflammation that can suppress immune function. Oxidative stress triggers the release of pro-inflammatory cytokines, contributing to a cycle of inflammation and immune dysfunction. Compounds like quercetin, found in elderflower infusions, have been shown to inhibit the production of these cytokines, dampening the inflammatory response and allowing the immune system to focus on combating pathogens. The modulation of inflammation by antioxidants indirectly supports immune function by preventing it from being overwhelmed by chronic inflammatory signals.
- Support for Gut Microbiome Health
Antioxidants can promote a healthy gut microbiome, which plays a vital role in immune regulation. The gut microbiome influences immune development and function through various mechanisms, including the production of short-chain fatty acids (SCFAs) and the modulation of immune cell activity. Polyphenols, abundant in many herbal infusions, act as prebiotics, nourishing beneficial gut bacteria and promoting a balanced microbiome. A healthy gut microbiome, supported by antioxidants, strengthens the immune system’s ability to defend against pathogens.
- Enhancement of Cellular Repair Mechanisms
Antioxidants support cellular repair mechanisms, allowing immune cells to recover from oxidative damage and maintain their function. Oxidative stress can impair DNA repair processes, leading to accumulation of cellular damage and increased risk of mutations. Compounds such as glutathione, an endogenous antioxidant, are crucial for repairing damaged proteins and maintaining cellular integrity. Herbal infusions that boost glutathione levels or provide other antioxidants can enhance cellular repair, ensuring the long-term health and functionality of immune cells.
In conclusion, the antioxidant content of herbal infusions is integral to their potential to bolster immune function. By protecting immune cells, modulating inflammation, supporting the gut microbiome, and enhancing cellular repair, antioxidants contribute to a robust and balanced immune response. The careful selection of herbs rich in antioxidants and the appropriate preparation of infusions can maximize these benefits, promoting overall immune health.
5. Immunomodulation Potential
The immunomodulation potential of herbal infusions forms a central rationale for their use in supporting immune function. Immunomodulation refers to the ability of a substance to alter the immune system’s response, either by enhancing it when weak or suppressing it when overactive. This regulatory effect is crucial for maintaining immune homeostasis and preventing both immunodeficiency and autoimmunity. Herbal infusions, through their diverse phytochemical profiles, may exert significant immunomodulatory effects.
- Enhancement of Immune Cell Activity
Certain herbal constituents can stimulate the activity of immune cells such as macrophages, natural killer cells, and T lymphocytes. For example, polysaccharides found in herbs like Astragalus membranaceus and medicinal mushrooms can bind to receptors on immune cells, triggering signaling pathways that enhance their phagocytic activity (the ability to engulf and destroy pathogens) and cytokine production. This enhancement of immune cell activity can lead to a more robust and effective response to infections. In the context of herbal infusions, this facet implies that regular consumption may prime the immune system to respond more quickly and efficiently to invading pathogens.
- Regulation of Cytokine Production
Cytokines are signaling molecules that regulate the immune response. An imbalance in cytokine production can lead to chronic inflammation or immunosuppression. Herbal compounds, such as flavonoids and terpenoids, can modulate cytokine production, promoting a balanced inflammatory response. For example, curcuminoids in turmeric have been shown to inhibit the production of pro-inflammatory cytokines like TNF- and IL-6, while simultaneously promoting the production of anti-inflammatory cytokines like IL-10. In herbal infusions, this regulatory effect on cytokine production translates to a reduced risk of chronic inflammation and a more appropriate immune response to acute infections.
- Modulation of the Gut Microbiota
The gut microbiota plays a critical role in immune development and function. Herbal constituents can influence the composition and activity of the gut microbiota, promoting a balanced microbial ecosystem that supports immune health. For example, polyphenols in green tea and other herbs can act as prebiotics, nourishing beneficial gut bacteria and inhibiting the growth of pathogenic bacteria. A healthy gut microbiota, in turn, produces short-chain fatty acids (SCFAs) that have anti-inflammatory and immunomodulatory effects. In herbal infusions, the prebiotic effect of certain compounds can contribute to improved gut health and enhanced immune function.
- Support of Adaptive Immunity
Adaptive immunity involves the development of antigen-specific immune responses mediated by T and B lymphocytes. Certain herbal compounds can support adaptive immunity by promoting the differentiation and activation of these lymphocytes. For instance, compounds in Echinacea purpurea have been shown to enhance the proliferation of T lymphocytes and the production of antibodies by B lymphocytes. By supporting adaptive immunity, herbal infusions can contribute to long-term immune protection against specific pathogens. This facet implies that consistent consumption of specific herbal infusions might improve the body’s ability to mount effective adaptive immune responses upon subsequent exposures to the same pathogens.
In summary, the immunomodulation potential of herbal infusions is multifaceted, encompassing the enhancement of immune cell activity, regulation of cytokine production, modulation of the gut microbiota, and support of adaptive immunity. These effects are mediated by the diverse phytochemicals present in various herbs, which interact with the immune system in complex and often synergistic ways. While further research is needed to fully elucidate the mechanisms and clinical benefits of these botanical interventions, the evidence suggests that herbal infusions can be valuable tools for supporting immune health, provided they are used responsibly and in consultation with qualified healthcare professionals.
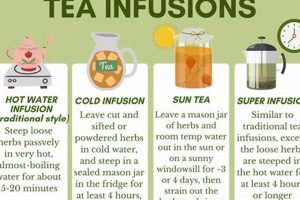
6. Preparation Method
The preparation method significantly influences the efficacy of botanical infusions intended to support immune function. The extraction of bioactive compounds from plant material is contingent on factors such as water temperature, steeping time, and the form of the herb utilized. Improper preparation can result in suboptimal extraction, reducing the potential benefits of the infusion.
- Water Temperature and Compound Extraction
Water temperature dictates the degree to which various compounds are extracted from the herb. Delicate aromatic compounds and volatile oils are best extracted at lower temperatures, typically between 170-185F (77-85C), while tougher roots and barks may require boiling water (212F or 100C) for optimal extraction of their constituents. Overheating can degrade certain compounds, reducing their potency. For example, overheating chamomile can denature some of its beneficial volatile oils, diminishing its calming properties. Precise temperature control, guided by the specific herb, is therefore crucial.
- Steeping Time and Bioactive Release
Steeping time is a critical variable in determining the concentration of bioactive compounds in the final infusion. Insufficient steeping may not allow for adequate extraction, resulting in a weak infusion with limited benefits. Conversely, excessive steeping can lead to the release of undesirable compounds, such as tannins, which impart a bitter taste and may interfere with the absorption of other beneficial compounds. A typical steeping time for most herbal infusions ranges from 5 to 15 minutes, but specific herbs may require longer or shorter durations. Knowledge of the appropriate steeping time for each herb is essential for maximizing the therapeutic potential of the infusion.
- Herb Form and Surface Area
The form of the herbwhole, cut, powdered, or encapsulatedaffects the surface area available for extraction. Cut and sifted herbs generally offer a larger surface area than whole herbs, leading to more efficient extraction. Powdered herbs, while offering the largest surface area, may also release sediment into the infusion, potentially affecting palatability. Encapsulated herbs are not typically used for infusions. The choice of herb form should be guided by the desired extraction efficiency and the impact on the overall quality and taste of the infusion. For instance, using coarsely cut ginger root will yield a different extraction profile compared to finely powdered ginger.
- Water Quality and Solvent Properties
The quality of the water used for infusion can influence the extraction and stability of bioactive compounds. Filtered or spring water, free from chlorine and other contaminants, is generally preferred. The pH of the water can also affect extraction efficiency; slightly acidic water may enhance the extraction of certain compounds. The solvent properties of water itself play a role, as some compounds are more water-soluble than others. For example, the use of distilled water might not provide the minerals needed for some compounds to properly extract.
In conclusion, a nuanced understanding of the preparation method is essential for maximizing the immune-supporting potential of botanical infusions. Precise control over water temperature, steeping time, herb form, and water quality is critical for ensuring the optimal extraction of bioactive compounds and the production of a high-quality, therapeutically effective infusion. The selected preparation method should align with the specific properties of the herbs being used, as well as the desired therapeutic outcome. Further research may clarify the effect of preparation method on specific herbs.
7. Consumption Frequency
The frequency with which botanical infusions are consumed significantly impacts their potential to support immune function. Consistent, regular intake allows for sustained exposure to bioactive compounds, potentially leading to more pronounced and lasting immunomodulatory effects. Erratic or infrequent consumption, conversely, may not provide sufficient stimulus to elicit a meaningful immune response. Therefore, establishing an appropriate consumption frequency is a critical consideration for individuals seeking to leverage botanical infusions for immune support.
The concept of “loading dose” and “maintenance dose”, known in pharmacology, bears relevance here. An initial period of more frequent consumption might serve as a “loading dose,” establishing a baseline level of bioactive compounds in the system. Subsequently, a less frequent “maintenance dose” could sustain these levels and continue to provide ongoing immune support. For example, an individual preparing for cold and flu season might consume a daily elderberry infusion for several weeks leading up to the season, then reduce intake to a few times per week throughout the season. Such an approach aims to proactively bolster immune defenses during periods of heightened risk. It is important to note that this framework requires empirical validation via clinical trials specific to each herb. In cases of acute illness, short-term but more frequent consumption might be appropriate, such as drinking ginger tea several times a day to alleviate cold symptoms, leveraging the anti-inflammatory action discussed previously.
Determining the optimal consumption frequency should also consider potential cumulative effects, both positive and negative. While consistent exposure to beneficial compounds is desirable, excessive consumption could potentially lead to adverse effects or interactions with medications. Individual tolerance and sensitivity to specific herbs must be factored into the equation. Ultimately, the ideal consumption frequency is a personalized determination, guided by individual needs, health status, and the specific properties of the botanical infusion being consumed. Consultation with a qualified healthcare professional or herbalist can provide valuable guidance in establishing a safe and effective consumption schedule.
Frequently Asked Questions
The following section addresses common inquiries regarding the use of botanical infusions to support immune function. These responses aim to provide clarity and evidence-based information on the topic.
Question 1: Are botanical infusions a substitute for conventional medical treatments for immune-related conditions?
Botanical infusions are not a replacement for conventional medical care. They should be viewed as complementary strategies to support overall wellness, not as primary treatments for diagnosed illnesses. Individuals with existing health conditions or those experiencing concerning symptoms should seek appropriate medical attention.
Question 2: Can excessive consumption of botanical infusions lead to adverse effects on the immune system?
Yes, immoderate consumption of botanical infusions has the potential to negatively impact immune function. Overstimulation of the immune system through excessive use of certain herbs may result in unintended consequences. Adherence to recommended dosages and consultation with a healthcare professional are advised.
Question 3: Are all botanical infusions equally effective in supporting immune function?
No, the efficacy of botanical infusions in supporting immune function varies depending on the specific herbs used, their preparation, and individual factors. Not all herbs possess equal immunomodulatory properties. Researching the properties of each herb and selecting blends appropriate for individual needs is essential.
Question 4: Do botanical infusions interact with prescription medications?
Botanical infusions can potentially interact with prescription medications. Certain herbal compounds may affect the absorption, metabolism, or excretion of drugs, leading to altered drug efficacy or increased risk of side effects. Individuals taking prescription medications should consult with their healthcare provider before incorporating botanical infusions into their routine.
Question 5: Is the quality of commercially available botanical infusions consistent across different brands?
The quality of commercial botanical infusions can vary significantly between brands. Factors such as sourcing practices, processing methods, and ingredient standardization influence the potency and purity of the final product. Selecting reputable brands that adhere to quality control standards is recommended.
Question 6: How can individuals determine the appropriate dosage of botanical infusions for immune support?
Determining the appropriate dosage of botanical infusions requires careful consideration of several factors, including age, weight, health status, and the specific herbs being used. Consulting with a qualified herbalist or healthcare professional is recommended to establish a safe and effective dosage regimen.
The information provided in this FAQ section is intended for educational purposes and should not be construed as medical advice. Individuals with specific health concerns should consult with a qualified healthcare professional.
The following section will discuss practical recommendations for selecting and incorporating botanical infusions into a holistic wellness plan.
Concluding Remarks
This exploration has examined the multifaceted role of botanical infusions in supporting immune function, encompassing botanical composition, antimicrobial properties, anti-inflammatory actions, antioxidant content, immunomodulation potential, preparation methods, and consumption frequency. A thorough understanding of these factors is essential for informed and responsible utilization.
The judicious incorporation of these botanical preparations into a comprehensive wellness strategy, coupled with ongoing scientific inquiry, holds the promise of enhanced immune resilience. Individuals are encouraged to approach these practices with discernment, guided by evidence-based information and professional consultation, to maximize potential benefits and minimize risks.