A natural approach to managing bladder control issues involves utilizing plant-derived substances. This encompasses various preparations aimed at alleviating symptoms of urinary leakage and strengthening the urinary system. Examples include specific botanical extracts, traditional formulations, and dietary supplements incorporating herbs believed to possess diuretic, anti-inflammatory, or muscle-strengthening properties, intended to improve bladder function and reduce the frequency or severity of involuntary urination.
The employment of botanicals for addressing bladder weakness offers potential advantages rooted in traditional medicine and natural compounds. Historically, diverse cultures have relied on plants to support overall health, including urinary tract function. Benefits might include a reduced risk of side effects compared to some pharmaceutical interventions, a holistic approach considering the interconnectedness of bodily systems, and the potential for long-term management through lifestyle integration. Further research aims to validate efficacy and understand the mechanisms of action.
Subsequent sections will delve into specific plant-based options commonly considered for bladder support, exploring their purported mechanisms of action, potential benefits, and considerations for their appropriate use. These discussions will evaluate the evidence base and highlight areas requiring further investigation to establish their role in comprehensive bladder management strategies.
Guidance on Natural Approaches to Bladder Control
The following recommendations offer informed strategies for individuals exploring natural support for bladder function. These suggestions are intended to complement, not replace, professional medical advice.
Tip 1: Prioritize Pelvic Floor Exercises: Regularly engage in Kegel exercises to strengthen the muscles supporting the bladder and urethra. Consistent practice can enhance bladder control and reduce leakage incidents.
Tip 2: Maintain a Bladder Diary: Document fluid intake, urination frequency, and episodes of leakage. This record aids in identifying patterns and triggers, facilitating targeted interventions.
Tip 3: Evaluate Dietary Choices: Limit consumption of caffeine, alcohol, and artificial sweeteners, as these substances can irritate the bladder and exacerbate symptoms. Consider keeping a food diary to identify potential personal triggers.
Tip 4: Optimize Fluid Intake Timing: Distribute fluid consumption evenly throughout the day, avoiding large volumes close to bedtime. This strategy can reduce nighttime urination frequency.
Tip 5: Explore Herbal Supplementation (with caution): Certain botanicals, such as pumpkin seed extract or horsetail, are traditionally used to support bladder function. Prior to use, consultation with a qualified healthcare professional is essential to ensure safety and appropriateness.
Tip 6: Address Underlying Medical Conditions: Bladder control problems can sometimes be linked to underlying health issues. Seek evaluation for conditions such as diabetes, constipation, or urinary tract infections, and manage these appropriately.
Tip 7: Maintain a Healthy Weight: Excess weight can place additional pressure on the bladder and pelvic floor muscles. Achieving and maintaining a healthy weight through diet and exercise can contribute to improved bladder control.
Adherence to these strategies, coupled with professional guidance, may contribute to enhanced bladder control and overall well-being. However, individual responses can vary, and consistent monitoring is advised.
The subsequent section will explore advanced considerations and the importance of professional medical oversight in the comprehensive management of bladder dysfunction.
1. Plant-derived compounds
Plant-derived compounds form the basis of many approaches to bladder control issues classified under the broader umbrella of utilizing botanicals. These natural constituents, extracted from various plants, are investigated for their potential to address symptoms and improve bladder function. The selection and application of these compounds require careful consideration of their properties and potential interactions.
- Phytoestrogens and Bladder Muscle Tone
Certain plants contain phytoestrogens, compounds that mimic estrogen in the body. These may influence bladder muscle tone and elasticity, potentially improving bladder control, particularly in post-menopausal women where estrogen levels decline. However, the efficacy and safety of phytoestrogens for this purpose remain areas of ongoing research and require cautious evaluation.
- Antispasmodic Properties and Bladder Relaxation
Some plant-derived compounds exhibit antispasmodic properties, meaning they can help relax smooth muscles, including those in the bladder. This relaxation may reduce the urge to urinate frequently and alleviate symptoms of overactive bladder. Examples include specific terpenes and flavonoids found in certain herbs; however, definitive clinical evidence is still evolving.
- Anti-inflammatory Effects and Urinary Tract Health
Inflammation in the urinary tract can contribute to bladder irritation and dysfunction. Certain plant compounds possess anti-inflammatory properties, potentially reducing inflammation and promoting urinary tract health. Compounds such as quercetin and curcumin, found in various plants, are investigated for their anti-inflammatory effects, although their specific impact on bladder health requires further study.
- Diuretic Effects and Fluid Balance
Some plants contain diuretic compounds that increase urine production. While this might seem counterintuitive for bladder control, controlled diuretic effects can help flush out irritants and maintain fluid balance. However, it is crucial to use diuretics judiciously, as excessive fluid loss can exacerbate dehydration and electrolyte imbalances. Examples include dandelion and parsley, but their use should be carefully monitored.
The use of plant-derived compounds in bladder control strategies, classified as utilizing botanicals, hinges on understanding the specific properties of each compound and its potential impact on bladder function. While some compounds show promise, rigorous scientific research is essential to confirm efficacy, establish safe dosages, and identify potential interactions. As such, consulting with a qualified healthcare professional is vital before incorporating any using botanicals as part of a bladder management regimen.
2. Bladder muscle support
Bladder muscle integrity is fundamentally linked to urinary continence. Compromised bladder muscle strength or function is often a primary contributor to urinary incontinence, resulting in involuntary urine leakage. Herbal interventions frequently target bladder muscle support as a key mechanism for addressing this condition. The rationale posits that strengthening the detrusor muscle (the bladder’s main muscle) and the pelvic floor muscles, which provide crucial support to the bladder and urethra, can improve bladder control and reduce leakage episodes.
Several plant-derived compounds are investigated for their potential role in enhancing bladder muscle function. For example, some herbs are believed to possess properties that promote smooth muscle tone, potentially strengthening the detrusor muscle. Other herbs target the pelvic floor muscles, aiding in their contraction and relaxation. An example includes the use of pumpkin seed extract, which some studies suggest may improve pelvic floor muscle strength, leading to better urinary control. Understanding this connection enables a more targeted approach to natural interventions, focusing on addressing the specific deficits contributing to the incontinence.
In summary, bladder muscle support represents a critical component of botanical approaches to managing urinary incontinence. By focusing on strengthening and improving the function of the bladder’s muscles and surrounding pelvic floor, botanical remedies aim to address the underlying causes of incontinence and improve overall bladder control. However, individual responses to these interventions can vary significantly, and a comprehensive assessment, including lifestyle modifications and professional guidance, is essential for optimal outcomes and to ensure that any botanical strategy is both safe and appropriate.
3. Urinary tract health
Urinary tract health profoundly influences bladder function and, consequently, the efficacy of natural interventions aimed at mitigating urinary incontinence. Compromised urinary tract health, often manifested as infections or inflammation, can directly exacerbate bladder irritability and contribute to involuntary urine leakage. This interconnectedness underscores the importance of addressing underlying urinary tract issues as a foundational step in any incontinence management strategy. For instance, recurrent urinary tract infections (UTIs) can lead to chronic bladder inflammation, resulting in an overactive bladder and frequent urges to urinate, thereby undermining the effectiveness of approaches targeting muscle strength alone. A holistic approach prioritizes both the immediate relief of symptoms and the long-term maintenance of urinary tract integrity.
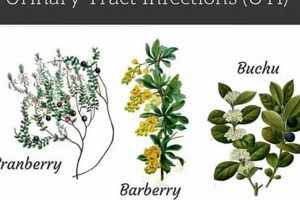
Specific plant-derived compounds are often incorporated into strategies for their antimicrobial or anti-inflammatory properties, directly targeting potential causes of urinary tract compromise. Cranberry extract, for example, is frequently recommended for its purported ability to prevent bacterial adhesion to the urinary tract walls, reducing the likelihood of UTIs. Similarly, certain herbs are believed to possess anti-inflammatory effects, helping to soothe irritated bladder linings and improve overall urinary tract function. The strategic selection of such interventions recognizes the interplay between a healthy urinary tract and optimal bladder control. However, it is critical to recognize these interventions as adjunctive, not primary, treatments for established UTIs, which require prompt medical attention and appropriate antibiotic therapy.
In summary, urinary tract health serves as a critical cornerstone in the successful management of urinary incontinence. Addressing underlying infections, inflammation, or other urinary tract abnormalities is essential for creating an environment conducive to effective bladder control. Natural interventions, such as cranberry extract or anti-inflammatory herbs, may play a supportive role in maintaining urinary tract integrity and reducing the risk of incontinence associated with compromised urinary tract health. A comprehensive approach, guided by professional medical advice, that incorporates both targeted interventions and preventive measures offers the best prospects for long-term bladder health and continence.
4. Symptom alleviation
Symptom alleviation constitutes a primary objective in the application of botanical approaches to managing urinary incontinence. The reduction of undesirable symptoms, such as frequent urination, urgent need to urinate, and involuntary urine leakage, directly impacts an individual’s quality of life. Botanical interventions are often sought as a means to mitigate these symptoms, offering an alternative or complementary approach to conventional medical treatments. The degree of symptom alleviation experienced informs the perceived efficacy of any given botanical intervention, and therefore plays a crucial role in patient adherence and long-term management. For example, an individual experiencing frequent nighttime urination might seek a botanical remedy believed to reduce bladder spasms, thereby achieving fewer nocturnal awakenings and improved sleep. The realization of this symptom alleviation directly contributes to the individual’s perception of the remedy’s value.
The relationship between botanical interventions and symptom alleviation is not always direct or consistent. The complex interplay of factors contributing to urinary incontinence, including muscle weakness, nerve damage, and underlying medical conditions, can influence the effectiveness of botanical remedies. Furthermore, individual responses to botanical compounds can vary significantly due to differences in metabolism, genetics, and the severity of the underlying condition. Thus, symptom alleviation may be more pronounced in some individuals than others, and the degree of relief achieved may not always correlate with the expected pharmacological action of the botanical compound. Consider the example of two individuals with overactive bladder both using the same herbal supplement; one may experience a significant reduction in urinary urgency, while the other experiences minimal change. This variability underscores the need for personalized approaches to treatment and careful monitoring of symptom response.
The practical significance of understanding the link between botanical interventions and symptom alleviation lies in fostering realistic expectations and promoting informed decision-making. Botanical remedies are not a guaranteed solution for urinary incontinence, and the extent of symptom relief achieved can vary. Effective management requires a comprehensive assessment of the underlying causes of incontinence, a careful selection of appropriate botanical remedies based on individual needs and medical history, and ongoing monitoring of symptom response. Furthermore, a holistic approach that integrates botanical interventions with lifestyle modifications, such as pelvic floor exercises and bladder training, may yield the most substantial symptom alleviation. Ultimately, the goal is to empower individuals to actively participate in their own care, making informed choices that optimize symptom control and enhance their overall well-being.
5. Traditional usage history
The historical use of botanicals to address urinary incontinence provides a crucial foundation for understanding current applications. Traditional medicine systems across diverse cultures have long employed specific plants and formulations to manage bladder control issues. These practices, often documented through centuries of accumulated knowledge, offer insights into the potential efficacy and safety of certain botanical approaches. The underlying principle rests on the observation that specific plants, utilized traditionally for their perceived therapeutic properties, might exert beneficial effects on bladder function, muscle tone, or inflammation within the urinary tract. The traditional use serves as a potential indicator, suggesting directions for modern scientific investigation to validate these historical claims.
For instance, the use of saw palmetto in traditional Native American medicine to address urinary problems, including those associated with an enlarged prostate (which can contribute to incontinence), has spurred modern research into its effects on prostate health and lower urinary tract symptoms. Similarly, traditional Chinese medicine incorporates various herbal formulas believed to strengthen the kidneys and bladder, reducing urinary frequency and urgency. These historical applications provide starting points for identifying specific plant compounds that may warrant further investigation for their mechanisms of action and clinical effectiveness in managing incontinence. However, it is imperative to recognize that traditional use alone does not constitute scientific proof. Modern research methodologies, including randomized controlled trials, are essential to confirm the purported benefits and assess potential risks.
The historical context surrounding the application of plant-based substances offers invaluable insight. However, that information must be viewed through a cautious and scientific lens. Understanding the connection between past practices and potential applications can guide the exploration and development of novel interventions. But, it also serves as a cautionary reminder that traditional use alone does not guarantee efficacy or safety. Modern science is needed to confirm benefits and exclude potential harms. Therefore, professional consultation with a healthcare provider is vital before incorporating any historical herbal remedy into current health strategies to ensure safety and appropriateness.
6. Potential side effects
The consideration of potential side effects is an indispensable component when evaluating botanical interventions for urinary incontinence. Although often perceived as “natural” and therefore inherently safe, plant-derived compounds can induce adverse reactions in certain individuals. These side effects stem from the inherent pharmacological activity of the plants, influencing various physiological processes, including hormone regulation, digestive function, and cardiovascular activity. The absence of rigorous regulatory oversight comparable to pharmaceuticals further necessitates careful assessment of potential risks.
Examples of potential side effects include gastrointestinal distress (nausea, diarrhea, constipation), allergic reactions (skin rashes, itching, respiratory difficulties), and interactions with prescription medications. Specific herbs may exhibit contraindications for individuals with pre-existing medical conditions, such as bleeding disorders or liver disease. For instance, saw palmetto, often used for prostate health and indirectly for related incontinence issues, can increase the risk of bleeding, especially in individuals taking anticoagulant medications. Similarly, certain diuretic herbs can lead to electrolyte imbalances if not used judiciously. Understanding these potential risks is paramount for informed decision-making and minimizes the likelihood of adverse events.
In summary, a thorough understanding of potential side effects is crucial when utilizing botanical approaches to urinary incontinence. Individuals should seek professional medical advice before initiating any course, disclosing all existing health conditions and medications. Careful monitoring of symptoms and prompt reporting of any adverse reactions are essential for safe and effective utilization. Botanical interventions represent one aspect of an effective strategy, but are not without inherent risks.
7. Dosage considerations
Appropriate dosage is a critical determinant of safety and efficacy when employing plant-derived substances to manage urinary incontinence. The concentration of active compounds within these substances can vary significantly, influencing the potential therapeutic effect and the risk of adverse reactions. Precise dosage is not simply a matter of quantity, but also depends on individual physiology, the specific botanical agent used, and the intended therapeutic outcome.
- Variability in Herbal Potency
The concentration of active constituents within a plant can vary considerably based on factors such as growing conditions, harvesting techniques, and processing methods. This variability presents a challenge in establishing standardized dosages, as a seemingly identical product from different sources may possess vastly different potencies. Accurate dosing necessitates sourcing from reputable manufacturers who employ rigorous quality control measures to ensure consistency in active compound concentrations. Failure to account for this variability can lead to either ineffective treatment or, conversely, adverse effects due to overexposure.
- Individual Physiological Factors
Individual characteristics such as age, weight, liver and kidney function, and concurrent medical conditions significantly impact drug metabolism and excretion. These physiological factors influence the optimal dosage of botanical remedies. For example, individuals with impaired liver or kidney function may require lower doses to prevent accumulation of active compounds and minimize the risk of toxicity. Similarly, elderly individuals often exhibit altered drug metabolism, necessitating dosage adjustments. Ignoring these individual differences can lead to unpredictable therapeutic outcomes and potential harm.
- Interactions with Medications and Supplements
Botanical agents can interact with prescription medications and other supplements, either potentiating or diminishing their effects. These interactions can alter the optimal dosage of both the botanical agent and the concurrent medications. For instance, certain herbs may affect the metabolism of drugs metabolized by the cytochrome P450 enzyme system, requiring dosage adjustments to maintain therapeutic drug levels. Failure to consider potential interactions can result in therapeutic failure, adverse drug reactions, or both. Consulting with a qualified healthcare professional is crucial to identify and manage potential drug interactions.
- Titration and Monitoring
Due to the inherent variability in individual responses to botanical agents, a titration approach, involving gradual dose adjustments based on symptom response and tolerance, is often recommended. Starting with a low dose and gradually increasing it until the desired therapeutic effect is achieved, while carefully monitoring for adverse effects, allows for personalized dose optimization. Regular monitoring of kidney and liver function may also be warranted, particularly with long-term use or in individuals with pre-existing medical conditions. Titration and monitoring enable the practitioner to tailor the dosage to the individual’s specific needs, maximizing therapeutic benefits while minimizing the risk of harm.
The effectiveness and safety of botanical interventions for urinary incontinence hinge on appropriate dosage considerations. Variability in herbal potency, individual physiological factors, potential interactions with medications, and the need for titration and monitoring all contribute to the complexity of dosage management. Professional guidance from a qualified healthcare practitioner is essential to navigate these complexities and ensure the safe and effective use of plant-derived substances.
Frequently Asked Questions
The following section addresses common inquiries regarding the use of botanical substances for the management of urinary incontinence. The information provided is intended for educational purposes and does not substitute professional medical advice.
Question 1: Are “herbal incontinence remedies” a scientifically proven cure for urinary incontinence?
Botanical interventions for urinary incontinence are not universally recognized as cures. While some plant-derived compounds exhibit potential benefits in alleviating symptoms or supporting bladder function, rigorous scientific evidence supporting their efficacy as standalone cures is often limited. Treatment of underlying causes, in conjunction with lifestyle adjustments, is paramount.
Question 2: What specific botanicals are commonly used for urinary incontinence, and what are their purported mechanisms of action?
Commonly used botanicals include pumpkin seed extract (believed to strengthen pelvic floor muscles), saw palmetto (primarily used for prostate-related urinary issues), and various herbs with diuretic or anti-inflammatory properties. Purported mechanisms of action vary, including muscle relaxation, reduced inflammation, and improved urinary tract health. Scientific validation of these mechanisms is ongoing.
Question 3: Are “herbal incontinence remedies” safe for everyone to use?
Botanical interventions are not universally safe. Potential side effects, interactions with medications, and contraindications for individuals with pre-existing medical conditions exist. Professional medical consultation is essential prior to initiating any botanical regimen, particularly for individuals with underlying health issues or those taking prescription medications.
Question 4: How do “herbal incontinence remedies” differ from conventional medical treatments for urinary incontinence?
Botanical interventions often take a more holistic approach, focusing on symptom alleviation and supporting overall bladder function. Conventional medical treatments may include medications targeting specific bladder mechanisms or surgical interventions. Botanical remedies lack standardization found in pharmaceuticals and require cautious dosage approaches.
Question 5: Can “herbal incontinence remedies” completely replace conventional medical treatments for urinary incontinence?
Botanical remedies are typically not intended to completely replace conventional medical treatments. In many cases, a combined approach, integrating botanical interventions with lifestyle modifications and professional medical care, yields the most favorable outcomes. Botanical remedies may serve as useful adjunctive measures.
Question 6: What factors should individuals consider when selecting a “herbal incontinence remedy”?
Factors to consider include the specific type of urinary incontinence, potential side effects and drug interactions, product quality and standardization, and the individual’s medical history. Professional medical advice is critical to ensuring appropriate selection and safe usage. The advice of experienced herbalists or naturopaths may be sought, although a medical doctor remains the primary point of contact.
It is important to remember that botanical approaches to urinary incontinence should be approached with careful consideration and professional medical guidance. These are not guaranteed solutions.
The subsequent article section will summarize important aspects of our discussion.
Conclusion
This exploration of “herbal incontinence remedy” highlights the complexities inherent in utilizing plant-derived substances for bladder control. While traditional usage and anecdotal evidence suggest potential benefits, rigorous scientific validation remains limited for many botanical interventions. Key considerations include the variability in herbal potency, individual physiological factors, potential side effects and drug interactions, and the lack of standardized dosages. Furthermore, herbal remedies are not universally safe.
Individuals considering “herbal incontinence remedy” should prioritize professional medical consultation to ensure appropriate selection and safe utilization. A combined approach, integrating lifestyle modifications and professional medical care, may offer optimal outcomes. Continued scientific investigation is crucial to fully elucidate the efficacy and safety profiles of botanical interventions for urinary incontinence, ultimately empowering informed decision-making and responsible self-care.