Certain botanical remedies have been explored as alternative or complementary approaches to managing a common fungal skin infection characterized by discolored patches. This approach focuses on utilizing plant-derived substances believed to possess antifungal properties. An example is the application of tea tree oil, diluted in a carrier oil, to the affected areas, based on its known antimicrobial characteristics.
The appeal of using plant-based interventions stems from several factors, including perceived lower risk of side effects compared to conventional medications and the potential for broader accessibility in certain regions. Historically, various cultures have relied on traditional medicinal practices involving herbs and plants to address dermatological conditions, often incorporating these into their healthcare routines.
The subsequent discussion will examine specific plant-derived substances commonly investigated for their potential in addressing this skin condition, reviewing the available evidence regarding their efficacy and safety, and outlining considerations for individuals contemplating their use.
Guidance on Botanical Approaches for a Fungal Skin Condition
The following guidelines are provided to offer comprehensive insight for those considering plant-derived solutions for addressing a common dermatological fungal infection.
Tip 1: Identify Qualifying Conditions: Ensure accurate diagnosis by a qualified healthcare professional. Self-treating without confirmation of the specific fungal infection may lead to inappropriate remedy selection and potentially exacerbate the skin condition.
Tip 2: Research Botanical Options Thoroughly: Investigate the evidence supporting the use of specific herbs or plants. Peer-reviewed studies and reputable sources are crucial for determining efficacy and understanding potential risks.
Tip 3: Understand Dilution and Application: Most botanical treatments require appropriate dilution in a carrier oil, such as coconut or almond oil. Adhere to recommended concentrations to minimize potential irritation or adverse reactions. Patch testing on a small, inconspicuous area of skin is advised before widespread application.
Tip 4: Maintain Realistic Expectations: Plant-derived solutions may require consistent and prolonged use before visible improvements are observed. Do not anticipate immediate results, as outcomes can vary based on individual factors and the severity of the infection.
Tip 5: Be Aware of Potential Interactions: Certain herbs may interact with existing medications or supplements. Consult a healthcare provider or pharmacist to assess potential drug-herb interactions and ensure safety.
Tip 6: Source Reputable Products: Obtain botanical treatments from reputable suppliers that adhere to quality control standards. Look for certifications or third-party testing to verify purity and potency.
Tip 7: Monitor for Adverse Reactions: Discontinue use immediately if any adverse reactions, such as redness, itching, or swelling, occur. Seek medical attention if symptoms persist or worsen.
Key considerations include accurate diagnosis, meticulous research, proper application techniques, and awareness of potential interactions. Plant-derived solutions may offer a complementary approach, but careful consideration and professional guidance are essential.
The subsequent section will delve into detailed discussions of individual botanical treatments commonly explored for the management of this fungal skin condition.
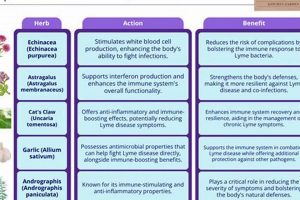
1. Antifungal properties
The effectiveness of any approach targeting a fungal skin condition relies fundamentally on the presence and potency of antifungal properties within the chosen treatment. In the context of “tinea versicolor herbal treatment,” the rationale for employing plant-derived substances rests on the premise that these substances contain compounds capable of inhibiting fungal growth or disrupting fungal cell structures. The absence of such properties renders the treatment ineffective, irrespective of other purported benefits. The cause-and-effect relationship is direct: the presence of antifungal agents leads to fungal inhibition, thereby alleviating the infection. For instance, the use of certain plant extracts, like those derived from garlic or oregano, is predicated on their documented antifungal activity against Malassezia furfur, the fungus implicated in the skin condition.
The importance of antifungal properties as a core component of “tinea versicolor herbal treatment” cannot be overstated. Without verified antifungal activity, botanical remedies are merely placebos. Rigorous testing, often involving in-vitro studies or clinical trials, is necessary to ascertain the specific compounds responsible for antifungal effects and to determine the minimum inhibitory concentration required for effective treatment. Consider the example of tea tree oil; while anecdotal evidence may suggest its efficacy, scientific studies have identified terpinen-4-ol as the primary antifungal component, allowing for standardized formulations and informed application.
In conclusion, the selection and application of “tinea versicolor herbal treatment” hinge on the documented presence and potency of antifungal properties. Understanding the mechanisms by which plant-derived substances inhibit fungal growth is crucial for informed decision-making and effective treatment. A key challenge lies in accurately identifying and quantifying these properties, ensuring consistent efficacy and safety. Therefore, a discerning approach, integrating scientific evidence with traditional knowledge, is essential for successful application.
2. Traditional usage
Traditional usage represents a significant historical and cultural context for understanding the application of botanical remedies for skin conditions. Within the domain of “tinea versicolor herbal treatment,” this encompasses the accumulated knowledge of various cultures regarding plant-based substances employed over generations to address symptoms associated with the fungal infection.
- Identification of Effective Botanicals
Traditional systems of medicine, such as Ayurveda and Traditional Chinese Medicine, have long cataloged plants believed to possess antifungal and anti-inflammatory properties. These historical records offer a starting point for modern investigations, identifying botanical candidates worthy of scientific scrutiny. For example, the use of turmeric, with its active compound curcumin, has been documented for its anti-inflammatory effects and is now being investigated for its potential antifungal properties relevant to the skin condition. The identification process through traditional use involves observing the plant’s effect on the ailment over time, a form of empirical testing.
- Methods of Preparation and Application
Traditional practices often detail specific methods for preparing botanical treatments, including extraction techniques, dilutions, and forms of application. These methods, honed over centuries, may optimize the bioavailability and efficacy of active compounds. For example, the preparation of herbal decoctions or poultices involves precise ratios of plant material to liquid, and specific heating or fermentation processes aimed at extracting desired components. These methods, when applied to “tinea versicolor herbal treatment,” could influence the effectiveness and safety profile of the resulting remedy.
- Cultural Significance and Belief Systems
The use of herbal remedies is often intertwined with cultural beliefs and spiritual practices, which can influence patient adherence and perceived effectiveness. Understanding these cultural contexts is crucial for culturally sensitive healthcare practices. In some traditions, the act of applying a botanical treatment is accompanied by rituals or prayers, which may contribute to the placebo effect or reinforce the patient’s belief in the treatment’s efficacy. When considering “tinea versicolor herbal treatment,” acknowledging and respecting these cultural dimensions is essential for promoting patient well-being.
- Limitations and Potential Risks
Traditional usage, while valuable, is not without limitations. The absence of rigorous scientific validation and standardized quality control in traditional practices can pose potential risks. For instance, the misidentification of plants, improper preparation, or lack of dosage standardization may lead to adverse effects. Therefore, it is crucial to critically evaluate traditional claims and subject them to scientific scrutiny before integrating them into contemporary treatment protocols for “tinea versicolor herbal treatment.” The lack of standardized methods might lead to inconsistent outcomes and potential harm.
In conclusion, traditional usage provides a rich tapestry of knowledge concerning botanical remedies for skin conditions. However, a discerning approach is essential, integrating traditional insights with scientific evidence to ensure the safe and effective application of “tinea versicolor herbal treatment.” Balancing historical wisdom with modern scientific rigor is vital for maximizing the potential benefits while minimizing potential risks.
3. Application method
The efficacy of any botanical intervention for a fungal skin condition is intricately linked to the chosen application method. With respect to “tinea versicolor herbal treatment,” the mode of delivery dictates the extent to which the active compounds reach the affected skin layers and exert their antifungal effects. Improper application can nullify the potential benefits of even the most potent herbal remedy. The application method is not merely a procedural detail but a determinant factor in achieving therapeutic outcomes. For instance, a simple topical application may suffice for superficial infections, while more complex formulations or delivery systems may be necessary for deeper-seated fungal colonies.
Practical considerations in application methods include factors such as skin permeability, the concentration of active compounds, and the frequency of application. The choice between an ointment, cream, lotion, or oil-based formulation directly influences the rate of absorption and retention of the herbal treatment. For example, an occlusive ointment may enhance penetration but could also exacerbate fungal growth in a moist environment. Conversely, a light lotion may provide insufficient contact time for the active compounds to exert their effects. Moreover, the application method must account for the specific characteristics of the affected area, such as skin thickness, presence of hair follicles, and susceptibility to irritation. The instructions with regards to tinea versicolor herbal treatment should have proper guaidance, as it is very crucial.
In summary, the application method constitutes a critical element in the effective deployment of “tinea versicolor herbal treatment.” Understanding the interplay between formulation, application technique, and skin physiology is essential for optimizing therapeutic outcomes. Challenges remain in standardizing application protocols and tailoring them to individual patient needs. However, a rigorous approach to application, guided by scientific principles and clinical experience, can significantly enhance the success of botanical interventions for fungal skin conditions.
4. Potential interactions
The consideration of potential interactions is paramount when evaluating the safety profile of any therapeutic intervention. In the context of “tinea versicolor herbal treatment,” this facet addresses the possibility that plant-derived substances may interact with other medications, supplements, or underlying medical conditions, potentially leading to adverse effects or diminished therapeutic efficacy.
- Herb-Drug Interactions
Herb-drug interactions occur when a botanical remedy alters the absorption, metabolism, or excretion of a pharmaceutical drug. This can result in either increased drug toxicity or decreased drug effectiveness. For example, certain herbs may induce or inhibit cytochrome P450 enzymes in the liver, which are responsible for metabolizing many medications. If an individual is taking an antifungal medication concurrently with an herbal treatment that affects these enzymes, the levels of the antifungal drug in the bloodstream could be altered, leading to subtherapeutic concentrations or increased risk of side effects. The importance of being aware of interactions in “tinea versicolor herbal treatment” is significant.
- Herb-Supplement Interactions
Similar to herb-drug interactions, botanical remedies may also interact with dietary supplements, vitamins, or minerals. This can occur through synergistic or antagonistic effects. For instance, combining two or more herbs with similar antifungal properties could potentially increase the risk of skin irritation or allergic reactions. Alternatively, an herbal remedy may interfere with the absorption or utilization of essential nutrients. Individuals contemplating “tinea versicolor herbal treatment” should therefore disclose all supplements they are currently taking to a healthcare provider.
- Interactions with Medical Conditions
Certain botanical remedies may exacerbate or contraindicate underlying medical conditions. For example, some herbs may possess anticoagulant properties and should be used with caution in individuals with bleeding disorders or those taking anticoagulant medications. Similarly, individuals with liver or kidney disease may be more susceptible to adverse effects from herbal treatments due to impaired detoxification or excretion. When considering “tinea versicolor herbal treatment,” it is essential to evaluate the patient’s medical history and assess the potential impact of botanical remedies on pre-existing conditions.
- Allergic Reactions and Sensitivities
Allergic reactions and skin sensitivities represent a common form of interaction associated with botanical remedies. Individuals may develop allergic contact dermatitis or other hypersensitivity reactions to specific plant-derived substances. Symptoms can range from mild itching and redness to severe blistering and swelling. Patch testing is often recommended to identify potential allergens before initiating “tinea versicolor herbal treatment.” Individuals with known allergies to specific plant families should exercise caution when using related herbal remedies.
In conclusion, the potential for interactions represents a critical safety consideration in the application of “tinea versicolor herbal treatment.” Healthcare providers should conduct a thorough assessment of patient history, medication use, and underlying medical conditions to identify potential risks. Open communication between patients and healthcare providers is essential to ensure the safe and effective use of botanical remedies for fungal skin conditions. Therefore, understanding the interactions of “tinea versicolor herbal treatment” is the first step to know before starting.
5. Efficacy evidence
The presence and strength of supporting data are paramount when considering the use of any therapeutic intervention. In the context of “tinea versicolor herbal treatment,” efficacy evidence refers to the scientific data that demonstrates the effectiveness of specific botanical remedies in addressing the fungal infection. The absence of robust efficacy evidence raises concerns regarding the validity and reliability of the treatment, potentially leading to ineffective or even harmful outcomes.
- Randomized Controlled Trials (RCTs)
RCTs represent the gold standard for evaluating therapeutic efficacy. These studies involve randomly assigning participants to either a treatment group receiving the herbal remedy or a control group receiving a placebo or standard treatment. The outcomes are then compared to determine whether the herbal remedy demonstrates a statistically significant benefit. In the context of “tinea versicolor herbal treatment,” RCTs would provide the most compelling evidence of efficacy. However, well-designed RCTs are often lacking for many herbal remedies, highlighting a critical gap in the evidence base.
- In Vitro and In Vivo Studies
In vitro studies involve testing the effects of herbal extracts or compounds on fungal cultures in a laboratory setting. These studies can provide preliminary evidence of antifungal activity but do not necessarily translate to clinical efficacy. In vivo studies involve testing herbal remedies on animal models with fungal infections. While in vivo studies can provide additional insights into mechanisms of action and potential toxicity, they may not accurately predict human responses. For “tinea versicolor herbal treatment,” in vitro and in vivo studies can offer supportive evidence but should not be relied upon as definitive proof of efficacy.
- Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analyses
Systematic reviews involve a comprehensive and unbiased evaluation of all available evidence on a particular topic. Meta-analyses statistically combine the results of multiple studies to provide a more precise estimate of the treatment effect. Systematic reviews and meta-analyses can provide a valuable overview of the efficacy evidence for “tinea versicolor herbal treatment.” However, the quality of the conclusions depends on the quality of the included studies. If the available studies are of poor quality or are too heterogeneous, the conclusions of the systematic review may be unreliable.
- Observational Studies and Case Reports
Observational studies, such as cohort studies and case-control studies, can provide insights into the potential benefits of herbal remedies in real-world settings. Case reports describe the experiences of individual patients who have used herbal treatments. While observational studies and case reports can generate hypotheses and provide preliminary evidence, they are subject to biases and confounding factors. Therefore, they should be interpreted with caution. For “tinea versicolor herbal treatment,” observational studies and case reports may offer anecdotal evidence but do not provide strong support for efficacy.
The evaluation of efficacy evidence forms a cornerstone in the responsible consideration of “tinea versicolor herbal treatment.” Without robust and reliable data, the use of botanical remedies remains speculative and potentially exposes individuals to unwarranted risks. A critical appraisal of the available evidence, integrating data from various study designs, is essential for informed decision-making and ethical practice. The responsibility lies with both researchers and practitioners to generate and disseminate high-quality efficacy data to guide the appropriate use of herbal remedies for fungal skin conditions.
Frequently Asked Questions
The following addresses frequently raised inquiries regarding the use of botanical remedies for managing a common fungal skin condition.
Question 1: What constitutes a legitimate “tinea versicolor herbal treatment”?
A legitimate intervention involves plant-derived substances with demonstrated antifungal properties against Malassezia furfur, the fungus primarily responsible for the skin condition. Traditional usage alone does not validate a treatment; scientific evidence supporting antifungal activity is essential.
Question 2: How does “tinea versicolor herbal treatment” compare to conventional antifungal medications?
Conventional medications typically exhibit faster and more consistent results due to standardized formulations and rigorous clinical testing. Botanical remedies may offer a gentler approach but often require prolonged use, and their efficacy can vary depending on the quality of the plant material and the individual’s response.
Question 3: What are the potential risks associated with “tinea versicolor herbal treatment”?
Risks include allergic reactions, skin irritation, and potential interactions with other medications or supplements. Improper dilution or application of botanical remedies can exacerbate these risks. Consultation with a healthcare professional is advised before initiating any herbal treatment.
Question 4: How can the efficacy of “tinea versicolor herbal treatment” be assessed?
Efficacy assessment requires monitoring the size and severity of the affected areas over time. Photographic documentation can be helpful. If symptoms persist or worsen despite consistent application of the herbal treatment, alternative interventions should be considered.
Question 5: Is “tinea versicolor herbal treatment” suitable for all individuals?
Individuals with sensitive skin, allergies to plants, compromised immune systems, or those who are pregnant or breastfeeding should exercise caution and seek medical advice before using botanical remedies. “Tinea versicolor herbal treatment” is often unsuitable in this cases.
Question 6: Where can reliable information about “tinea versicolor herbal treatment” be found?
Reliable information can be obtained from peer-reviewed scientific journals, reputable botanical databases, and qualified healthcare professionals. Avoid relying solely on anecdotal evidence or unsubstantiated claims from non-credible sources.
In summary, the application of botanical remedies for addressing this condition should be approached with caution, supported by scientific evidence, and guided by qualified healthcare professionals.
The following section will explore other treatment modalities and preventative measures relevant to managing this fungal skin condition.
Conclusion
The preceding discussion has explored the various facets of employing botanical interventions for managing a fungal skin condition. Key considerations include the presence of antifungal properties, traditional usage, application methods, potential interactions, and the availability of efficacy evidence. A discerning approach, integrating scientific data with historical context, is essential for informed decision-making. It is important to understand the proper ways to do tinea versicolor herbal treatment.
The judicious use of plant-derived substances may offer a complementary approach to conventional therapies. However, the absence of rigorous scientific validation for many botanical remedies necessitates a cautious and critical perspective. Continued research, coupled with responsible clinical application, will be crucial in determining the long-term role of botanical interventions in addressing this and other dermatological conditions. Further studies is very important to “tinea versicolor herbal treatment”.