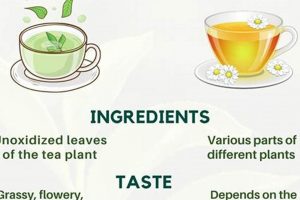
The subject of this exploration pertains to infusions made from various plants, excluding Camellia sinensis, that are cultivated and consumed within a specific European nation. These beverages, widely available in that region, are prepared by steeping dried herbs, flowers, roots, or spices in hot water. A prevalent example includes chamomile, peppermint, and fennel infusions, all frequently produced and enjoyed locally.
These botanical beverages hold significant cultural and economic importance. They are often valued for perceived health benefits, ranging from digestive aid to relaxation promotion. Historically, herbal remedies have played a crucial role in traditional medicine within this country, and the practice of consuming herbal infusions has persisted through generations. The market for these products reflects a blend of traditional knowledge and modern consumer preferences.
The subsequent discussion will delve into specific types of these plant-based infusions, examining their production, quality standards, and their place within the broader context of the nation’s food and beverage industry.
Tips Regarding German Herbal Infusions
The following are guidelines intended to enhance the understanding and appreciation of plant-based beverages sourced from Germany.
Tip 1: Source Authentically: Prioritize products labeled with clear German origin. Look for certifications or indications that the herbs were cultivated and processed within the country to ensure quality and authenticity.
Tip 2: Understand Ingredient Profiles: Familiarize oneself with the specific herbs used in each blend. Chamomile, peppermint, and fennel offer distinct properties and flavors. Knowledge of these profiles allows for informed selection based on desired effects.
Tip 3: Observe Brewing Instructions: Adhere to the recommended steeping time and water temperature. Over-steeping can result in bitter or astringent flavors, while insufficient steeping may not fully extract the beneficial compounds.
Tip 4: Inspect Packaging for Freshness: Examine the packaging for signs of damage or improper sealing. The presence of a strong aroma upon opening suggests freshness, while a muted or musty odor indicates potential degradation.
Tip 5: Consider Blends Carefully: Evaluate the composition of blended infusions. Some blends may contain ingredients that complement each other, while others may offer conflicting effects. Research the individual components before consumption.
Tip 6: Store Properly: Maintain the integrity of dried herbs by storing them in airtight containers, away from direct sunlight and moisture. This helps to preserve flavor and prevent spoilage.
Tip 7: Be Aware of Potential Allergens: Individuals with known plant allergies should exercise caution when consuming herbal infusions. Review the ingredient list carefully and discontinue use if any adverse reactions occur.
These guidelines serve to promote a discerning and informed approach to the consumption of German herbal infusions, ensuring optimal enjoyment and potential health benefits.
The article will now proceed to discuss specific popular varieties and their associated attributes.
1. Cultivation Practices
Cultivation practices are inextricably linked to the quality, character, and sustainability of herbal infusions originating from Germany. The methods employed in growing and harvesting these plants directly influence the resulting product, impacting flavor profiles, efficacy, and environmental footprint.
- Organic Farming Methods
The prevalence of organic farming in Germany significantly influences the composition of herbal infusions. Organic methods, such as crop rotation, composting, and natural pest control, minimize the use of synthetic pesticides and fertilizers. This results in herbs with reduced chemical residues and often enhanced flavor complexity. Example: Chamomile sourced from certified organic farms in Bavaria exhibit a more pronounced floral aroma compared to conventionally grown varieties.
- Sustainable Harvesting Techniques
Sustainable harvesting techniques ensure the long-term viability of wild-harvested or cultivated herbal populations. Methods such as selective harvesting, rotational cutting, and seed saving prevent over-exploitation and promote biodiversity. Example: Peppermint growers in certain regions of Germany employ rotational harvesting to allow plants to regenerate, ensuring a consistent supply of high-quality leaves without depleting natural resources.
- Soil Management and Enrichment
Proper soil management is crucial for the health and vigor of herbal plants. German cultivation practices often involve soil testing, amendment with organic matter, and the use of cover crops to improve soil structure and nutrient content. This results in herbs with higher concentrations of essential oils and active compounds. Example: Farmers cultivating fennel in the Palatinate region amend their soil with composted manure to increase its fertility, resulting in fennel seeds with a more intense anise flavor.
- Seed Selection and Propagation
The selection of appropriate seed varieties and propagation methods plays a key role in ensuring the quality and consistency of herbal harvests. German growers often prioritize locally adapted varieties that are well-suited to the region’s climate and soil conditions. Example: The use of heirloom varieties of lavender, propagated through cuttings, ensures the preservation of desirable traits such as high oil content and distinctive fragrance.
These cultivation practices are fundamental to the integrity of German herbal infusions. By prioritizing organic methods, sustainable harvesting, responsible soil management, and careful seed selection, producers contribute to the creation of high-quality, flavorful, and environmentally responsible beverages.
2. Traditional Remedies
The connection between traditional remedies and plant-based beverages in Germany is deeply rooted in historical practices. These infusions have long been employed within the framework of folk medicine to address a variety of ailments, influencing both cultural practices and the modern consumer market.
- Historical Use and Documentation
Historically, plant-based remedies in Germany were often passed down through generations, with knowledge residing within families or local healers. Detailed documentation, sometimes found in old manuscripts or herbal compendiums, outlines the preparation methods, dosages, and purported therapeutic properties of various plants. Examples include recipes for chamomile infusions to soothe digestive upset or peppermint tea for headaches, remedies prevalent even today.
- Commonly Used Herbs and Their Purposes
Certain herbs hold a prominent place in traditional German remedies. Chamomile is frequently used for its calming and anti-inflammatory effects. Peppermint is valued for its digestive benefits and ability to relieve tension. Fennel is often administered to infants and young children to alleviate colic. These applications stem from long-standing traditions and anecdotal evidence.
- Integration into Modern Wellness Practices
While not replacing conventional medicine, many traditional uses of herbal infusions have been integrated into contemporary wellness practices in Germany. Naturopathic practitioners often recommend specific plant-based infusions as complementary therapies. Consumers actively seek out these remedies for their perceived health benefits, contributing to the demand for high-quality herbal products.
- Scientific Validation and Regulation
Increasingly, scientific research is examining the efficacy of herbs used in traditional German remedies. Studies are exploring the potential health benefits of chamomile, peppermint, and other common ingredients. However, regulation surrounding the health claims of these infusions remains strict. Marketing materials are often careful to avoid unsubstantiated claims, focusing instead on the traditional use and historical context.
The enduring legacy of traditional remedies significantly shapes the perception and consumption of plant-based beverages in Germany. While scientific scrutiny continues, the cultural significance and historical use of these infusions remain central to their appeal, influencing consumer choices and informing modern wellness practices.
3. Quality Standards
Quality standards play a critical role in the production and distribution of plant-based infusions originating from Germany. These standards, encompassing various aspects from cultivation to packaging, directly affect product safety, consistency, and consumer confidence. The adherence to rigorous quality control measures is not merely a procedural requirement; it is a fundamental component of the reputation and market position of these products.
The connection between quality standards and these botanical beverages is evident in several key areas. Agricultural practices are governed by regulations that dictate the permissible use of pesticides and fertilizers. Processing facilities must adhere to Good Manufacturing Practices (GMP) to ensure hygienic handling and prevent contamination. Finished products are subject to testing for purity, heavy metals, and microbial content. For example, adherence to the German Food and Feed Code (LFGB) mandates strict limits on pesticide residues in herbal infusions intended for human consumption. Similarly, organic certifications, such as those issued by Bioland or Demeter, impose additional standards related to sustainable farming practices and ingredient sourcing. This robust framework has a direct effect on the quality of ingredients and the end product, promoting product safety and ensuring consumers receive what they expect.
In summary, quality standards are essential to maintaining the integrity and value of plant-based beverages produced in Germany. The practical significance of this understanding lies in its ability to inform consumer choices, guide industry practices, and uphold the reputation of these products in both domestic and international markets. Challenges remain in harmonizing international standards and ensuring consistent enforcement, but the commitment to quality remains a defining characteristic of the industry.
4. Regional Variations
The diverse geography and cultural traditions within Germany contribute to distinct regional variations in plant-based infusions. These variations are evident in the types of herbs cultivated, the specific blends favored, and the traditional uses associated with these beverages. Regionality is not merely a matter of taste; it reflects distinct agricultural practices, historical influences, and local knowledge.
- Alpine Herb Cultivation
The Alpine regions of Germany, characterized by mountainous terrain and cooler climates, support the cultivation of specific herbs not commonly found in other parts of the country. Examples include arnica and gentian, which are traditionally used in medicinal preparations and sometimes incorporated into regional blends. The shorter growing season and unique soil conditions influence the flavor profiles and chemical composition of these herbs.
- North Sea Coastal Blends
The coastal regions of northern Germany, influenced by maritime climates, exhibit preferences for blends that incorporate herbs believed to possess invigorating or respiratory benefits. Sea buckthorn berries, rich in Vitamin C, are frequently added to infusions. The historical reliance on maritime trade and the prevalence of respiratory ailments in these areas may contribute to this specific regional preference.
- Bavarian Herbal Traditions
Bavaria, with its strong cultural identity and agricultural heritage, boasts a rich tradition of herbal remedies and specific infusion blends. Chamomile, peppermint, and fennel are commonly cultivated and consumed. Local folklore often attributes specific health benefits to these herbs, and traditional Bavarian restaurants may offer custom-blended infusions as digestifs.
- Palatinate Wine-Growing Herbs
The Palatinate region, renowned for its wine production, also cultivates various herbs as companion plants in vineyards or in nearby fields. Lemon balm and verbena are frequently used to create refreshing infusions. The region’s agricultural expertise and culinary traditions contribute to the development of unique herbal blends that complement local cuisine.
These regional variations demonstrate that plant-based beverages in Germany are not a homogenous product. Local climate conditions, agricultural practices, cultural traditions, and historical influences all contribute to a diverse landscape of herbal infusions. Understanding these regional nuances allows for a deeper appreciation of the cultural significance and variety within the realm of “herbal tea germany.”
5. Export Regulations
Export regulations significantly impact the ability of German producers to distribute plant-based infusions internationally. These regulations, encompassing various legal and administrative requirements, dictate the conditions under which these products can be shipped, marketed, and sold in foreign markets. Compliance with these regulations is essential for accessing global consumers and maintaining a competitive position.
- Food Safety Standards
Export regulations often mandate adherence to specific food safety standards imposed by importing countries. These standards may address issues such as pesticide residues, heavy metal contamination, and microbial content. German producers must demonstrate compliance through testing and certification to gain access to foreign markets. The European Union’s Rapid Alert System for Food and Feed (RASFF) plays a critical role in monitoring food safety and can trigger import restrictions if non-compliant products are detected. For example, a shipment of chamomile tea exceeding permitted pesticide residue levels could be denied entry into the United States.
- Labeling Requirements
Importing countries typically have specific labeling requirements for food products, including herbal infusions. These requirements may dictate the language used on labels, the information that must be disclosed (e.g., ingredients, nutritional information, country of origin), and the format in which this information is presented. German producers must ensure their product labels comply with these requirements to avoid delays or rejection at customs. For example, exporting to Japan requires accurate translations and adherence to specific font size requirements for ingredient lists.
- Customs and Tariffs
Exporting herbal infusions involves navigating customs procedures and paying applicable tariffs imposed by importing countries. These procedures can be complex and may require the involvement of customs brokers. Tariffs, which are taxes levied on imported goods, can significantly affect the price competitiveness of German products in foreign markets. Trade agreements between Germany and other countries can reduce or eliminate tariffs, creating more favorable conditions for exporters. For instance, a free trade agreement with Canada may eliminate tariffs on German herbal infusions, making them more affordable for Canadian consumers.
- Organic Certification and Recognition
Many consumers, particularly in developed countries, prefer organic products. Exporting organically certified herbal infusions requires obtaining recognized certifications and complying with the organic standards of the importing country. Mutual recognition agreements between certification bodies can facilitate trade by allowing German organic certifications to be recognized in foreign markets. For example, a German organic certification from Naturland may be recognized as equivalent to the USDA organic standard in the United States, simplifying the export process.
In conclusion, export regulations form a critical framework that determines the accessibility of international markets for “herbal tea germany”. The interplay between food safety standards, labeling requirements, customs procedures, and organic certifications creates a complex environment that producers must navigate to ensure compliance and maintain competitiveness. Success in the global market depends on a thorough understanding of these regulations and a commitment to meeting the requirements of importing countries.
Frequently Asked Questions About German Herbal Infusions
The following questions address common inquiries and potential misconceptions regarding plant-based infusions originating from Germany. The information provided aims to offer clarity and promote informed decision-making.
Question 1: Are German herbal infusions subject to pesticide regulations?
German and European Union regulations strictly limit the use of pesticides in agriculture. Herbal infusions produced in Germany are subject to these regulations, with mandatory testing to ensure compliance with maximum residue levels. Products exceeding these levels are prohibited from sale.
Question 2: How can the authenticity of a German herbal infusion be verified?
Authenticity can be partially verified by examining the product labeling. Look for clear indications of German origin, such as “Hergestellt in Deutschland” or similar phrases. Organic certifications from recognized German bodies (e.g., Bioland, Demeter) provide additional assurance of origin and production methods. Contacting the manufacturer directly for traceability information may also be helpful.
Question 3: Are all “Krutertee” blends caffeine-free?
The term “Krutertee” generally refers to herbal infusions that do not contain caffeine. However, it is essential to review the ingredient list carefully. Some blends may include ingredients that naturally contain caffeine, such as mat or guarana. A thorough examination of the ingredients is crucial to confirm the absence of caffeine.
Question 4: Are German herbal infusions suitable for pregnant or breastfeeding individuals?
Certain herbs are not recommended for consumption during pregnancy or breastfeeding. It is advisable to consult with a healthcare professional or a qualified herbalist before consuming any herbal infusion during these periods. This consultation ensures the safety of both the individual and the child.
Question 5: What is the proper storage method for German herbal infusions?
To maintain quality and freshness, herbal infusions should be stored in airtight containers, away from direct sunlight, heat, and moisture. Proper storage helps to prevent oxidation and the degradation of volatile compounds responsible for flavor and aroma.
Question 6: Are there any known allergens in German herbal infusions?
Individuals with plant allergies should exercise caution when consuming herbal infusions. Review the ingredient list carefully to identify potential allergens. Common allergens may include chamomile, ragweed, or specific spices. Discontinue use immediately if any adverse reactions occur.
In summary, understanding regulations, verifying authenticity, considering specific needs (pregnancy, allergies), and practicing proper storage are vital when engaging with German herbal infusions. Diligence promotes a safer and more fulfilling experience.
The subsequent section will provide a glossary of common terms associated with the “herbal tea germany.”
Conclusion
This exploration of “herbal tea germany” has illuminated key aspects of its production, cultural significance, and regulatory environment. From traditional cultivation practices and the historical use of herbs in remedies to the stringent quality standards governing exports and the nuanced regional variations, a complex picture emerges. Understanding these facets provides crucial context for both consumers and producers navigating the market for these plant-based infusions.
The future of “herbal tea germany” hinges on continued adherence to quality standards, sustainable agricultural practices, and a nuanced understanding of evolving consumer preferences. Further research into the efficacy of traditional herbal remedies, coupled with transparent labeling and diligent compliance with export regulations, will be essential to maintaining the reputation and expanding the reach of these products in the global market. The enduring appeal of “herbal tea germany” rests on its connection to tradition, its perceived health benefits, and its commitment to quality and sustainability.