Infusions crafted from dried fruits, flowers, herbs, and spices, cultivated without synthetic fertilizers or pesticides, offer a flavorful and healthful beverage option. Chamomile, peppermint, and rooibos are examples of popular varieties within this category, each possessing unique characteristics and potential advantages.
The consumption of these natural beverages is often associated with various wellness benefits, including relaxation, digestive support, and immune system enhancement. Historically, cultures worldwide have utilized plant-based infusions for both medicinal and culinary purposes, recognizing their inherent properties and potential to promote overall well-being.
Further discussion will explore the sourcing, preparation, and specific health-related aspects of these plant-derived infusions, along with a comparative analysis of different varieties and considerations for responsible consumption.
Tips for Selecting and Enjoying Plant-Based Infusions
This section provides practical guidance for choosing, preparing, and maximizing the benefits of infusions derived from organically grown herbs and botanicals.
Tip 1: Prioritize Certification. Look for recognized organic certifications on product packaging to ensure adherence to established standards for cultivation and processing, minimizing exposure to synthetic chemicals.
Tip 2: Examine Ingredient Lists. Review ingredient lists carefully, opting for products with clearly labeled, recognizable ingredients, avoiding those with artificial additives or flavorings.
Tip 3: Consider the Source. Research the brand or supplier to understand their sourcing practices and commitment to sustainability, ethical labor standards, and environmental responsibility.
Tip 4: Observe Appearance and Aroma. Assess the visual appearance and aroma of the dried herbs or tea bags. High-quality products typically exhibit vibrant colors and characteristic, natural fragrances.
Tip 5: Use Filtered Water. Prepare infusions using filtered water to eliminate impurities and chlorine, which can negatively impact the taste and aroma of the beverage.
Tip 6: Steep According to Instructions. Adhere to recommended steeping times and temperatures specified by the manufacturer or based on the specific type of herb or botanical used. Over-steeping can result in bitterness, while under-steeping may compromise flavor extraction.
Tip 7: Store Properly. Store unused portions in airtight containers away from direct sunlight, heat, and moisture to preserve freshness and prevent degradation of the active compounds.
Tip 8: Consult Healthcare Professionals. Be mindful of potential interactions with medications or existing health conditions. Individuals with specific allergies or health concerns should consult with healthcare professionals before incorporating new herbal infusions into their routine.
By adhering to these guidelines, individuals can enhance their experience and maximize the potential benefits associated with these natural and flavorful beverages.
The following sections will delve into specific varieties and their associated properties, further equipping readers with the knowledge to make informed choices.
1. Pesticide-free Cultivation
Pesticide-free cultivation forms a fundamental pillar of the entire philosophy and practice surrounding the production of infusions from herbs, flowers, and other botanicals. The absence of synthetic pesticides in the growing process directly addresses concerns regarding human health and environmental safety. Conventional agriculture often relies on chemical pesticides to control pests and maximize yields. However, residues from these substances can persist on the plants, potentially contaminating the final product and posing risks to consumers. Selecting produce grown without these chemicals eliminates or drastically reduces this risk.
The consequences of pesticide use extend beyond direct human consumption. Chemical runoff from agricultural fields can pollute waterways, harming aquatic ecosystems and impacting biodiversity. Pesticides can also negatively affect beneficial insects, such as pollinators, disrupting the delicate balance of natural ecosystems. Choosing pesticide-free options supports farming practices that prioritize environmental stewardship and minimize ecological damage. For example, many farms are implementing integrated pest management (IPM) strategies that incorporate natural pest control methods, promoting a healthier and more sustainable agricultural system.
Ultimately, pesticide-free cultivation is not merely an absence of harmful substances; it represents a commitment to a holistic approach to agriculture. This method prioritizes soil health, biodiversity, and the long-term well-being of both humans and the environment. Choosing these products represents a conscious decision to support sustainable farming practices and promote a healthier future. Further sections will delve into specific certification standards and consumer resources that facilitate the selection of legitimately pesticide-free products.
2. Ingredient Transparency
Ingredient transparency, within the context of plant-based infusions, denotes the comprehensive disclosure of all components present in the final product. This extends beyond simply listing ingredients to include information about their origin, processing methods, and potential presence of allergens or contaminants. It’s a crucial element in building consumer trust and enabling informed purchasing decisions.
- Detailed Ingredient Listing
This facet involves providing a complete and unambiguous list of all ingredients, including botanical names (e.g., Mentha piperita for peppermint) alongside common names. Vague descriptions like “herbal blend” are insufficient. Transparency requires specifying each herb and its relative proportion, when possible, to allow consumers to assess potential allergens or sensitivities. Real-world examples include brands that list the precise cultivars of chamomile used in their infusions, as differences in cultivars can affect taste and chemical composition.
- Sourcing Information
Transparency extends to the origin of the ingredients. Knowing where the herbs were grown and harvested provides insights into environmental practices and quality control measures. Some companies specify the geographical region or even the specific farm where their ingredients are sourced. For example, a tea might indicate that its rooibos comes from a specific region in South Africa known for its superior quality or adherence to sustainable farming practices.
- Processing Methods
Disclosure of processing methods, such as drying techniques, sterilization procedures, and extraction processes, is vital. Different methods can influence the flavor, aroma, and bioactive compound content of the final product. For instance, steam sterilization is often used to reduce microbial contamination in herbs, but over-steaming can diminish the volatile oils responsible for flavor. Transparency regarding these processes allows consumers to assess whether the processing aligns with their preferences and health concerns.
- Certification and Testing
Indicating relevant certifications (e.g., organic, fair trade, non-GMO) and providing access to testing results for contaminants like heavy metals or pesticides enhances transparency. Third-party certifications provide independent verification of claims related to sourcing, processing, and quality. Access to testing data, even if summary reports, allows consumers to verify that the product meets established safety standards. Brands that readily provide this information demonstrate a commitment to accountability and consumer well-being.
These facets of ingredient transparency collectively empower consumers to make informed choices about the plant-based infusions they consume. By demanding greater transparency, consumers can support brands that prioritize ethical sourcing, sustainable practices, and product safety, ultimately contributing to a more responsible and trustworthy industry.
3. Health Benefits
The potential health advantages associated with plant-based infusions have contributed significantly to their increasing popularity. These benefits are often attributed to the bioactive compounds present in the herbs and botanicals, which may exert various physiological effects. The absence of synthetic additives and pesticides in organically grown varieties further enhances their appeal.
- Antioxidant Properties
Many herbs and botanicals contain antioxidants, which can help neutralize free radicals in the body and protect against cellular damage. Examples include rooibos, green, and hibiscus, each containing distinct types of antioxidants. The presence of these compounds may contribute to reduced risk of chronic diseases and improved overall health.
- Stress Reduction and Relaxation
Certain herbs possess calming properties that can promote relaxation and reduce stress levels. Chamomile and lavender are well-known examples, often consumed before bedtime to improve sleep quality. The mechanisms of action may involve modulating neurotransmitter activity in the brain.
- Digestive Support
Several herbs are traditionally used to aid digestion and alleviate gastrointestinal discomfort. Peppermint and ginger are commonly employed to soothe upset stomachs, reduce bloating, and promote healthy digestion. These effects may be mediated by their ability to relax smooth muscles in the digestive tract.
- Immune System Support
Some herbs contain compounds that can support the immune system and enhance its ability to fight off infections. Echinacea and elderberry are examples often used during cold and flu season. They may stimulate immune cell activity and possess antiviral properties.
These health benefits, while promising, should be considered within the context of a balanced lifestyle and not as a substitute for conventional medical treatment. While anecdotal evidence and traditional uses abound, rigorous scientific research is ongoing to fully elucidate the mechanisms of action and validate the efficacy of these plant-based infusions. Individuals should consult with healthcare professionals before incorporating them into their routines, especially if they have underlying health conditions or are taking medications.
4. Sustainable Sourcing
Sustainable sourcing, in the context of botanicals intended for infusion, encompasses practices that minimize environmental impact, uphold social responsibility, and ensure the long-term viability of resource availability. It is a critical consideration for consumers seeking organically certified herbal teas, as organic certification alone does not guarantee sustainability across the entire supply chain.
- Environmental Stewardship
Environmental stewardship involves minimizing the ecological footprint of cultivation and harvesting practices. This includes preserving biodiversity, protecting water resources, and reducing carbon emissions. For example, farms committed to sustainability may employ agroforestry techniques, integrating trees and shrubs into the agricultural landscape to enhance soil health, sequester carbon, and provide habitat for wildlife. Harvesting practices must also be carefully managed to prevent over-exploitation of wild populations and ensure the regeneration of plant resources.
- Ethical Labor Practices
Sustainable sourcing necessitates fair and ethical treatment of workers throughout the supply chain, from farm laborers to processing plant employees. This includes providing fair wages, safe working conditions, and opportunities for professional development. Independent certifications, such as Fair Trade, verify adherence to ethical labor standards and ensure that workers receive a fair share of the profits. Consumers can support sustainable sourcing by purchasing teas bearing these certifications.
- Traceability and Transparency
Traceability refers to the ability to track the origin and journey of botanical ingredients from the field to the consumer. Transparency involves openly communicating sourcing practices and supply chain information to consumers. These elements enable consumers to make informed purchasing decisions and hold companies accountable for their sustainability commitments. Blockchain technology is increasingly being used to enhance traceability in the botanical supply chain, allowing consumers to verify the origin and authenticity of their tea.
- Resource Conservation
Sustainable sourcing emphasizes the efficient use of natural resources, including water, energy, and soil. This may involve implementing water-saving irrigation techniques, utilizing renewable energy sources, and adopting soil conservation practices such as cover cropping and no-till farming. By minimizing resource consumption, sustainable sourcing contributes to the long-term resilience of agricultural systems and reduces their environmental impact.
The integration of these sustainable sourcing principles is paramount for ensuring that the production of organic herbal teas does not come at the expense of environmental degradation or social injustice. By prioritizing sustainability throughout the supply chain, producers can safeguard the availability of botanical resources for future generations and contribute to a more equitable and environmentally responsible industry. This includes ensuring that the herbs used are not only grown without synthetic pesticides but also harvested and processed in a manner that respects both the environment and the communities involved.
5. Flavor Profiles
Flavor profiles are an intrinsic attribute of each unique botanical infusion, directly influenced by factors such as plant species, cultivation conditions, processing methods, and the presence of specific volatile compounds. Within the realm of organically grown herbal teas, the absence of synthetic chemicals and fertilizers, alongside careful harvesting and drying techniques, permits the inherent flavors of the plants to express themselves more authentically. For instance, chamomile cultivated in organically managed fields may exhibit a distinctly sweeter and more nuanced floral character compared to conventionally grown varieties. This differential is attributable to the avoidance of chemical interference with the plant’s natural metabolic pathways and the soil microbiome.
The appreciation of flavor profiles is not merely a sensory experience; it also plays a vital role in discerning the quality and authenticity of organic herbal teas. Experienced tea connoisseurs can often identify subtle nuances indicative of specific geographical origins, growing practices, or processing methods. A mint infusion displaying an overly pungent or artificial flavor, for example, may raise concerns regarding the potential use of synthetic flavor enhancers or the presence of pesticide residues. Conversely, a well-balanced and complex flavor profile suggests meticulous attention to detail throughout the production process, from cultivation to packaging. The ability to recognize and differentiate these nuances enables consumers to make informed choices and select teas that align with their preferences and values.
Understanding the connection between organically certified status and resultant flavor profiles underscores the importance of considering the entire lifecycle of the tea. From the initial cultivation of the botanical to its eventual infusion, each stage contributes to the overall sensory experience. Consumers who prioritize authentic and unadulterated flavors should actively seek out organically grown options and develop their palate to appreciate the subtleties that distinguish them from conventionally produced alternatives. The continued exploration and documentation of flavor profiles within the organically certified herbal tea sector are crucial for promoting greater transparency and fostering a deeper appreciation for the inherent qualities of these natural beverages.
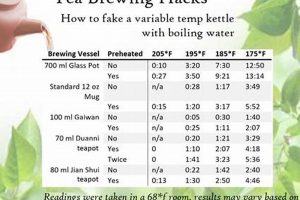
6. Brewing Methods
Brewing methods exert a significant influence on the final flavor, aroma, and concentration of bioactive compounds extracted from infusions of organically grown herbs and botanicals. The selection of an appropriate brewing technique is not merely a matter of preference but a critical factor in optimizing the sensory experience and potentially maximizing the health benefits associated with the beverage. Factors such as water temperature, steeping time, and the type of brewing vessel employed directly impact the release of volatile oils, flavonoids, and other beneficial constituents from the plant material. For instance, delicate floral varieties like chamomile and lavender often require lower water temperatures and shorter steeping times to prevent the development of bitter or undesirable flavors. Conversely, more robust herbs such as peppermint and ginger may benefit from higher temperatures and longer steeping times to fully extract their characteristic compounds.
The particle size and form of the plant materialwhether loose leaf, tea bag, or coarsely groundalso necessitate adjustments in brewing parameters. Loose leaf preparations typically require more precise control over steeping time and water temperature compared to tea bags, which offer greater convenience but may compromise the quality of the infusion. Different types of brewing vessels, such as teapots made of ceramic, glass, or stainless steel, can influence the heat retention and overall brewing process. Furthermore, the pH of the water used for brewing can affect the extraction of certain compounds, potentially altering the flavor profile and antioxidant activity of the infusion. For example, water with a slightly acidic pH may enhance the extraction of anthocyanins from hibiscus flowers, resulting in a more vibrant color and potent antioxidant effect.
In conclusion, the brewing process represents a crucial step in unlocking the full potential of organically grown herbal teas. Careful consideration of factors such as water temperature, steeping time, brewing vessel, and the form of the plant material is essential for achieving optimal flavor, aroma, and bioactive compound extraction. While general guidelines exist for brewing different types of infusions, experimentation and personal preference ultimately play a role in determining the ideal brewing technique. Further research into the effects of specific brewing parameters on the chemical composition and sensory properties of organic herbal teas is warranted to provide consumers with more precise guidance.
7. Storage Conditions
Proper storage constitutes a critical factor in preserving the quality, flavor, and potential health benefits of botanical infusions. Organically grown herbal teas, lacking synthetic preservatives, are particularly susceptible to degradation under suboptimal storage conditions. Therefore, adherence to specific storage guidelines is essential to ensure longevity and maintain the integrity of these natural products.
- Protection from Light
Exposure to light, particularly ultraviolet (UV) radiation, can accelerate the degradation of bioactive compounds and volatile oils in herbal teas. This degradation can lead to a loss of flavor, aroma, and antioxidant activity. Storing teas in opaque or dark-colored containers shields them from light exposure. Examples include airtight tins, dark glass jars, or resealable bags made of materials that block UV rays. Light exposure during retail display can also impact the quality of teas, highlighting the importance of proper packaging and storage practices throughout the supply chain.
- Control of Humidity
High humidity levels promote the growth of mold and bacteria, which can compromise the safety and quality of herbal teas. Moisture absorption can also cause the herbs to clump together, reducing their surface area and hindering proper infusion. Storing teas in airtight containers helps prevent moisture absorption. Desiccant packets, commonly found in food packaging, can further reduce humidity levels within the storage container. Avoid storing teas in areas with high humidity, such as near stoves or sinks.
- Maintenance of Temperature
Elevated temperatures can accelerate the oxidation and degradation of volatile compounds in herbal teas, leading to a loss of flavor and aroma. Fluctuations in temperature can also create condensation inside the storage container, increasing the risk of mold growth. Storing teas in a cool, dry place with a stable temperature is recommended. Avoid storing teas near heat sources, such as ovens or radiators. Optimal storage temperatures typically range between 60F and 70F (15C and 21C).
- Prevention of Odor Absorption
Herbal teas can readily absorb odors from their surrounding environment, altering their flavor profile and reducing their appeal. Strong odors from spices, coffee, or other food items can easily permeate the tea leaves. Storing teas in airtight containers and away from strong-smelling substances prevents odor absorption. Dedicated tea storage containers, separate from other food storage areas, are recommended. Regular cleaning of storage containers also helps eliminate residual odors.
By adhering to these storage guidelines, consumers can effectively preserve the quality and integrity of organically grown herbal teas. Proper storage practices not only maintain the flavor and aroma of the teas but also help to safeguard their potential health benefits. The attention to detail in storage conditions complements the commitment to quality inherent in organic cultivation and processing, ensuring a premium and satisfying experience for the consumer.
Frequently Asked Questions
This section addresses common inquiries regarding botanical infusions derived from plants cultivated without synthetic pesticides or fertilizers. The information presented aims to clarify misconceptions and provide factual insights.
Question 1: What constitutes “organic” in the context of herbal tea?
The term “organic” signifies that the herbs and botanicals used are grown and processed in accordance with specific organic standards, typically certified by a recognized third-party organization. These standards prohibit the use of synthetic pesticides, herbicides, fertilizers, and genetically modified organisms (GMOs).
Question 2: Are organically grown herbal teas inherently healthier than conventionally grown varieties?
While organically grown options eliminate or minimize exposure to synthetic chemicals, the direct health benefits compared to conventionally grown teas may vary. Research suggests potential advantages, such as reduced pesticide residue intake. However, the specific health effects depend on the individual herbs and botanicals used and the consumer’s individual health status.
Question 3: How can one verify the organic certification of herbal tea products?
Look for recognizable organic certification logos on the packaging, such as the USDA Organic seal or certifications from other accredited organizations. These logos indicate that the product has been independently verified to meet established organic standards.
Question 4: Do all herbal teas labeled “natural” also meet organic standards?
The term “natural” is not synonymous with “organic.” Products labeled as “natural” may not necessarily adhere to the same stringent standards as certified organic products. Organic certification provides a more reliable assurance of pesticide-free and sustainable farming practices.
Question 5: How should organic herbal tea be stored to maintain its quality?
Proper storage involves protecting the tea from light, moisture, and strong odors. Store the tea in an airtight container, preferably made of opaque material, in a cool, dry place away from direct sunlight and other potential contaminants.
Question 6: Are there any potential risks associated with consuming organic herbal tea?
While generally considered safe, certain herbs may interact with medications or exacerbate existing health conditions. Individuals with allergies or specific health concerns should consult with a healthcare professional before incorporating new herbal infusions into their routine. Excessive consumption of certain herbs may also have adverse effects.
In summary, informed decision-making regarding plant-based infusions cultivated without synthetic chemicals requires careful consideration of certification, sourcing, and potential health implications. Consultation with healthcare professionals is advised for individuals with specific health concerns.
The subsequent section will explore specific types of botanicals and their traditional uses, providing further insights into the diverse world of plant-derived infusions.
Conclusion
This exploration of organic herbal tea has illuminated several critical facets. From the stringent requirements for pesticide-free cultivation to the importance of ingredient transparency and sustainable sourcing, a clear understanding of these aspects is crucial for informed consumption. Furthermore, the potential health benefits, diverse flavor profiles, appropriate brewing methods, and proper storage conditions collectively contribute to the overall quality and experience associated with these beverages.
The conscious selection of organic herbal tea represents a commitment to personal well-being and environmental responsibility. Continued research and consumer awareness will further refine the industry, ensuring both the integrity of these products and the long-term sustainability of their production. Diligence in verifying certifications and understanding the nuances of these infusions remains paramount for maximizing their potential benefits and minimizing potential risks.