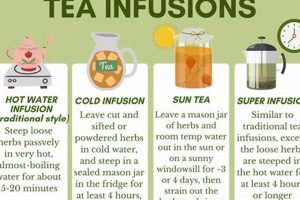
Beverages crafted from infusions or decoctions of herbs, spices, or other plant material, excluding true teas (Camellia sinensis), are frequently considered for their potential therapeutic properties. These preparations, specifically formulated for individuals experiencing skin blemishes, are explored as a complementary approach to conventional dermatological treatments.
The significance of plant-based remedies stems from a long history of traditional medicine, where botanicals were employed to address various health concerns. Advocates propose that certain herbs possess anti-inflammatory, antibacterial, or antioxidant characteristics, potentially contributing to skin health improvement. Their use is often integrated within a holistic wellness strategy, encompassing diet and lifestyle adjustments.
This exploration will delve into commonly cited botanicals, examining available evidence, mechanisms of action, potential benefits, and any associated precautions. The objective is to provide an understanding of the scientific and traditional rationale underpinning the utilization of these beverages in addressing skin imperfections.
Recommendations for Incorporating Botanical Infusions
The following suggestions are offered for individuals considering the inclusion of plant-derived beverages as a component of their skincare regimen. Strict adherence to recommended dosages and awareness of potential interactions with existing medications are essential.
Tip 1: Prioritize Research: Before incorporating any new botanical infusion, conduct thorough research. Investigate potential benefits, side effects, and interactions with current medications. Consult reputable sources, such as peer-reviewed scientific journals and established herbal medicine references.
Tip 2: Source Reputable Products: Select products from established and reputable suppliers. Verify that the source adheres to quality control standards, including testing for contaminants and accurate labeling of ingredients. Organic certification can offer assurance of pesticide-free cultivation.
Tip 3: Begin with Moderation: Introduce new infusions gradually and in small quantities. Monitor for any adverse reactions, such as skin irritation, digestive upset, or allergic responses. Discontinue use immediately if any concerning symptoms arise.
Tip 4: Consistency is Key: Botanical interventions often require sustained use to yield noticeable results. Integrate the chosen infusion into a regular routine, adhering to recommended serving sizes and frequency. Track progress through objective measures, such as photographic documentation or journaling.
Tip 5: Complement Existing Treatments: Plant-derived beverages are typically most effective when used in conjunction with conventional dermatological therapies. Do not discontinue prescribed medications or alter treatment plans without consulting a qualified healthcare professional.
Tip 6: Hydration Considerations: While these infusions can contribute to overall hydration, they should not be considered a substitute for adequate water intake. Maintain sufficient water consumption throughout the day to support overall health and skin function.
Tip 7: Monitor for Interactions: Certain botanicals can interact with prescription medications or over-the-counter remedies. Inform your healthcare provider of all supplements and infusions being used to ensure safety and avoid potential complications.
Consistent research, careful product selection, and mindful integration into a comprehensive skincare strategy are paramount. Benefits may include improved skin health, reduced inflammation, and a potential contribution to overall well-being, but should always be approached with caution and awareness of individual sensitivities.
These recommendations serve as a basis for informed decision-making, and further detailed exploration of specific botanicals is warranted.
1. Anti-inflammatory Properties
Inflammation is a key component of acne pathogenesis, contributing to redness, swelling, and pain associated with lesions. Botanical infusions are investigated for their potential to modulate inflammatory pathways, providing symptomatic relief and potentially influencing the progression of the condition.
- Reduction of Cytokine Production
Certain herbs contain compounds that can inhibit the production of pro-inflammatory cytokines, such as TNF-alpha and IL-1beta. These cytokines play a critical role in the inflammatory cascade within acne lesions. For example, compounds in chamomile and ginger have demonstrated the ability to reduce cytokine release in vitro. Reducing cytokine production can lead to decreased inflammation within acne lesions.
- Inhibition of Inflammatory Enzymes
Specific enzymes, such as cyclooxygenase-2 (COX-2), are involved in the synthesis of prostaglandins, which mediate inflammation and pain. Some botanical constituents have been shown to inhibit COX-2 activity. Compounds found in green tea and turmeric, for example, have exhibited COX-2 inhibitory effects in laboratory studies. This inhibition can potentially decrease the inflammatory response in acne.
- Modulation of Immune Cell Activity
Immune cells, such as macrophages and neutrophils, contribute to inflammation in acne by releasing inflammatory mediators. Certain herbs may modulate the activity of these immune cells, reducing their contribution to the inflammatory process. For instance, components in licorice root have demonstrated the ability to influence macrophage activity, potentially mitigating inflammation.
- Antioxidant Activity
Oxidative stress can exacerbate inflammation in acne. Antioxidant compounds can neutralize free radicals, reducing oxidative damage and subsequent inflammation. Many botanical infusions are rich in antioxidants, such as flavonoids and polyphenols. Green tea and rooibos, for example, contain high levels of antioxidants, which may help to reduce inflammation by protecting skin cells from oxidative damage.
The potential anti-inflammatory effects of botanical infusions represent a compelling area of investigation in the context of acne management. While further research is warranted to fully elucidate the mechanisms of action and clinical efficacy, the ability of these herbs to modulate inflammatory pathways offers a rationale for their use as a complementary approach to conventional treatments. It is crucial to note that individual responses may vary, and consultation with a healthcare professional is advised before incorporating any new herbal remedy.
2. Antimicrobial Actions
The presence and activity of Cutibacterium acnes (C. acnes) within pilosebaceous units are significant factors in the development of acne vulgaris. Consequently, investigating botanicals with potential antimicrobial properties represents a pertinent avenue for exploration within skin health management.
- Disruption of Bacterial Cell Walls
Certain herbal constituents exhibit the capacity to compromise the integrity of bacterial cell walls. This disruption can lead to cell lysis and subsequent bacterial death. Tea tree oil, containing terpinen-4-ol, is an example. Studies indicate that terpinen-4-ol can disrupt the cell membrane of C. acnes, leading to a reduction in bacterial load. This mechanism is significant because it directly targets the structural integrity of the bacteria.
- Inhibition of Bacterial Protein Synthesis
Protein synthesis is essential for bacterial survival and replication. Some botanical compounds can interfere with this process, effectively halting bacterial growth. Manuka honey, applied topically and consumed, contains methylglyoxal (MGO) which exhibits antimicrobial activity by inhibiting protein synthesis. This mode of action disrupts fundamental bacterial processes.
- Interference with Bacterial Biofilm Formation
C. acnes can form biofilms, which are structured communities of bacteria that are more resistant to antimicrobial agents. Certain herbal extracts have demonstrated the ability to disrupt or prevent biofilm formation. Cranberry extract contains proanthocyanidins, which have been shown to interfere with bacterial adhesion and biofilm development. Preventing biofilm formation increases bacterial susceptibility to other antimicrobial agents and the body’s immune defenses.
- Reduction of Bacterial Quorum Sensing
Quorum sensing is a cell-to-cell communication system that bacteria use to coordinate their behavior, including biofilm formation and virulence factor production. Some botanical compounds can interfere with quorum sensing, reducing bacterial virulence. Garlic extract contains allicin, which has been shown to inhibit quorum sensing in various bacterial species. By disrupting communication, allicin can reduce the overall virulence and pathogenicity of C. acnes.
The antimicrobial properties inherent in certain botanicals, when delivered via infusions, suggest a potential role in mitigating the bacterial component of acne. The varied mechanisms of action, targeting cell walls, protein synthesis, biofilm formation, and quorum sensing, underscore the complexity and potential of these natural interventions. This represents a field where traditional knowledge and scientific inquiry converge, suggesting future pathways for acne management. However, standardized extracts with validated antimicrobial activity may demonstrate more consistent results than herbal infusions, due to variability in bioactive compound concentration.
3. Antioxidant Effects
Oxidative stress, resulting from an imbalance between free radical production and antioxidant defense, is implicated in the pathogenesis of acne. The following details illustrate how antioxidant effects, potentially derived from botanical infusions, may influence acne development and progression.
- Neutralization of Free Radicals
Acne inflammation generates free radicals that damage skin cells and exacerbate inflammation. Antioxidant compounds, such as polyphenols and flavonoids found in certain herbs, neutralize these free radicals, preventing further cellular damage. Green tea, rich in epigallocatechin gallate (EGCG), exemplifies this, as EGCG scavenges free radicals, thereby mitigating oxidative stress within acne lesions. This process reduces inflammation and promotes healing.
- Reduction of Lipid Peroxidation
Lipid peroxidation, the oxidative degradation of lipids, contributes to comedogenesis (formation of blackheads and whiteheads) and inflammation in acne. Antioxidants can inhibit lipid peroxidation, preventing the formation of oxidized sebum, which is highly comedogenic. Rooibos tea, containing aspalathin and nothofagin, demonstrates this capability. These compounds protect sebum from oxidation, thereby reducing the formation of comedones and decreasing the severity of acne lesions.
- Protection of Skin Cells
Skin cells, including keratinocytes and sebocytes, are vulnerable to oxidative damage caused by free radicals. Antioxidants protect these cells from damage, preserving their function and integrity. White tea, with its high antioxidant content, shields skin cells from oxidative stress-induced damage. This protection supports the skin’s natural barrier function and reduces the likelihood of acne development.
- Modulation of Inflammatory Pathways
Oxidative stress activates inflammatory pathways, contributing to the inflammatory cascade in acne. Antioxidants can modulate these pathways, reducing the production of pro-inflammatory mediators. Chamomile tea, containing apigenin, is noted for its anti-inflammatory and antioxidant properties. Apigenin can suppress the activation of inflammatory signaling pathways, reducing the overall inflammatory response in acne and promoting healing.
The cumulative effect of these antioxidant actions suggests that specific herbal infusions could offer a protective and therapeutic role in acne management. By neutralizing free radicals, inhibiting lipid peroxidation, protecting skin cells, and modulating inflammatory pathways, antioxidant compounds contribute to a reduction in inflammation and promote skin health. However, it is essential to acknowledge that further controlled clinical trials are needed to fully validate the efficacy of these interventions.
4. Hormonal Balance
Hormonal fluctuations, particularly increases in androgens, contribute significantly to acne development. Androgens stimulate sebum production, leading to oily skin and an increased likelihood of pore clogging. Additionally, hormonal imbalances can trigger inflammation and affect the skin’s natural shedding process, further exacerbating acne. Thus, the endocrine system plays a pivotal role, establishing hormonal balance as a significant consideration in acne management. Specific botanical infusions are explored for their potential to modulate hormonal activity, thereby impacting acne severity. For example, some propose that spearmint interacts with androgen receptors. Consumption of botanicals with this property may have a positive influence.
Certain herbal infusions are investigated for their potential to influence hormone metabolism or receptor activity. These botanicals are believed to act through various mechanisms, including influencing the production or clearance of hormones, modulating the sensitivity of hormone receptors, or affecting the conversion of one hormone into another. For instance, some studies suggest that spearmint consumption may reduce levels of circulating androgens in women with polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS), a condition often associated with acne. These proposed effects, while warranting further rigorous investigation, highlight a potential pathway through which botanical infusions might exert their influence on skin health.
The utilization of botanicals to address hormonal imbalances related to acne represents a complex and nuanced approach. While some infusions may demonstrate promise in modulating hormone levels or activity, their efficacy and safety remain subjects of ongoing research. Consequently, consulting a healthcare provider is crucial before integrating these beverages into a treatment plan, ensuring that potential benefits are weighed against potential risks, and that treatment aligns with individual health needs and considerations. Addressing hormonal factors may offer symptom management for acne.
5. Detoxification Support
The concept of detoxification, often linked to the function of organs such as the liver and kidneys, is sometimes associated with efforts to improve skin health and alleviate acne. Proponents suggest that supporting these natural detoxification pathways can lead to a reduction in systemic toxins, potentially minimizing their impact on the skin. Certain herbal infusions are purported to aid this process, though scientific evidence supporting direct causation between herbal teas and enhanced detoxification leading to improved acne is generally limited. The practical significance lies in the belief that by supporting overall bodily function, the skin may benefit secondarily.
Examples of herbal infusions associated with detoxification include those containing ingredients such as dandelion root, burdock root, and milk thistle. These botanicals are traditionally used to support liver function, which is a primary organ for processing and eliminating toxins from the body. The mechanism of action is thought to involve enhancing bile production and promoting the elimination of waste products. Indirectly, this may reduce the burden on other elimination pathways, including the skin. However, it’s important to note that acne is a multifactorial condition, and while supporting detoxification pathways may be beneficial for overall health, it is unlikely to be a sole solution for acne management. Furthermore, some individuals may experience side effects from certain herbal infusions, necessitating careful consideration and consultation with healthcare professionals.
In summary, the connection between detoxification support and acne, particularly through the use of herbal infusions, remains a topic of ongoing investigation. While the premise of supporting natural elimination pathways holds logical appeal, robust clinical evidence directly linking specific infusions to improved acne outcomes is needed. If considering herbal infusions for detoxification support as part of an acne management strategy, a comprehensive approach that addresses other contributing factors, such as diet, skincare, and hormonal balance, is essential. It is also paramount to consult with qualified healthcare providers to ensure safety and avoid potential interactions with other treatments.
6. Scarring Reduction
Acne lesions can lead to scarring, a long-term sequela that significantly impacts skin texture and appearance. The potential role of herbal infusions in mitigating acne scarring is an area of growing interest, albeit one with limited direct scientific evidence. The underlying hypothesis is that certain botanicals, through their anti-inflammatory, antioxidant, and wound-healing properties, may indirectly contribute to reducing the severity or incidence of acne scars. The effectiveness of scar reduction is dependent on the type of scar, such as ice pick, rolling, boxcar, or hyperthrophic, and the severity of the acne. Prevention of inflammation is important to consider because acne lesions can lead to scarring, a long-term sequela that significantly impacts skin texture and appearance.
Examples of botanicals considered for their potential scar-reducing properties include those containing compounds known for promoting collagen synthesis, such as Centella asiatica (Gotu Kola), or those with anti-inflammatory effects, such as calendula. The mechanisms proposed involve stimulating fibroblast activity, improving skin elasticity, and reducing inflammation, all of which are critical factors in scar formation. However, most of the existing research focuses on topical application of these botanicals rather than internal consumption via infusions. The transition to real-life impact is unclear, as herbal infusions provide a diluted form of the active compounds, and their bioavailability and efficacy for scar reduction remain uncertain. The practical significance of this understanding is that while herbal infusions may contribute to overall skin health, their direct impact on reducing established acne scars is likely limited compared to targeted topical treatments or professional procedures like laser therapy or chemical peels.
In summary, while the connection between specific herbal infusions and acne scar reduction is plausible based on the known properties of certain botanicals, the available evidence is insufficient to support definitive claims. The focus of acne scar management remains on preventative measures, such as early and effective treatment of acne lesions to minimize inflammation, as well as targeted treatments aimed at stimulating collagen production and remodeling scar tissue. Individuals seeking to address acne scarring should consult with a dermatologist or qualified skincare professional to explore evidence-based treatment options, considering herbal infusions as a complementary approach to overall skin health rather than a primary solution for scar reduction.
7. Hydration Benefits
Adequate hydration is a fundamental aspect of physiological health, influencing a multitude of bodily functions, including skin integrity and barrier function. In the context of acne management, proper hydration contributes to maintaining optimal skin health, potentially impacting the severity and healing of lesions. Herbal infusions, consumed as an alternative to conventional beverages, can contribute to daily fluid intake, offering supplementary hydration alongside potential botanical benefits.
- Improved Skin Barrier Function
Hydration plays a crucial role in maintaining the skin’s barrier function, the outermost layer that protects against external irritants and pathogens. When the skin is adequately hydrated, this barrier remains intact and effective, preventing the entry of substances that can exacerbate acne. Herbal infusions contribute to this hydration, supporting the skin’s natural defense mechanisms. For example, consistent hydration helps to maintain the lipid matrix within the stratum corneum, preventing transepidermal water loss and ensuring the skin remains resilient against external aggressors. Compromised barrier function leads to increased inflammation, which in turn intensifies acne symptoms.
- Enhanced Nutrient Delivery
Water serves as a medium for transporting essential nutrients to skin cells, including vitamins, minerals, and antioxidants necessary for cellular function and repair. Optimal hydration ensures these nutrients are efficiently delivered to the skin, supporting its ability to heal and regenerate. Herbal infusions, as a source of hydration, facilitate this process, promoting the delivery of botanical compounds and other beneficial substances to the skin. Efficient nutrient delivery supports skin cell metabolism and renewal, leading to improved overall skin health and a reduced susceptibility to acne.
- Regulation of Sebum Production
While seemingly counterintuitive, dehydration can paradoxically lead to increased sebum production in some individuals. When the body senses a lack of hydration, it may trigger compensatory mechanisms to produce more oil in an attempt to prevent water loss. This excess sebum can contribute to clogged pores and acne formation. Adequate hydration, achieved in part through herbal infusions, can help regulate sebum production, maintaining a balanced skin environment. Balanced sebum production prevents the overproduction of oil, reducing the likelihood of pore clogging and subsequent acne breakouts.
- Support for Detoxification Processes
Adequate hydration is essential for supporting the body’s natural detoxification processes, primarily through the kidneys and liver. These organs filter waste products and toxins from the blood, preventing their accumulation within the body and potential impact on the skin. Herbal infusions contribute to this detoxification by promoting fluid intake and supporting kidney function. Efficient detoxification reduces the burden on the skin as an elimination pathway, minimizing the potential for toxins to contribute to inflammation and acne development. Effective kidney and liver function support the elimination of metabolic waste, potentially leading to clearer skin.
The relationship between hydration and acne is multifaceted, with adequate fluid intake supporting critical aspects of skin health, ranging from barrier function to nutrient delivery and waste elimination. Herbal infusions, serving as a hydrating beverage, can contribute to maintaining optimal skin hydration alongside the potential benefits of their botanical constituents. However, hydration alone is not a singular solution for acne, and should be integrated within a comprehensive approach encompassing appropriate skincare, diet, and medical consultation, as needed. It is an important factor because maintaining appropriate hydration is crucial for managing acne.
Frequently Asked Questions
The following questions address common inquiries and misconceptions regarding the use of plant-derived beverages as a complementary approach to acne management. The responses provided aim to offer clarity and evidence-based information.
Question 1: Are botanical infusions a substitute for prescription acne medications?
Botanical infusions are not a replacement for prescribed dermatological treatments. They may serve as a supportive measure, but adherence to a physician’s recommended protocol is paramount. Discontinuing or altering prescribed medications without medical consultation is inadvisable.
Question 2: How long does it take to observe noticeable improvements in acne when consuming botanical infusions?
The timeframe for observing discernible changes varies considerably. Factors such as the severity of the condition, individual physiology, and consistency of consumption influence outcomes. Some individuals may experience improvements within weeks, while others may require several months. Establishing realistic expectations is crucial.
Question 3: What are the potential side effects associated with botanical infusions targeting acne?
Adverse reactions are possible, ranging from mild gastrointestinal discomfort to allergic responses. It is essential to introduce new infusions gradually and monitor for any untoward symptoms. Individuals with pre-existing medical conditions or sensitivities should exercise caution and seek medical guidance.
Question 4: Can botanical infusions interact with other medications?
Certain botanical compounds possess the potential to interact with prescription and over-the-counter medications. For instance, some herbs may affect blood clotting, blood pressure, or liver enzyme activity. Transparency with a healthcare provider regarding all supplements and infusions being used is crucial to avoid potential complications.
Question 5: Are all botanical infusions equally effective in treating acne?
The efficacy of botanical infusions varies based on the specific herbs utilized and their respective concentrations of active compounds. Some botanicals may exhibit more pronounced anti-inflammatory or antimicrobial properties than others. Researching specific herbs and their purported benefits is advisable.
Question 6: Is organic certification necessary when selecting botanical infusions for acne?
Organic certification indicates that the herbs were cultivated without the use of synthetic pesticides or herbicides. While not a guarantee of efficacy, it minimizes the risk of exposure to potentially harmful chemicals. Opting for certified organic products is a prudent measure, particularly for individuals with sensitivities.
Botanical infusions should be considered as one element within a holistic approach to acne management. A comprehensive strategy encompasses appropriate skincare practices, a balanced diet, stress management, and, when necessary, medical intervention. Self-treating acne solely with botanical infusions may not yield optimal results and could delay appropriate care.
The subsequent section will explore the potential role of dietary modifications in conjunction with plant-based beverages in promoting skin health.
Herbal Tea for Acne
This exploration has presented an overview of the potential role of herbal tea for acne management, focusing on aspects such as anti-inflammatory, antimicrobial, antioxidant effects, hormonal balance, detoxification support, scarring reduction, and hydration benefits. The information outlined highlights the mechanisms by which specific botanical compounds may influence acne pathogenesis, while consistently emphasizing the need for rigorous scientific validation.
The responsible integration of herbal tea into a comprehensive acne treatment plan necessitates informed decision-making, guided by evidence-based research and professional medical advice. Individuals considering this approach should proceed with caution, recognizing that herbal tea, while potentially beneficial, should not replace established medical interventions or delay seeking appropriate dermatological care. Further investigation into the efficacy and safety of specific herbal formulations is warranted to fully understand their impact on acne and overall skin health.