An infusion derived from plants, excluding Camellia sinensis (the tea plant), offers a diverse range of flavors and potential wellness properties. Examples include infusions made from chamomile flowers, peppermint leaves, or ginger root.
These botanical beverages have a long history in traditional medicine and culinary practices globally. Their appeal lies in the perceived health benefits, ranging from relaxation and digestive support to potential antioxidant effects. The absence of caffeine in many varieties also makes them a popular alternative to traditional caffeinated beverages.
The subsequent sections will delve into specific types of these plant-based infusions, examining their unique characteristics, preparation methods, and the scientific evidence supporting their purported advantages.
Tips for Optimal Consumption
The following guidelines aim to maximize the potential benefits and minimize potential drawbacks associated with plant-based infusions.
Tip 1: Prioritize sourcing from reputable suppliers. This ensures product quality, purity, and minimizes the risk of contamination with pesticides or heavy metals. Look for certifications verifying organic or sustainable farming practices.
Tip 2: Adhere to recommended steeping times and temperatures. Over-steeping can result in a bitter taste and the release of unwanted compounds. Using water that is too hot can damage delicate herbs and diminish their beneficial properties. Generally, follow package instructions or established guidelines for each specific botanical.
Tip 3: Consider potential interactions with medications. Certain botanicals may interact with prescription or over-the-counter drugs. Consulting a healthcare professional is advisable, particularly for individuals with pre-existing medical conditions or those taking multiple medications.
Tip 4: Be mindful of potential allergens. Individuals with known plant allergies should exercise caution when trying new infusions. Start with small amounts and monitor for any adverse reactions such as skin irritation, respiratory distress, or digestive upset.
Tip 5: Rotate varieties to prevent overexposure to specific compounds. Regularly consuming the same botanical infusion may lead to the accumulation of certain substances in the body. Varying choices helps to ensure a more balanced intake of nutrients and phytochemicals.
Tip 6: Understand the potential diuretic effects. Some botanical infusions can have diuretic properties, increasing urine production. Adequate hydration is essential when consuming these beverages regularly.
Implementing these suggestions can contribute to a more positive and informed experience with these botanical beverages. It’s imperative to approach consumption responsibly and with awareness of individual health needs.
The subsequent section will offer an evaluation of the scientific evidence supporting commonly touted health benefits.
1. Botanical Sources
The origin of plant-derived infusions lies in the selection of botanical material. The chosen plant partsflowers, leaves, roots, seeds, or barkfundamentally determine the infusion’s chemical profile, flavor characteristics, and potential therapeutic properties.
- Plant Species and Chemotype
The specific plant species used is the primary determinant of the infusion’s composition. Even within a single species, different chemotypes (chemical races) exist, exhibiting variations in the concentrations of key compounds. For example, two different varieties of peppermint Mentha piperita, may yield infusions with varying levels of menthol and menthone, influencing the flavor and potential effects.
- Plant Part Utilized
Different plant parts contain varying concentrations and types of bioactive compounds. Chamomile flowers are rich in apigenin, known for its calming properties, while chamomile stems contain significantly less. Similarly, ginger rhizome offers a different profile compared to ginger leaves, affecting the resulting infusion’s flavor and physiological activity.
- Geographical Origin and Growing Conditions
Environmental factors such as soil composition, climate, altitude, and sunlight exposure influence a plant’s secondary metabolite production. Plant infusions sourced from different geographical regions can therefore exhibit subtle yet significant differences in their chemical composition and sensory qualities. For instance, lavender grown at higher altitudes may produce a more fragrant infusion compared to lavender grown at lower altitudes.
- Harvesting and Processing Methods
The timing of harvest and the post-harvest processing techniques employed impact the quality and stability of the botanical material. Harvesting at peak maturity, when the plant has accumulated the highest concentration of desired compounds, is crucial. Proper drying and storage methods are necessary to prevent degradation and preserve the integrity of the plant material.
In conclusion, the careful selection and handling of botanical sources are paramount in influencing the characteristics of plant-derived infusions. These factors collectively shape the resulting beverage’s flavor, aroma, and potential therapeutic effects, underscoring the importance of understanding the origin and processing of the plant material.
2. Preparation Methods
The process of preparing plant-derived infusions significantly impacts the extraction of bioactive compounds, flavor profile, and overall quality of the final product. Methodical application of specific techniques is critical to achieving desired results and maximizing potential benefits.
- Water Temperature
Water temperature plays a crucial role in solubilizing the desired compounds from the botanical material. Excessive heat can degrade delicate volatile oils and potentially extract undesirable bitter substances. Conversely, insufficient heat may result in incomplete extraction and a weaker infusion. The optimal temperature varies depending on the botanical being used; delicate flower infusions typically require lower temperatures (170-180F/77-82C), while tougher roots and barks may benefit from higher temperatures (200-212F/93-100C).
- Steeping Time
The duration of steeping directly affects the concentration of extracted compounds and the intensity of the infusion. Shorter steeping times (3-5 minutes) generally yield a lighter, more nuanced flavor profile, while longer steeping times (7-10 minutes or more) result in a bolder, more concentrated infusion. Prolonged steeping can, however, lead to the extraction of tannins and other undesirable compounds, contributing to a bitter or astringent taste. The ideal steeping time is dependent on the specific botanical, with finer plant material typically requiring shorter steeping periods.
- Water Quality
The quality of the water used significantly influences the taste and appearance of the infusion. Tap water containing chlorine or other impurities can negatively impact the flavor and aroma. Filtered or spring water is generally recommended to ensure optimal extraction and a clean, refreshing taste. Water pH can also affect the extraction process, with slightly acidic water often enhancing the release of certain compounds.
- Infusion Vessel and Filtration
The material of the infusion vessel can impact the heat retention and potential leaching of unwanted flavors into the infusion. Glass, ceramic, or stainless steel vessels are generally preferred for their inert properties. Effective filtration is essential to remove particulate matter and prevent a gritty or cloudy beverage. Tea bags, infusers, or fine-mesh strainers are commonly employed for this purpose. The type of filter used can influence the clarity and mouthfeel of the final infusion.
These preparation methods collectively determine the final characteristics of plant infusions, highlighting the importance of precise execution. Variations in water temperature, steeping time, water quality, and filtration techniques can dramatically alter the taste, aroma, and potential benefits of the beverage. Careful attention to these details allows for a tailored experience, maximizing enjoyment and efficacy.
3. Chemical Composition
The characteristics of plant-derived infusions are directly determined by their chemical makeup. The specific compounds present, their concentrations, and their interactions dictate the infusions sensory qualities, potential physiological effects, and overall stability. Understanding this fundamental connection is crucial for both consumers and producers seeking to maximize benefits and ensure safety. For instance, chamomile infusions contain apigenin, a flavonoid known for its anxiolytic properties; the concentration of apigenin directly influences the infusion’s potential to promote relaxation. Similarly, peppermint infusions derive their characteristic flavor and cooling sensation from menthol, the concentration of which varies based on the peppermint cultivar and preparation method. This variation impacts the infusion’s perceived intensity and potential efficacy as a digestive aid.
The influence of chemical composition extends to the stability and shelf-life of plant-derived infusions. Antioxidant compounds, such as polyphenols found in many herbal infusions, contribute to their ability to scavenge free radicals. This antioxidative activity not only offers potential health benefits but also helps to prevent the degradation of other sensitive compounds, thereby preserving the infusions quality over time. However, the presence of unstable compounds can also lead to degradation; for example, certain volatile oils may evaporate or oxidize if not properly stored, altering the infusion’s aroma and taste. The interaction of chemical constituents also influences the color of plant-based drinks. Compounds present will react with each other to form color pigments.
In conclusion, the chemical composition is the cornerstone of understanding the properties and potential uses of plant-derived infusions. While individual components contribute specific effects, the overall profile dictates the ultimate value and application. Identifying challenges like batch-to-batch variability in chemical composition and developing methods for standardization are crucial for ensuring consistent quality. This knowledge contributes to a more informed approach to production, consumption, and scientific evaluation of these botanical beverages.
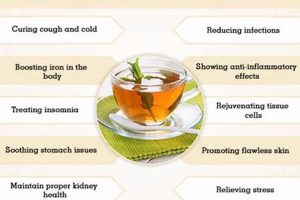
4. Potential Benefits
Plant-derived infusions have gained popularity due to perceived beneficial effects on health and well-being. These effects are attributed to the diverse array of bioactive compounds present in the plants from which they are derived.
- Antioxidant Activity
Many plant-based infusions contain polyphenols and other antioxidant compounds that neutralize free radicals in the body. This can reduce oxidative stress and may contribute to the prevention of chronic diseases. Green infusions can also be source of this activity to neutralizing free radicals.
- Relaxation and Stress Reduction
Certain botanicals, such as chamomile and lavender, are traditionally used for their calming effects. These infusions may help to reduce anxiety, promote relaxation, and improve sleep quality. Infusions can trigger various psychological process from drinking that create relaxation to one’s body.
- Digestive Support
Ginger, peppermint, and fennel infusions are known for their digestive properties. They can alleviate symptoms of indigestion, bloating, and nausea. These beverages can aid the digestion of consumers.
- Immune System Support
Some plants, like elderberry and echinacea, are believed to support the immune system. Infusions made from these plants may help to shorten the duration and severity of colds and flu. Immune can be aided by drinking more plant-based infusions.
While these potential benefits are promising, it is essential to note that scientific evidence varies for different plants. Further research is needed to fully understand the efficacy and safety of various botanical infusions. Consulting with a healthcare professional is recommended before using plant-based infusions for medicinal purposes.
5. Sensory Qualities
The consumption of plant-derived infusions involves a multi-sensory experience, where aroma, taste, visual appearance, and tactile sensations collectively contribute to the perceived quality and enjoyment. These sensory attributes are critical determinants of consumer preference and play a significant role in shaping the overall perception of these beverages.
- Aroma Profile
The aromatic compounds released from botanical materials during infusion significantly influence the sensory experience. Volatile oils, terpenes, and other aromatic substances contribute to the characteristic scent profiles. For instance, lavender-based infusions impart floral notes, while peppermint-based infusions yield a menthol aroma. The intensity and complexity of the aroma are determined by the botanical source, preparation method, and the concentration of volatile compounds. It is important to measure these key attributes, and how they effect human response, to see if the production of various te are following industry standards.
- Taste Perception
Taste perception in plant-based infusions encompasses a spectrum of flavors, including sweet, sour, bitter, and umami. These flavors are derived from various chemical compounds present in the botanical material, such as sugars, acids, alkaloids, and amino acids. The balance and interplay of these flavors contribute to the overall taste profile. The key in plant based infusions is to derive the various taste that appeals to consumers that want to add more flavor in water.
- Visual Appearance
The visual appearance of plant-derived infusions, including color, clarity, and the presence of particulate matter, influences the consumer’s initial impression. The color of the infusion is determined by the pigments extracted from the botanical material, such as chlorophyll, carotenoids, and anthocyanins. Clarity is affected by the presence of suspended solids or colloids. A visually appealing presentation enhances the overall sensory experience, as humans are visual creatures and are appeal by various color types.
- Tactile Sensations (Mouthfeel)
The tactile sensations experienced in the mouth, commonly referred to as mouthfeel, contribute to the overall sensory experience. Attributes such as astringency, viscosity, and temperature influence the perceived texture and body of the infusion. Astringency, often associated with tannins, creates a drying sensation in the mouth, while viscosity contributes to the perceived thickness or smoothness. Optimal mouthfeel enhances the overall enjoyment of plant based infusions as sensory functions plays a role to consumers.
These sensory qualities collectively define the characteristics of plant-derived infusions and guide consumer preferences. Subtle variations in aroma, taste, visual appearance, and tactile sensations can significantly impact the overall perceived quality and enjoyment. This interaction of various senses shows how consumers view plant based infusions and want more of such beverage.
6. Safety Considerations
Plant-derived infusions, despite their natural origins, necessitate careful consideration of potential safety issues. Risks associated with these beverages stem from various sources, including the inherent toxicity of certain plants, potential contaminants, and interactions with medications. Improper identification of plant species can lead to the consumption of toxic botanicals, resulting in adverse health effects. Contamination with pesticides, heavy metals, or microorganisms during cultivation, harvesting, or processing poses a significant hazard. Furthermore, bioactive compounds in specific plant materials may interact with prescription or over-the-counter drugs, altering their efficacy or increasing the risk of side effects. Individuals with pre-existing medical conditions, such as liver or kidney disease, may be more susceptible to adverse reactions. For example, consumption of comfrey-derived drinks, containing pyrrolizidine alkaloids, can cause liver damage, while interactions between St. John’s Wort and certain antidepressants have been well-documented.
Accurate identification of plants, sourcing from reputable suppliers committed to quality control, and adherence to recommended dosage guidelines are critical risk mitigation strategies. Proper storage of dried herbs is essential to prevent mold growth and degradation of bioactive compounds. Individuals with allergies or sensitivities should exercise caution when trying new plant infusions. Pregnant or breastfeeding women and individuals with chronic health conditions must consult with healthcare professionals before consuming these products. Regulatory oversight and standardized testing for contaminants are necessary to ensure product safety. The absence of such measures increases the risk of exposure to harmful substances. For instance, arsenic in some herbal products has been reported, highlighting the need for stringent monitoring.
In summary, while plant-derived infusions offer potential benefits, a thorough understanding of associated safety considerations is paramount. By prioritizing accurate identification, sourcing from reputable suppliers, adhering to recommended usage guidelines, and consulting with healthcare professionals, individuals can minimize the risks and maximize the safe enjoyment of these beverages. Ongoing research and regulatory efforts are crucial to ensure the safety and quality of plant-derived infusions available to consumers. The safe consumption of these beverages require a collaboration of consumers, business, and regulatory bodies to ensure all requirements are met.
Frequently Asked Questions About Herbal Te
This section addresses common inquiries and clarifies misconceptions concerning plant-based infusions, commonly referred to as herbal te.
Question 1: What exactly constitutes “herbal te?”
The term “herbal te” designates any infusion made from plants other than Camellia sinensis (the tea plant). These infusions are derived from flowers, leaves, roots, seeds, or bark of various botanicals. They are technically not teas, as that term is reserved for beverages made from the Camellia sinensis plant.
Question 2: Are “herbal tes” inherently safe due to their natural origin?
No. While derived from natural sources, some plants contain compounds that can be toxic or interact negatively with medications. Sourcing from reputable suppliers, verifying plant identification, and consulting a healthcare professional is crucial to ensure safety. The “natural” label does not guarantee safety.
Question 3: Do “herbal tes” provide significant health benefits?
The purported health benefits vary depending on the specific plant used. Some plants have demonstrated antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, or calming properties in scientific studies. However, rigorous clinical trials are often lacking. Claims of substantial health benefits should be critically evaluated.
Question 4: Can “herbal tes” replace conventional medical treatments?
No. Plant-based infusions should not be considered a replacement for conventional medical treatments. They may complement such treatments, but it is crucial to consult a healthcare professional before using them for medicinal purposes. Self-treating serious conditions with plant-based infusions can be dangerous.
Question 5: How should “herbal te” be properly prepared?
Preparation methods vary depending on the specific plant. Generally, steeping dried herbs in hot water for a specified duration is required. Water temperature and steeping time significantly influence the extraction of bioactive compounds and the resulting flavor profile. Adhering to recommended preparation guidelines is essential.
Question 6: Are there any potential side effects associated with “herbal te” consumption?
Yes. Some individuals may experience allergic reactions or digestive upset. Certain plant infusions can also interact with medications or exacerbate existing health conditions. Discontinue use and consult a healthcare professional if any adverse reactions occur.
It is imperative to approach the consumption of plant-based infusions with caution and a critical mindset. While some may offer potential benefits, the scientific evidence is often limited, and safety concerns must be addressed.
The next section will explore specific varieties of plant-based infusions in greater detail.
Conclusion
This exploration of plant-derived infusions, commonly referenced by the keyword phrase, has elucidated their diverse properties, potential benefits, and associated safety considerations. From botanical sources and preparation methods to chemical compositions and sensory qualities, a comprehensive understanding of these beverages requires careful consideration of numerous factors. The significance of proper sourcing, preparation, and an awareness of individual health conditions cannot be overstated.
Ultimately, the informed consumption of these botanical preparations necessitates a commitment to ongoing research, standardized quality control measures, and transparent communication between producers, consumers, and healthcare professionals. As interest in natural wellness solutions continues to grow, a responsible and evidence-based approach is essential to maximizing the potential benefits and mitigating the inherent risks associated with plant-based infusions.


![Best Herbal Grinder Shop Near You: [Your City] Prices The Ultimate Herbal Remedies Guide: Natural Healing for a Healthier Life Best Herbal Grinder Shop Near You: [Your City] Prices | The Ultimate Herbal Remedies Guide: Natural Healing for a Healthier Life](https://umangherbals.com/wp-content/uploads/2026/03/th-289-300x200.jpg)