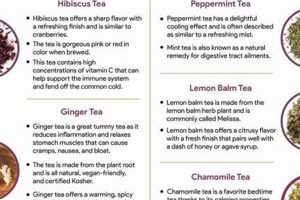
The effects of various herbal infusions on the human body are diverse, encompassing a wide range of potential health benefits. Different plants contain unique chemical compounds that, when extracted into hot water, can influence physiological processes. For example, chamomile is often associated with relaxation, while peppermint may aid digestion.
Understanding the properties inherent in these botanical preparations is significant due to their potential role in supporting wellness. Historically, many cultures have relied on herbal remedies for both preventative and therapeutic purposes. The continued interest in herbal infusions reflects a desire for natural approaches to health maintenance and minor ailment relief.
The following sections will detail the specific attributes and purported benefits of several commonly consumed herbal teas, examining their traditional uses and exploring available research.
Understanding Herbal Tea Effects
Maximizing the benefits derived from herbal infusions requires a discerning approach to selection and consumption. Consider these guidelines for informed use.
Tip 1: Identify Specific Needs: Prioritize herbal teas based on individual health goals. For instance, individuals seeking sleep support may consider valerian or lavender infusions, while those aiming to alleviate digestive discomfort may find relief with ginger or fennel.
Tip 2: Research Potential Interactions: Be aware of potential interactions between herbal teas and medications or pre-existing health conditions. Consultation with a healthcare professional is advisable, particularly for individuals with chronic ailments or those taking prescription drugs.
Tip 3: Source Reputable Brands: Opt for herbal teas from established and trusted suppliers to ensure product quality and purity. Look for certifications or third-party testing that verify the absence of contaminants.
Tip 4: Adhere to Recommended Dosages: Follow suggested brewing times and serving sizes indicated on product packaging. Excessive consumption may lead to adverse effects in some individuals.
Tip 5: Consider Brewing Methods: Different herbs may release their beneficial compounds more effectively with specific brewing techniques. Research optimal water temperatures and steeping durations for the chosen herbal tea.
Tip 6: Monitor Individual Responses: Pay attention to the body’s reaction to each herbal tea. Discontinue use if any adverse symptoms, such as allergic reactions or gastrointestinal distress, occur.
By adhering to these guidelines, individuals can make informed choices about herbal tea consumption, potentially optimizing their experience and minimizing potential risks.
The subsequent sections will explore specific herbal teas and their documented effects in greater detail.
1. Specific Plant Properties
The inherent chemical composition of a plant is the foundational determinant of its effects when consumed as an herbal tea. The presence, concentration, and interaction of various bioactive compounds within the plant material dictate the potential physiological impact of the resulting infusion.
- Phytochemical Composition
Each plant species possesses a unique profile of phytochemicals, including alkaloids, flavonoids, terpenes, and tannins. These compounds interact with the human body in various ways, influencing processes such as inflammation, neurotransmission, and antioxidant activity. The specific types and quantities of these compounds present in a given plant directly correlate with its potential effects. For example, the presence of rosmarinic acid in rosemary contributes to its purported anti-inflammatory properties.
- Synergistic Effects
The combined action of multiple phytochemicals within a plant can result in synergistic effects, where the overall impact is greater than the sum of the individual components. Understanding these interactions is crucial, as the isolated study of single compounds may not accurately reflect the holistic effect of the plant. The combination of compounds in St. John’s Wort, for instance, is thought to contribute to its purported mood-regulating properties.
- Varietal and Environmental Influences
The phytochemical profile of a plant can vary depending on factors such as its variety, growing conditions (soil composition, climate, altitude), and harvesting methods. These factors can influence the concentration of active compounds, thereby affecting the potency and potential efficacy of the herbal tea. For example, the level of essential oils in chamomile flowers can vary based on the geographic location where the plant is cultivated.
- Bioavailability
The bioavailability of phytochemicals the extent to which they are absorbed and utilized by the body is a critical factor in determining their effectiveness. Some compounds may be poorly absorbed or rapidly metabolized, limiting their potential impact. The brewing process and the presence of other substances in the tea can influence bioavailability. Piperine in black pepper, for instance, is known to enhance the bioavailability of certain other compounds.
The understanding of specific plant properties, including their phytochemical composition, synergistic effects, environmental influences, and bioavailability, is essential for predicting and explaining the effects of various herbal teas. These factors are inextricably linked to the question of what herbal teas do, shaping the diverse range of potential benefits and influencing their overall efficacy.
2. Bioactive Compound Extraction
The process of bioactive compound extraction is fundamentally linked to the question of “what herbal teas do what.” The degree to which beneficial compounds are drawn out of the plant material during brewing directly influences the potency and ultimately the effects of the resulting infusion. Inadequate extraction yields a weak tea with minimal impact, while optimal extraction maximizes the presence of active constituents, potentially enhancing the intended health benefits. For example, if ginger tea is brewed using water that is not hot enough or for an insufficient duration, the gingerol and shogaol compounds responsible for its anti-inflammatory and digestive properties will not be adequately released, thereby diminishing its potential efficacy. The cause-and-effect relationship between extraction and tea effects is, therefore, critical.
Different bioactive compounds require specific conditions for optimal extraction. Water temperature, steeping time, and the physical form of the herb (e.g., whole leaves, cut and sifted, powdered) all play a crucial role. For instance, the extraction of tannins from certain herbs, while potentially providing antioxidant benefits, can also lead to a bitter taste if over-extracted. This necessitates a careful balance to maximize the desirable compounds while minimizing the undesirable ones. The preparation of green tea serves as a practical illustration: excessively hot water can scorch the leaves, releasing unwanted bitter compounds and diminishing the desirable catechin content, thereby altering its intended antioxidant and potential health benefits.
In summary, the effectiveness of herbal teas is inextricably connected to the successful extraction of bioactive compounds. Understanding the optimal conditions for extracting specific compounds from different herbs is essential for maximizing the potential health benefits. While traditional knowledge often guides brewing practices, scientific understanding of extraction processes provides a more precise and reliable approach to achieving the desired effects and ensures consistency in the final product. Further research into optimizing extraction methods remains vital for fully unlocking the therapeutic potential of herbal teas.
3. Individual Physiological Response
The effects of herbal teas are subject to notable inter-individual variation. This variability arises from a complex interplay of genetic factors, physiological states, pre-existing health conditions, and concurrent medication use, all of which influence how a given individual responds to the bioactive compounds present in herbal infusions. Consequently, the same herbal tea may elicit different responses in different individuals, ranging from pronounced therapeutic effects to negligible impacts or even adverse reactions.
Genetic polymorphisms, for example, can affect the expression and activity of enzymes involved in the metabolism of herbal constituents. This impacts the bioavailability and duration of action of these compounds. An individual with a genetic predisposition for rapid metabolism of certain compounds may experience a diminished or shorter-lived effect from a specific herbal tea compared to someone with slower metabolism. Pre-existing conditions such as liver or kidney dysfunction can further alter drug metabolism, leading to unexpected or amplified responses. The co-administration of certain pharmaceuticals can also interfere with herbal constituents, potentially altering their efficacy or increasing the risk of adverse events.
Therefore, while generalizations regarding the effects of herbal teas can be made based on traditional use and scientific research, it is crucial to recognize the significance of individual physiological responses. A careful and observant approach is advised when incorporating herbal teas into one’s regimen, with close monitoring for any beneficial or adverse effects. Consulting with a healthcare professional is especially important for individuals with pre-existing health conditions or those taking prescription medications to ensure safe and appropriate use.
4. Traditional Use Evidence
The correlation between traditional use evidence and the observable effects of herbal teas constitutes a fundamental aspect of understanding their potential benefits. Across diverse cultures, the consistent application of specific herbal infusions for particular ailments provides a historical basis for investigating their efficacy. This empirical knowledge, accumulated over generations, suggests a causal relationship between the consumption of certain herbal teas and the alleviation of specific symptoms or the promotion of particular physiological states. For example, the traditional use of chamomile tea for its calming properties, documented in numerous historical texts and folk practices, offers a compelling rationale for investigating its potential as a sleep aid.
Traditional use evidence is not merely anecdotal; it represents a form of observational data collection over extended periods, albeit lacking the rigor of controlled clinical trials. The widespread and consistent use of specific herbs for similar purposes across different geographical regions and historical periods lends credence to the potential for genuine therapeutic effects. The traditional application of ginger tea for the management of nausea, validated by contemporary research into gingerol and shogaol compounds, demonstrates the potential for aligning traditional knowledge with modern scientific understanding. Similarly, the long-standing use of peppermint tea to alleviate digestive discomfort has prompted scientific investigation into its effects on gastrointestinal motility and inflammation.
While traditional use evidence provides a valuable starting point, it is crucial to acknowledge its limitations. Confounding factors, such as placebo effects, lifestyle influences, and the lack of standardized preparation methods, can complicate the interpretation of historical data. Nevertheless, the integration of traditional knowledge with rigorous scientific investigation offers a comprehensive approach to unraveling the complexities of “what herbal teas do what.” By systematically validating traditional uses through controlled trials and mechanistic studies, the potential benefits of herbal teas can be substantiated and integrated into evidence-based healthcare practices.
5. Scientific Research Validation
Rigorous scientific investigation serves as a critical lens through which the purported effects of herbal teas are evaluated. Claims based on traditional use or anecdotal evidence necessitate corroboration through controlled studies to establish both efficacy and safety.
- Randomized Controlled Trials (RCTs)
RCTs represent the gold standard for assessing the effects of interventions, including herbal teas. These trials involve randomly assigning participants to either a treatment group (receiving the herbal tea) or a control group (receiving a placebo or standard treatment). By comparing outcomes between groups, researchers can determine whether the observed effects are attributable to the herbal tea itself, rather than chance or other confounding factors. For instance, RCTs have been conducted to evaluate the efficacy of chamomile tea in improving sleep quality, providing evidence to support or refute traditional claims.
- Mechanistic Studies
Mechanistic studies delve into the biological mechanisms by which herbal teas exert their effects. These studies investigate the interaction of herbal constituents with specific cellular targets or physiological processes. By elucidating the underlying mechanisms, researchers can gain a deeper understanding of how herbal teas work and identify potential therapeutic targets. For example, mechanistic studies have explored the effects of green tea catechins on antioxidant activity and cellular signaling pathways, providing insights into their potential role in cancer prevention.
- Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analyses
Systematic reviews and meta-analyses synthesize the findings from multiple independent studies to provide a comprehensive overview of the evidence. These analyses employ rigorous methodologies to assess the quality of included studies and to pool data, thereby increasing statistical power and reducing the risk of bias. Systematic reviews and meta-analyses can help to resolve conflicting findings from individual studies and to provide a more definitive assessment of the effects of herbal teas. For example, meta-analyses have examined the effects of peppermint oil, often consumed as a tea, on irritable bowel syndrome symptoms, providing a summary of the available evidence.
- Dosage and Safety Evaluations
Scientific research also plays a crucial role in determining appropriate dosages and evaluating the safety of herbal teas. Studies are conducted to assess the potential toxicity of herbal constituents and to identify any potential drug interactions. These evaluations are essential for ensuring the safe and responsible use of herbal teas. For instance, research has investigated the potential hepatotoxicity of certain herbal ingredients, informing recommendations regarding safe consumption levels.
In conclusion, scientific research validation is paramount for substantiating the claims associated with “what herbal teas do what.” Through the application of rigorous methodologies, including RCTs, mechanistic studies, systematic reviews, and safety evaluations, the potential benefits and risks of herbal teas can be elucidated, providing a foundation for evidence-based recommendations and informed consumer choices.
6. Potential Side Effects
The inquiry into “what herbal teas do what” necessarily encompasses a thorough consideration of potential adverse effects. The bioactive compounds responsible for therapeutic actions can also trigger unintended and undesirable physiological responses in certain individuals. A comprehensive understanding of herbal tea effects requires recognizing that potential benefits are invariably coupled with potential risks. The absence of perceived benefit does not equate to the absence of potential harm; even seemingly benign infusions can precipitate adverse reactions in susceptible individuals. For example, while chamomile is generally regarded as safe, some individuals may experience allergic reactions, particularly those with known sensitivities to plants in the Asteraceae family. Likewise, excessive consumption of licorice root tea can lead to elevated blood pressure due to its glycyrrhizic acid content.
The relationship between dosage and adverse effects is often a critical determinant of safety. Many herbal teas, when consumed in moderate amounts, may be well-tolerated. However, exceeding recommended dosages can increase the likelihood of adverse events. Furthermore, interactions with pre-existing medical conditions or pharmaceutical medications can potentiate the risk of side effects. Individuals with bleeding disorders, for instance, should exercise caution when consuming herbal teas with anticoagulant properties, such as ginger or garlic. Similarly, pregnant or breastfeeding women should consult with healthcare professionals before consuming herbal teas, as some constituents may pose risks to fetal or infant development. The understanding that specific herbal teas do specific things, both positive and negative, is fundamental to their responsible and informed use.
Therefore, the responsible exploration of “what herbal teas do what” demands a balanced assessment of both potential benefits and potential side effects. An informed approach necessitates careful consideration of individual health status, potential drug interactions, and recommended dosages. Awareness of potential adverse reactions, coupled with vigilance in monitoring the body’s response to herbal tea consumption, are crucial for mitigating risks and ensuring the safe and effective utilization of these botanical preparations.
Frequently Asked Questions
The following section addresses common inquiries regarding the potential effects of herbal teas, providing evidence-based insights and clarifying misconceptions.
Question 1: Are all herbal teas safe for consumption?
Not all herbal teas are universally safe. Individual sensitivities, pre-existing health conditions, and potential interactions with medications can influence safety. Consulting with a healthcare professional is advisable before incorporating new herbal teas into a regimen.
Question 2: Can herbal teas replace conventional medical treatments?
Herbal teas should not be regarded as replacements for prescribed medical treatments. While some herbal infusions may offer adjunctive support for certain conditions, they are not substitutes for professional medical care. Adhering to prescribed treatment plans is essential.
Question 3: Do herbal teas have standardized dosages?
Dosage recommendations for herbal teas can vary considerably depending on the specific herb, the concentration of active compounds, and individual factors. Following the guidelines provided by reputable manufacturers or consulting with a qualified herbalist is recommended to avoid potential adverse effects.
Question 4: How can the quality of herbal teas be ensured?
Selecting herbal teas from reputable suppliers that adhere to quality control standards is crucial. Look for certifications or third-party testing that verify the absence of contaminants and the authenticity of the herbal ingredients.
Question 5: Are there any known interactions between herbal teas and medications?
Yes, certain herbal teas can interact with pharmaceutical medications, potentially altering their efficacy or increasing the risk of side effects. Individuals taking prescription drugs should consult with a healthcare professional or pharmacist to assess potential interactions before consuming herbal teas regularly.
Question 6: How long does it typically take to experience the effects of herbal teas?
The timeframe for experiencing the effects of herbal teas can vary depending on the individual, the specific herb, and the intended outcome. Some individuals may notice subtle effects relatively quickly, while others may require more prolonged and consistent consumption to experience noticeable benefits. Maintaining realistic expectations is important.
In summary, the effects of herbal teas are multifaceted and influenced by various factors. A cautious and informed approach is essential for maximizing potential benefits while minimizing potential risks.
The following section will address the role of herbal teas in promoting relaxation and stress reduction.
What Herbal Teas Do
This exploration has illuminated the multifaceted nature of herbal tea effects, underscoring the critical interplay between plant properties, extraction methods, individual physiology, and rigorous scientific validation. Understanding what herbal teas do necessitates acknowledging both potential benefits and inherent risks, emphasizing the importance of informed selection, responsible consumption, and awareness of potential interactions. The historical context provided by traditional use evidence serves as a valuable foundation, while contemporary research endeavors to establish efficacy and elucidate underlying mechanisms.
Continued investigation into the specific effects of various herbal infusions remains essential for establishing evidence-based guidelines and optimizing their role in supporting well-being. Further research should prioritize standardized extraction methods, comprehensive safety evaluations, and the exploration of synergistic effects among herbal constituents, thereby enhancing the understanding of what herbal teas do and facilitating their integration into holistic healthcare practices.






![Is Herbal Tea Safe During Pregnancy? [Guide] The Ultimate Herbal Remedies Guide: Natural Healing for a Healthier Life Is Herbal Tea Safe During Pregnancy? [Guide] | The Ultimate Herbal Remedies Guide: Natural Healing for a Healthier Life](https://umangherbals.com/wp-content/uploads/2026/03/th-214-300x200.jpg)