The subject involves the application of plant-derived remedies to alleviate the discomfort and potentially reduce the size of benign, fluid-filled lumps that typically develop near joints or tendons. Such alternative approaches are sought as complementary or alternative methods for managing these common, often asymptomatic, growths. Advocates suggest specific plants may possess anti-inflammatory or analgesic properties that could offer relief. However, it is essential to acknowledge that rigorous scientific validation is often lacking.
This approach to wellness has garnered attention due to a rising interest in natural and holistic healthcare practices. Historically, various cultures have employed herbal remedies for a wide range of ailments. The appeal of botanical treatments stems from the perception that they are gentler or have fewer side effects than conventional medical interventions. However, this perception must be balanced against the need for evidence-based efficacy and safety data. The historical use of plants for wellness offers a rich tradition that continues to influence health practices, but must be carefully considered within the context of modern medical understanding.
The following article will delve into specific herbal preparations, their purported mechanisms of action, potential risks and benefits, and the critical need for consultation with qualified healthcare professionals prior to initiating any such regimen. Further sections will address the current state of scientific evidence supporting these treatments and the importance of integrating them responsibly with conventional medical care.
Guidance on Exploring Botanical Approaches for Ganglion Cysts
The following recommendations provide a framework for considering plant-derived interventions for ganglion cysts. Emphasis is placed on informed decision-making and integration with conventional medical advice.
Tip 1: Consultation with Healthcare Professionals: Prior to initiating any form of botanical intervention, a thorough consultation with a physician or qualified healthcare provider is essential. A medical professional can accurately diagnose the condition, rule out other potential causes, and provide comprehensive treatment options.
Tip 2: Research Reputable Sources: Investigate the scientific evidence supporting the use of specific herbs. Focus on peer-reviewed studies, systematic reviews, and meta-analyses to evaluate efficacy and safety.
Tip 3: Identify Potential Allergies and Interactions: Conduct a thorough assessment of personal allergies and potential interactions between herbs and any existing medications. Some botanical substances can have significant interactions with pharmaceuticals, leading to adverse effects.
Tip 4: Source High-Quality Products: Obtain herbal remedies from reputable sources that adhere to quality control standards. Look for products that have been tested for purity, potency, and contaminants.
Tip 5: Consider Topical Applications: Certain herbal preparations are available in topical forms, such as creams or ointments. Explore these options, as they may offer localized relief while minimizing systemic absorption.
Tip 6: Monitor for Side Effects: Closely monitor for any adverse reactions or side effects after initiating herbal treatments. Discontinue use immediately if any unusual symptoms arise and consult with a healthcare professional.
Tip 7: Establish Realistic Expectations: Understand that herbal treatments may provide symptomatic relief, such as pain reduction or inflammation management, but are not guaranteed to eliminate the cyst. The success of botanical approaches can vary depending on individual factors and the specific characteristics of the cyst.
Adherence to these guidelines emphasizes the importance of responsible and informed utilization of plant-derived remedies for ganglion cysts. A collaborative approach involving healthcare professionals and a commitment to evidence-based practices are crucial for safe and effective management.
The subsequent sections will explore conventional treatments alongside herbal considerations, enabling a comprehensive and informed perspective on addressing ganglion cysts.
1. Anti-inflammatory herbs
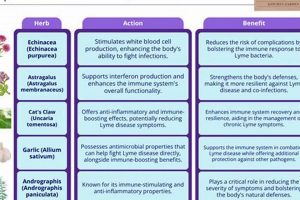
The purported connection between anti-inflammatory herbs and ganglion cyst management lies in the potential to alleviate associated discomfort. Ganglion cysts, while often asymptomatic, can cause pain and inflammation due to their location near joints or tendons. The rationale for employing anti-inflammatory herbs within a botanical treatment approach stems from the belief that these agents can reduce swelling and pain, thereby improving the individual’s comfort level. Curcumin, derived from turmeric, and ginger are often cited for their anti-inflammatory properties and are examples that frequently emerge when discussing alternative strategies for managing swelling.
The importance of anti-inflammatory herbs as a component of botanical approaches is predicated on addressing symptomatic relief rather than cyst resolution. Many individuals experience pain and limited range of motion, prompting the exploration of options beyond conventional interventions. For instance, topical applications of arnica or calendula, herbs recognized for their anti-inflammatory effects, are utilized with the intention of mitigating local inflammation and discomfort. However, it is critical to emphasize that such applications target the symptoms and not the underlying cause of the cyst’s formation.
In summary, the application of anti-inflammatory herbs in the context of ganglion cysts is primarily geared toward managing inflammation and pain associated with the condition. While these botanical agents might contribute to a temporary reduction in swelling and discomfort, they are not considered a primary treatment for eliminating the cyst itself. Understanding this distinction is critical to setting realistic expectations and ensuring that botanical approaches are integrated responsibly alongside, and not as a replacement for, conventional medical care, when necessary.
2. Topical application efficacy
The relevance of topical application efficacy to botanical interventions for ganglion cysts rests on the localized delivery of potentially therapeutic compounds. This approach aims to mitigate inflammation, reduce pain, and possibly influence the cyst’s size without systemic exposure to herbal constituents.
- Localized Delivery of Active Compounds
Topical applications allow for the direct application of herbal extracts to the affected area. For instance, a cream containing arnica extract can be applied to reduce inflammation in the tissues surrounding the cyst. This targeted delivery potentially minimizes the risk of systemic side effects associated with oral administration. However, the degree of absorption and the concentration of active compounds reaching the deeper tissues surrounding the cyst remain variable factors.
- Vehicle and Formulation Considerations
The efficacy of topical applications is significantly influenced by the vehicle used to deliver the herbal extract. Ointments, creams, gels, and lotions differ in their ability to penetrate the skin and release active compounds. For example, lipophilic compounds may be more readily absorbed through the skin when formulated in an oil-based ointment compared to a water-based lotion. The choice of vehicle and formulation plays a crucial role in determining the bioavailability of the herbal constituents at the target site.
- Limited Evidence and Standardization Challenges
While anecdotal evidence may support the use of topical herbal applications for ganglion cysts, rigorous scientific evidence is often lacking. Furthermore, the standardization of herbal extracts in topical formulations presents a challenge. Variations in the concentration of active compounds, sourcing of the plant material, and extraction methods can affect the consistency and predictability of the therapeutic effect. Therefore, evaluating the efficacy of these preparations is complicated by the inherent variability in herbal products.
- Potential for Skin Sensitivity and Allergic Reactions
Topical application of herbal extracts carries the risk of skin sensitivity and allergic reactions. Certain individuals may be susceptible to contact dermatitis or other adverse reactions to specific plant constituents. Patch testing before widespread application is advised to identify potential allergens. The presence of preservatives or other additives in the topical formulation can also contribute to skin irritation. Careful consideration of individual sensitivities is necessary when utilizing topical herbal treatments.
The efficacy of topical botanical applications for ganglion cysts hinges on factors ranging from the delivery mechanism of active compounds to the standardization of herbal products and potential for adverse reactions. The available evidence, while suggestive in some cases, requires further investigation to validate the true therapeutic potential. Responsible application necessitates an informed understanding of these factors and careful monitoring for any signs of adverse effects, combined with medical professional oversight.
3. Pain relief potential
The alleviation of pain stands as a primary objective when considering botanical interventions for ganglion cysts. While the cysts themselves are often asymptomatic, they can, depending on their size and location, exert pressure on adjacent nerves or tendons, resulting in localized pain, tingling, or numbness. Consequently, the potential for pain relief becomes a significant factor in the selection and application of herbal approaches.
Herbs possessing analgesic or anti-inflammatory properties are frequently explored for their capacity to mitigate the discomfort associated with ganglion cysts. For instance, topical applications of arnica or formulations containing essential oils such as lavender or peppermint are employed with the intention of reducing pain perception. Similarly, oral administration of herbs like turmeric, known for its curcumin content, is sometimes considered based on its purported anti-inflammatory effects, which may indirectly contribute to pain reduction. However, it is crucial to acknowledge that the evidence supporting the efficacy of these herbal interventions for ganglion cyst-related pain remains limited and requires further rigorous investigation. Furthermore, any potential interactions between herbal remedies and conventional pain medications must be carefully evaluated by a healthcare professional.
In summary, the pain relief potential of botanical approaches for ganglion cysts represents a key consideration, driven by the desire to alleviate discomfort arising from nerve or tendon compression. While certain herbs demonstrate analgesic and anti-inflammatory properties, the scientific evidence supporting their efficacy in this specific context is not definitive. Therefore, the integration of herbal remedies for pain management should be approached cautiously and in consultation with a qualified healthcare provider, ensuring that it complements, rather than replaces, evidence-based medical care.
4. Circulation enhancement
The improvement of blood flow in the vicinity of a ganglion cyst is sometimes considered within the framework of botanical interventions. The rationale rests on the premise that enhanced circulation may facilitate the delivery of nutrients and the removal of waste products, potentially influencing tissue health and reducing inflammation.
- Nutrient Delivery and Tissue Regeneration
Adequate blood flow is essential for delivering oxygen, nutrients, and immune cells to the tissues surrounding the cyst. Enhanced circulation could theoretically support tissue repair and regeneration, potentially aiding in the resolution of inflammation or preventing further growth of the cyst. For example, herbs like ginger or cayenne, known for their warming properties, are sometimes used topically to stimulate local blood flow. However, direct evidence of their impact on ganglion cyst size or symptoms is limited.
- Waste Removal and Detoxification
Effective circulation aids in the removal of metabolic waste products and toxins from the affected area. Improved blood flow may help clear inflammatory mediators and other substances that contribute to pain and swelling. Herbs with diuretic properties are occasionally employed to promote fluid drainage, although their specific impact on ganglion cysts remains unproven. The concept of “detoxification” through enhanced circulation is frequently discussed in traditional medicine systems, but its scientific validity requires careful evaluation.
- Anti-Inflammatory Effects through Enhanced Circulation
Increased blood flow can deliver anti-inflammatory compounds to the site of inflammation. This may contribute to a reduction in swelling and pain associated with ganglion cysts. However, it is crucial to distinguish between the effect of increased circulation itself and the specific anti-inflammatory properties of the herbs being used. The mere stimulation of blood flow does not guarantee a reduction in inflammation unless it is accompanied by the delivery of therapeutic compounds.
- Potential Risks and Limitations
While enhanced circulation is generally considered beneficial, certain precautions are necessary. Vigorous massage or excessive heat application could potentially exacerbate inflammation in some cases. Furthermore, individuals with underlying circulatory disorders should exercise caution and consult with a healthcare professional before attempting to enhance circulation through herbal remedies. The efficacy of this approach is also highly dependent on the specific location and characteristics of the ganglion cyst, as well as the individual’s overall health status.
The role of circulation enhancement in ganglion cyst management remains a complex and incompletely understood aspect of botanical interventions. While improved blood flow may contribute to tissue health and inflammation reduction, its direct impact on cyst size or symptom resolution requires further investigation. The integration of circulation-enhancing herbs should be approached cautiously and in consultation with qualified healthcare professionals, considering potential risks and limitations.
5. Cyst size reduction
The reduction of ganglion cyst size constitutes a primary therapeutic goal when considering botanical interventions. While symptom management offers relief, a decrease in the cyst’s dimensions is viewed as a more definitive measure of treatment success. The potential of plant-derived compounds to achieve this objective is a subject of ongoing exploration.
- Anti-inflammatory Mechanisms
Certain herbal remedies possess anti-inflammatory properties that may indirectly contribute to cyst size reduction. By mitigating inflammation in the tissues surrounding the cyst, these agents could potentially reduce fluid accumulation and swelling. Examples include topical applications of arnica or curcumin-containing preparations. However, it is crucial to note that while inflammation reduction might temporarily decrease the apparent size of the cyst, it does not necessarily address the underlying cause of its formation. Furthermore, the efficacy of these interventions in achieving sustained cyst size reduction remains limited.
- Promotion of Fluid Drainage
Some botanical approaches aim to enhance fluid drainage from the cyst. Diuretic herbs, such as dandelion, are occasionally used with the intent of promoting fluid excretion and thereby reducing cyst volume. However, the effectiveness of this strategy is questionable, as ganglion cysts are encapsulated structures and may not readily respond to systemic diuretic effects. Additionally, excessive fluid loss can lead to dehydration and electrolyte imbalances, highlighting the need for caution when employing such interventions.
- Alteration of Synovial Fluid Production
A theoretical mechanism for cyst size reduction involves altering the production of synovial fluid within the cyst itself. However, direct evidence of herbal remedies influencing synovial fluid production is scarce. Some traditional medicine systems propose that specific herbs can modulate fluid balance within the body, but these claims lack rigorous scientific validation in the context of ganglion cysts. Further research is necessary to determine whether botanical agents can effectively target synovial fluid production and achieve cyst size reduction.
- Stimulation of Tissue Repair
The potential for herbal remedies to stimulate tissue repair and remodeling is another factor considered in cyst size reduction. It is hypothesized that certain plant-derived compounds may promote the breakdown of the cyst wall or encourage the absorption of fluid back into the surrounding tissues. However, this concept remains largely theoretical, and the specific mechanisms by which herbs might influence tissue repair in ganglion cysts are poorly understood. Clinical trials are needed to assess the efficacy of these interventions and to identify potential risks.
The connection between cyst size reduction and botanical treatments for ganglion cysts involves various proposed mechanisms, including anti-inflammatory effects, promotion of fluid drainage, alteration of synovial fluid production, and stimulation of tissue repair. While some herbal remedies may offer symptomatic relief, the evidence supporting their ability to achieve sustained cyst size reduction remains limited. Responsible utilization of these treatments necessitates a comprehensive understanding of their potential benefits and risks, along with consultation with qualified healthcare professionals.
6. Safe herbal combinations
The principle of formulating safe herbal combinations is paramount when considering botanical interventions for ganglion cysts. The concurrent use of multiple herbs introduces complexities regarding potential synergistic, additive, or antagonistic effects, impacting both efficacy and safety.
- Understanding Herb-Drug Interactions
Many herbs possess bioactive compounds capable of interacting with pharmaceutical medications. For instance, St. John’s Wort can induce cytochrome P450 enzymes, potentially reducing the efficacy of prescription drugs. Prior to combining herbal remedies with conventional treatments for ganglion cysts or any other condition, a thorough assessment of potential herb-drug interactions is mandatory to avoid adverse outcomes. Pharmacists and physicians are valuable resources for identifying these potential conflicts.
- Considering Synergistic and Additive Effects
The combination of certain herbs may result in synergistic or additive effects, where the combined action is greater than the sum of their individual effects. While synergism can enhance therapeutic outcomes, it also increases the risk of adverse effects. For example, combining two herbs with sedative properties could lead to excessive drowsiness. A knowledgeable herbalist or healthcare professional can guide the selection of herb combinations that offer potential synergistic benefits while minimizing safety risks. The use of multiple anti-inflammatory herbs, for instance, may offer enhanced pain relief but necessitates careful monitoring for gastrointestinal distress.
- Addressing Antagonistic Effects
Antagonistic interactions occur when one herb diminishes the effectiveness of another. This can lead to therapeutic failure and potentially exacerbate the condition. For example, consuming herbs that counteract the actions of other herbs used to improve circulation could negate the intended benefit. Careful selection and dosage adjustments are necessary to avoid antagonistic effects. Comprehensive knowledge of herbal pharmacology is essential for formulating effective and safe combinations.
- Individual Variability and Sensitivity
Individuals exhibit varying degrees of sensitivity to herbal remedies. Factors such as age, weight, medical history, and genetic predisposition can influence an individual’s response to herbal combinations. What might be a safe and effective combination for one person could prove harmful to another. A personalized approach, guided by a qualified healthcare provider, is crucial for determining the appropriateness of herbal combinations and adjusting dosages based on individual needs and tolerance.
In summary, the formulation of safe herbal combinations within the context of botanical approaches for ganglion cysts demands a comprehensive understanding of herb-drug interactions, synergistic and antagonistic effects, and individual variability. A collaborative approach involving healthcare professionals, pharmacists, and knowledgeable herbalists is essential to mitigate potential risks and optimize therapeutic outcomes. The selection of herbal combinations should be based on evidence-informed principles, emphasizing safety and individualization.
7. Professional guidance needed
The intersection of botanical interventions and ganglion cyst management underscores the indispensable requirement for professional medical guidance. Self-directed approaches, without proper expertise, can pose risks and compromise effective care. Integrating herbal treatments necessitates a collaborative approach involving healthcare professionals.
- Accurate Diagnosis and Differential Diagnosis
A qualified physician can accurately diagnose a ganglion cyst and rule out other conditions presenting with similar symptoms. For example, a lump near the wrist could be a tumor, a lipoma, or another type of cyst. Misdiagnosis can lead to inappropriate treatment, delaying proper medical care. Professional assessment ensures that the appropriate course of action is pursued, considering all potential causes and complications.
- Assessment of Individual Health Factors
Individual health conditions, concurrent medications, and allergies influence the suitability of herbal treatments. For instance, individuals with liver or kidney disease may need to avoid certain herbs due to potential toxicity. Likewise, existing medications can interact with herbal remedies, altering their effectiveness or causing adverse effects. Professional guidance facilitates a thorough assessment of these factors, mitigating potential risks and optimizing treatment safety.
- Evidence-Based Treatment Selection
Healthcare professionals can provide evidence-based recommendations regarding the efficacy and safety of herbal interventions. While anecdotal reports and traditional use may suggest benefits, rigorous scientific evidence is often lacking. Medical professionals can evaluate the available research and guide patients toward treatments with demonstrated effectiveness, avoiding ineffective or potentially harmful approaches. For example, suggesting therapies like corticosteroid injections where botanical treatments are insufficient.
- Monitoring and Management of Adverse Effects
Herbal remedies can cause adverse effects, ranging from mild skin irritation to severe allergic reactions. Professional medical supervision allows for the prompt identification and management of these effects. Healthcare providers can monitor patients for signs of adverse reactions and adjust treatment plans accordingly. For instance, if a patient experiences skin irritation from a topical herbal application, a medical professional can recommend alternative treatments or adjust the dosage to minimize discomfort.
The facets presented highlight the multifaceted importance of professional oversight when integrating botanical remedies into the management of ganglion cysts. Healthcare professional consultation ensures accurate diagnosis, personalized treatment selection, monitoring of potential risks, and informed decision-making. By acknowledging and addressing these considerations, individuals can navigate the complexities of botanical interventions safely and effectively, complementing conventional medical approaches, where appropriate.
Frequently Asked Questions About Botanical Approaches
The following section addresses prevalent queries regarding plant-derived interventions for ganglion cysts. The information presented aims to provide clarity and informed understanding.
Question 1: Is “ganglion cyst herbal treatment” a scientifically proven method for eliminating ganglion cysts?
The term encompasses the use of plant-based remedies to address ganglion cysts. Current scientific evidence does not consistently support the use of herbal treatments as a primary method for complete cyst elimination. Some herbal preparations may provide symptomatic relief from pain or inflammation, but rigorous clinical trials demonstrating definitive cyst reduction are lacking.
Question 2: What are the potential risks associated with “ganglion cyst herbal treatment?”
Potential risks include allergic reactions, skin irritation from topical applications, and interactions with conventional medications. Some herbs may possess systemic effects that could be detrimental to individuals with underlying health conditions. It is essential to consult with a healthcare professional to assess individual risk factors and ensure the safe utilization of botanical remedies.
Question 3: Can “ganglion cyst herbal treatment” replace conventional medical treatment for ganglion cysts?
Under most circumstances, botanical interventions should not serve as a replacement for conventional medical treatments recommended by a healthcare professional. A medical doctor should evaluate diagnosis and conventional methods. If a person chooses to introduce an herbal treatment it should be discussed with their doctor.
Question 4: How should herbal remedies be sourced to ensure quality and safety?
Herbal remedies should be sourced from reputable suppliers who adhere to quality control standards. Look for products that have been tested for purity, potency, and contaminants. Avoid purchasing herbal products from unregulated sources or those with questionable manufacturing practices. Third-party certifications can provide assurance of product quality.
Question 5: What is the role of anti-inflammatory herbs in “ganglion cyst herbal treatment?”
Anti-inflammatory herbs may help alleviate pain and swelling associated with ganglion cysts. Topical applications or oral consumption of herbs such as turmeric, ginger, or arnica are sometimes employed for their anti-inflammatory properties. However, it is important to understand that these remedies primarily address symptoms and may not directly reduce the size of the cyst.
Question 6: What are some red flags to watch out for when considering “ganglion cyst herbal treatment?”
Red flags include claims of guaranteed cures, lack of scientific evidence, undisclosed ingredients, and absence of contact information for the manufacturer. Be wary of herbal products promoted through aggressive marketing tactics or those making unsubstantiated health claims. Always seek guidance from a healthcare professional before initiating any herbal treatment regimen.
Herbal remedies may provide some symptomatic benefit when dealing with a ganglion cyst. It is crucial to seek professional medical advice and rely on herbal treatments as adjuncts.
The following section will explore specific botanical agents commonly used in “ganglion cyst herbal treatment,” along with their purported mechanisms of action and potential risks.
Ganglion Cyst Herbal Treatment
The investigation into the realm of using plant-based remedies has revealed a landscape characterized by both potential and limitation. Botanical interventions may offer symptomatic relief, primarily in the areas of pain reduction and inflammation management. However, the existing body of scientific evidence does not consistently support the use of herbal treatments as a definitive method for eliminating the cysts themselves. Safety concerns, including potential allergic reactions and interactions with conventional medications, underscore the importance of professional medical guidance.
In light of these considerations, the responsible integration of herbal approaches into ganglion cyst care necessitates a cautious and informed perspective. Individuals exploring these options should prioritize consultation with qualified healthcare professionals, ensuring that botanical remedies serve as complementary measures rather than replacements for conventional medical interventions. Continued research is warranted to elucidate the true potential and limitations of plant-derived compounds in the context of ganglion cyst management, ultimately contributing to a more comprehensive and evidence-based approach to patient care.