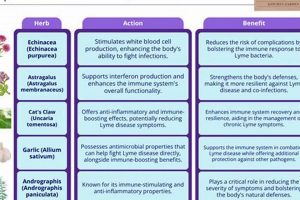
The utilization of botanical remedies to promote improved rest is a practice rooted in traditional medicine systems across diverse cultures. These remedies often involve the consumption of specific plants or plant extracts, typically in the form of teas, tinctures, or capsules, to induce relaxation and facilitate the onset of sleep. For instance, chamomile, a widely recognized option, is frequently consumed as a warm beverage before bedtime.
The appeal of plant-based sleep aids lies in their perceived naturalness and, for some, a preference for alternatives to conventional pharmaceutical interventions. Historically, various societies have relied on locally sourced plants to address sleep disturbances, reflecting a long-standing belief in the power of nature to regulate bodily functions. A potential advantage is the avoidance of certain side effects associated with prescription medications, although individual responses can vary.
This article will explore several commonly used botanicals for encouraging sleep, examining their proposed mechanisms of action, available scientific evidence, and potential considerations regarding safety and effectiveness. Further discussion will address factors to consider before initiating a regimen of this kind, including interactions with existing medications and the importance of consulting with a healthcare professional.
Guidance for Botanical Sleep Support
The following recommendations are intended to provide practical information regarding the responsible and informed use of plant-derived compounds for promoting healthy sleep patterns. These guidelines are not a substitute for professional medical advice.
Tip 1: Conduct Thorough Research. Before incorporating any new botanical supplement into your routine, investigate its potential effects, side effects, and interactions with any existing medications or health conditions. Utilize reputable sources of information, such as peer-reviewed scientific studies and established herbal medicine databases.
Tip 2: Prioritize Product Quality. Opt for products from reputable manufacturers that adhere to stringent quality control standards. Look for certifications from independent organizations that verify the identity, purity, and potency of the ingredients. Avoid products with vague labeling or unsupported claims.
Tip 3: Begin with a Low Dosage. When initiating use of a botanical intended to promote sleep, start with a low dose, as indicated on the product label or recommended by a qualified healthcare provider. Gradually increase the dosage if necessary, while closely monitoring for any adverse effects.
Tip 4: Establish a Consistent Routine. To maximize the potential benefits, administer the chosen botanical at a consistent time each evening, approximately 30-60 minutes before bedtime. This allows the compound to take effect as the body prepares for sleep.
Tip 5: Practice Good Sleep Hygiene. Supplement the use of plant-based remedies with sound sleep hygiene practices. This includes maintaining a regular sleep schedule, creating a dark and quiet sleep environment, avoiding caffeine and alcohol before bed, and engaging in relaxing activities in the evening.
Tip 6: Monitor for Adverse Reactions. Pay close attention to any potential side effects, such as digestive upset, allergic reactions, or interactions with other medications. Discontinue use immediately if any adverse effects are experienced and consult with a healthcare professional.
Tip 7: Seek Professional Guidance. Before starting any new botanical supplement regimen, particularly if you have underlying health conditions or are taking prescription medications, consult with a qualified healthcare provider or herbalist. They can provide personalized recommendations and monitor for potential interactions.
Adhering to these recommendations can help ensure the safe and effective incorporation of plant-derived remedies into a holistic approach to sleep health. Responsible use and professional guidance are essential for optimizing the potential benefits and minimizing potential risks.
The subsequent section will address potential contraindications and safety considerations associated with certain botanical options.
1. Botanical Identification
Botanical identification serves as the bedrock for the safe and effective application of plant-derived remedies for sleep disorders. Accurate identification ensures that the intended therapeutic properties are present and that potentially harmful substitutes are avoided. Lack of precision in this foundational step can render a treatment ineffective or, in more severe cases, dangerous.
- Species Specificity
The therapeutic compounds within a plant vary significantly not only between genera but also between species within the same genus. For instance, while various species of Valeriana exist, Valeriana officinalis is the species most widely studied and traditionally used for sleep enhancement. Utilizing a different Valeriana species may yield negligible or even counterproductive results.
- Chemotype Variation
Beyond species, plants of the same species can exhibit variation in their chemical composition based on geographic location, growing conditions, and genetic factors. These variations, known as chemotypes, can significantly impact the plant’s therapeutic profile. A specific chemotype of lavender, for example, might possess a higher concentration of linalool, a compound known for its calming effects, compared to another chemotype of the same species.
- Adulteration and Substitution
The herbal supplement market is susceptible to adulteration, where cheaper or unrelated plants are substituted for the intended ingredient. A study published in the journal Planta Medica revealed that a significant percentage of herbal products tested contained species not listed on the label. Such substitutions can introduce unintended pharmacological effects or allergens, posing a risk to consumers.
- Misidentification Risks
Even unintentional misidentification can have serious consequences. Certain plants bear a close resemblance to others, potentially leading to accidental consumption of toxic species. For example, some plants in the Apiaceae family, which includes herbs like parsley and dill, have poisonous look-alikes. Accurate botanical knowledge and, where appropriate, laboratory testing are crucial to mitigate these risks.
The preceding points underscore the critical importance of meticulous botanical identification in the realm of plant-based approaches to sleep enhancement. Whether sourcing raw plant material or purchasing commercially prepared supplements, verification of species and chemotype, alongside safeguards against adulteration and misidentification, are paramount for ensuring both efficacy and safety. Employing the remedy without verifying may pose danger.
2. Preparation Method
The method employed to prepare a botanical substance significantly influences its therapeutic potential for sleep enhancement. The selection of a specific preparation technique impacts the extraction of active constituents, their stability, bioavailability, and ultimately, their clinical efficacy. Inadequate or inappropriate preparation can lead to diminished potency or the introduction of undesirable compounds.
- Solvent Selection and Extraction Efficiency
The choice of solvent (e.g., water, alcohol, oil) dictates which compounds are extracted from the plant material. Water extracts, such as teas, effectively draw out water-soluble components, while alcohol-based tinctures are better suited for extracting resins, alkaloids, and other non-polar substances. The selection of an appropriate solvent is crucial for maximizing the yield of the desired therapeutic constituents in preparations for sleep.
- Temperature and Duration of Extraction
Both temperature and duration of extraction play a critical role in preserving the integrity of heat-sensitive compounds and preventing the extraction of unwanted substances. Excessive heat can degrade delicate molecules, reducing the remedy’s effectiveness. Prolonged extraction times can result in the extraction of tannins or other compounds that may cause adverse effects or interfere with sleep. Gentle heating over a moderate amount of time is suggested.
- Dosage Form Considerations
The ultimate dosage form (e.g., tea, capsule, tablet) influences the rate and extent of absorption of active compounds in the body. Teas offer a relatively rapid onset of effect but may contain lower concentrations of active constituents. Capsules and tablets, on the other hand, provide a more concentrated dose but may have a slower onset. Liposomes and nanoemulsions may increase the bioavailability. The selection of a suitable dosage form should consider both potency and speed of action as they are desired.
- Fresh vs. Dried Plant Material
The use of fresh versus dried plant material impacts the concentration of volatile compounds and water content. Fresh herbs generally contain a higher concentration of volatile oils, which may contribute to their therapeutic effects. Drying, however, can concentrate other active constituents and improve the shelf life of the preparation. This is one thing to consider to have a useful botanical administration.
In summary, the method of preparation represents a critical control point in harnessing the therapeutic benefits of botanicals for sleep. Each step in the preparation processfrom solvent selection to dosage formmust be carefully considered to optimize the extraction, stability, and bioavailability of active constituents, ultimately influencing the remedy’s efficacy in promoting restful sleep. This rigorous attention to detail should allow effective botanical administration.
3. Dosage Control
Dosage control constitutes a pivotal element in the safe and effective application of botanical remedies for sleep disturbances. The relationship between dosage and therapeutic effect is not linear; an insufficient dose may produce negligible results, while an excessive dose can lead to adverse effects, potentially exacerbating the initial sleep problem. For example, while a small dose of valerian root may promote relaxation, a higher dose may paradoxically cause agitation in some individuals. Similarly, an inadequate dose of chamomile tea may fail to induce sleepiness, whereas an excessively strong brew could lead to gastrointestinal discomfort. Precise dosage control, therefore, ensures that the therapeutic benefits are maximized while minimizing the risk of unwanted side effects.
The implementation of proper dosage control requires a comprehensive understanding of several factors, including the potency of the herbal product, the individual’s physiological characteristics, and any concurrent medications or health conditions. Herbal product potency can vary significantly depending on factors such as plant species, growing conditions, and extraction methods. Individuals with different body weights, metabolic rates, and sensitivities may respond differently to the same dose. Furthermore, certain herbal substances can interact with pharmaceutical drugs, potentially altering their effects or increasing the risk of side effects. Consequently, healthcare providers often recommend starting with a low dose and gradually increasing it until the desired therapeutic effect is achieved, all while monitoring for any adverse reactions.
In conclusion, the success of botanical approaches to sleep enhancement hinges on meticulous dosage control. This requires a nuanced understanding of the interplay between product potency, individual physiology, and potential drug interactions. While plant-based remedies are often perceived as gentler alternatives to conventional medications, they are not inherently devoid of risk. Exercising caution and seeking guidance from a qualified healthcare professional are essential to ensure that these remedies are used safely and effectively to promote restful sleep. Achieving optimal dosage could be challenging, further safety is needed.
4. Interaction Assessment
The concurrent use of botanicals intended to improve sleep and conventional pharmaceutical agents necessitates a thorough interaction assessment to mitigate potential adverse events. Many plant-derived compounds possess pharmacological activity that can modulate the absorption, distribution, metabolism, or excretion of prescription medications, leading to altered drug concentrations and therapeutic outcomes. A failure to account for these interactions can result in reduced drug efficacy, increased toxicity, or unpredictable physiological responses. For example, St. John’s Wort, a botanical sometimes used for mood regulation and, indirectly, sleep, is a known inducer of cytochrome P450 enzymes, which are responsible for metabolizing numerous drugs. Co-administration with medications such as warfarin or oral contraceptives can lead to decreased drug levels and potentially serious clinical consequences. Therefore, a careful evaluation of potential interactions is a critical component of responsible implementation.
Furthermore, interactions can occur not only between botanicals and pharmaceutical drugs but also between different botanical substances. Combining multiple plant-based remedies without a clear understanding of their individual and combined effects can lead to unexpected synergisms or antagonisms. For instance, the concurrent use of valerian and kava, both purported to have sedative properties, may potentiate their effects, leading to excessive drowsiness or impaired cognitive function. Interaction assessment also involves considering the individual’s health status and pre-existing conditions. Individuals with liver or kidney dysfunction may be more susceptible to adverse effects from botanical-drug interactions due to impaired drug metabolism or excretion. Likewise, individuals with bleeding disorders may need to exercise caution with botanicals that possess anticoagulant properties, such as garlic or ginger.
In conclusion, interaction assessment is not merely an optional consideration but a fundamental aspect of safely integrating botanical remedies for sleep management. A proactive approach, involving a comprehensive review of all medications and supplements, a thorough understanding of potential interactions, and close monitoring for adverse effects, is essential. Given the complexity of these interactions and the variability in individual responses, consultation with a qualified healthcare professional or clinical pharmacist is strongly recommended to ensure patient safety and optimize therapeutic outcomes. This step should not be omitted.
5. Quality Assurance
Quality assurance forms a critical framework for ensuring the safety, efficacy, and consistency of plant-derived products intended to promote sleep. The absence of rigorous quality control measures can expose consumers to adulterated, contaminated, or improperly formulated products, undermining the potential therapeutic benefits and posing health risks.
- Authentication of Botanical Identity
Correct identification of the plant species used in a product is paramount. Quality assurance protocols employ techniques such as macroscopic and microscopic examination, as well as DNA barcoding, to verify that the correct species is used and to detect potential adulteration with other plant materials. For example, independent laboratories may test chamomile products to confirm the absence of related, but less effective, species.
- Control of Contaminants
Herbal products can be susceptible to contamination from heavy metals, pesticides, microbial pathogens, and other toxins. Quality assurance programs implement testing procedures to ensure that products meet established safety limits for these contaminants. Products failing to meet these criteria are rejected to prevent potential harm to consumers. Routine testing for aflatoxins in herbal supplements serves as a practical example.
- Standardization of Active Compounds
The concentration of active compounds in herbal products can vary significantly depending on factors such as growing conditions, harvesting practices, and extraction methods. Quality assurance measures aim to standardize the levels of key active constituents, ensuring that each batch of product delivers a consistent therapeutic dose. For instance, valerian root extracts may be standardized to contain a specific percentage of valerenic acids, believed to contribute to its sleep-promoting effects.
- Stability Testing and Shelf Life
Herbal products can degrade over time, leading to a reduction in potency and the formation of potentially harmful degradation products. Quality assurance programs include stability testing to determine the shelf life of a product and to ensure that it retains its claimed potency throughout its intended use. This may involve storing products under controlled conditions of temperature and humidity and periodically testing for active compound levels and degradation markers. For example, a melatonin and lavender product needs to prove its efficiency till its expiry.
The principles of quality assurance are essential for safeguarding the integrity of botanical approaches to sleep health. By implementing rigorous controls at each stage of the production process, manufacturers can provide consumers with reliable, effective, and safe plant-based remedies. However, it is only one thing, other things may be involved. Independent verification of product quality, through third-party testing and certification, provides an additional layer of assurance.
6. Safety Profile
The safety profile of any substance, including botanical interventions for sleep modulation, warrants meticulous evaluation. It encompasses a comprehensive assessment of potential adverse effects, contraindications, and interactions that may arise from its use. Understanding this profile is paramount to ensuring responsible and beneficial application.
- Dose-Dependent Toxicity
The toxicity of botanical agents is often dose-dependent, meaning that the risk of adverse effects increases with higher dosages. While a low dose may elicit the desired sedative effect, exceeding a certain threshold can result in symptoms such as gastrointestinal distress, dizziness, or even more severe complications. For example, exceeding the recommended dosage of valerian root has been linked to headaches and excitability in some individuals, underscoring the importance of adhering to established dosage guidelines. Such a toxic environment may cause danger.
- Allergic Reactions and Sensitivities
Individuals can exhibit allergic reactions or sensitivities to specific botanical substances, even if they have previously tolerated them. These reactions can range from mild skin rashes to life-threatening anaphylaxis. Chamomile, for instance, although generally considered safe, can trigger allergic reactions in individuals sensitive to plants in the Asteraceae family, such as ragweed. Prior knowledge of allergies and careful monitoring for new symptoms are essential for mitigating such risks.
- Drug Interactions and Contraindications
Botanical agents can interact with prescription medications, over-the-counter drugs, and other supplements, potentially altering their efficacy or increasing the risk of adverse effects. Furthermore, certain botanical substances are contraindicated in individuals with specific medical conditions. For example, St. John’s Wort, sometimes used for mild depression and sleep disturbances, can interact with antidepressants and blood thinners, potentially leading to serious consequences. Prior knowledge of medical history may save an individual’s life.
- Quality Control and Adulteration
The safety profile of botanical products is heavily influenced by quality control measures and the potential for adulteration. Products that lack proper authentication, standardization, and testing may contain contaminants, undeclared ingredients, or incorrect plant species, increasing the risk of adverse effects. For instance, a study found that some herbal sleep supplements contained undisclosed pharmaceutical drugs, posing a significant health risk to unsuspecting consumers. The manufacturer is responsible for this event.
In summary, a thorough understanding of the safety profile is crucial when considering botanical interventions for sleep disturbances. By evaluating dose-dependent toxicity, allergic reactions, drug interactions, and quality control issues, individuals and healthcare practitioners can make informed decisions that prioritize safety and minimize potential risks. A complete history is required for better administration of the product.
7. Long-Term Efficacy
The long-term efficacy of plant-derived treatments for sleep-related disorders represents a critical, yet often underexplored, aspect of their overall value. While some botanicals demonstrate acute benefits, their sustained effectiveness and safety over extended periods require rigorous evaluation. The cause-and-effect relationship hinges on the ability of these treatments to address underlying sleep disturbances without inducing tolerance, dependence, or significant adverse effects over time. The importance of long-term efficacy as a component of plant-based sleep aids stems from the chronic nature of many sleep disorders; a treatment that loses its effectiveness or generates negative consequences with prolonged use offers limited practical benefit. For example, frequent users of valerian may experience diminishing returns over several months, potentially requiring escalating dosages or a shift to alternative approaches.
The assessment of long-term efficacy necessitates well-designed clinical trials that extend beyond short-term intervention periods. These studies should incorporate measures to track both sleep parameters and any adverse events that may emerge with continued use. Furthermore, research should investigate the potential for tolerance development, where the body adapts to the treatment, requiring higher doses to achieve the same effect. Understanding these nuances is paramount for crafting evidence-based recommendations for long-term management. As an illustration, continuous use of melatonin supplements may alter natural melatonin production patterns in some individuals, highlighting the need for careful monitoring and potentially intermittent use. Another study has found that individuals on herbal sleep remedies over long periods need to alternate treatment due to the body becoming immune to the plant’s sedative effect.
In conclusion, the long-term efficacy of botanical remedies for sleep remains a significant area requiring ongoing research. Addressing the challenges of tolerance, dependence, and sustained safety is crucial for establishing these treatments as viable long-term solutions. Integrating findings from extended clinical trials with real-world observational data will contribute to a more comprehensive understanding of their place in managing chronic sleep disturbances. Responsible application necessitates a cautious approach, characterized by individualized assessments, monitoring for adverse effects, and a willingness to adjust treatment strategies based on long-term outcomes. This careful management ensures that potential benefits are maximized while minimizing any risks associated with prolonged usage.
Frequently Asked Questions
This section addresses common inquiries regarding the utilization of plant-derived substances to promote sleep. The information provided is intended for educational purposes and should not be construed as medical advice. Consultation with a qualified healthcare professional is advised prior to initiating any new treatment regimen.
Question 1: Are botanical remedies inherently safer than conventional sleep medications?
The perception of increased safety associated with botanical substances is not always accurate. While some plant-derived compounds may have fewer side effects compared to certain pharmaceuticals, they are not devoid of potential risks. Factors such as dosage, individual sensitivities, interactions with other medications, and product quality can all influence the safety profile of botanical remedies. A false sense of security should be avoided.
Question 2: How long does it typically take for a botanical sleep aid to take effect?
The onset of action can vary depending on the specific botanical, the preparation method, the dosage, and individual physiological characteristics. Some individuals may experience a noticeable effect within 30-60 minutes, while others may require several days or weeks of consistent use before observing significant improvements in sleep. Expectations should be realistic, and patience may be necessary.
Question 3: Can botanical sleep remedies be used in conjunction with prescription sleep medications?
Combining botanical and pharmaceutical sleep aids can be hazardous and is generally not recommended without the explicit guidance of a healthcare professional. Interactions between these substances can lead to additive sedative effects, increased risk of side effects, or interference with the efficacy of either treatment. Careful consideration of potential interactions is essential.
Question 4: Are there specific botanical remedies that are generally considered more effective for sleep than others?
The effectiveness of different botanical remedies can vary depending on the individual and the underlying cause of their sleep disturbance. Chamomile, valerian root, and lavender are among the most commonly studied and utilized botanicals for sleep enhancement. However, individual responses can differ significantly, and what works well for one person may not be effective for another. This is often tested through trials.
Question 5: Is it possible to develop a tolerance to botanical sleep aids with long-term use?
Tolerance, a phenomenon where the body adapts to a substance and requires increasingly higher doses to achieve the same effect, can occur with some botanical sleep aids. Regularly increasing the dosage can exacerbate potential adverse effects, so it is imperative to consult with a healthcare professional to determine the most appropriate long-term strategy. The key is to not develop an immunity to the herbal treatment.
Question 6: How can one ensure the quality and purity of botanical sleep products?
Selecting products from reputable manufacturers that adhere to stringent quality control standards is crucial. Look for certifications from independent organizations that verify the identity, purity, and potency of the ingredients. Avoid products with vague labeling, unsupported claims, or ingredients that lack scientific evidence of efficacy. This is the most important step for the safety of the individual.
The information provided in this FAQ section serves as a starting point for understanding botanical approaches to sleep enhancement. A comprehensive assessment of individual needs and circumstances, coupled with professional guidance, is essential for safe and effective utilization.
The next article will summarize our ideas for herbal treatment for sleep.
Herbal Treatment for Sleep
This exploration has revealed that the administration of botanical substances to improve sleep presents a complex landscape, necessitating a multifaceted understanding. Key considerations extend beyond simple consumption, encompassing accurate botanical identification, appropriate preparation methods, precise dosage control, thorough interaction assessments, stringent quality assurance measures, careful evaluation of safety profiles, and diligent monitoring of long-term efficacy. Each of these elements contributes to the responsible and informed utilization of this mode of treatment.
The decision to incorporate herbal treatment for sleep warrants careful consideration, supported by consultation with qualified healthcare professionals. While promising benefits may exist, their realization depends on adherence to established safety principles and a commitment to evidence-based practices. Future research should continue to investigate the long-term effects and optimal application strategies to further define the role of botanicals in promoting healthy sleep patterns. The efficacy of treatment depends on the user’s care and precision.