In addressing parasitic infections caused by Giardia duodenalis, which leads to giardiasis, some individuals explore botanical options. This approach involves the use of various plants and their extracts, traditionally employed for their purported antiparasitic and supportive properties, aiming to alleviate symptoms and eradicate the infection.
The significance of investigating plant-derived therapies lies in their potential accessibility, affordability, and historical use in diverse cultures. Throughout history, many societies have relied on natural resources to manage parasitic ailments. The potential advantages may include reduced reliance on synthetic drugs, the possibility of fewer adverse effects, and a broader spectrum of action due to the complex chemical composition of some plants.
The subsequent sections will delve into specific botanicals researched for their activity against Giardia, examining available evidence, exploring possible mechanisms of action, and addressing potential considerations regarding safety and efficacy. Further exploration will include examining adjunctive therapies and lifestyle modifications that may complement botanical approaches to managing giardiasis.
Guidance on Addressing Giardiasis with Botanical Approaches
The following guidance provides information pertaining to the use of plant-based remedies in the context of managing Giardia infections. These points are for informational purposes only and should not replace consultation with qualified healthcare professionals.
Tip 1: Consultation with Healthcare Professionals: Prior to initiating any botanical regimen, a diagnosis from a medical doctor is essential. Self-diagnosis of giardiasis is discouraged, and a professional can determine the appropriateness of botanical remedies in conjunction with, or as an alternative to, conventional treatments.
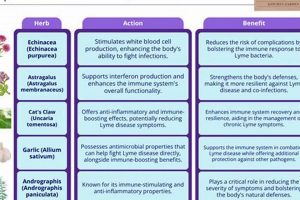
Tip 2: Researching Specific Botanicals: Certain plants, such as berberine-containing herbs (e.g., goldenseal, barberry), garlic, and wormwood, have been studied for their potential antiparasitic properties. Review available scientific literature to understand the rationale, potential benefits, and possible adverse effects of each plant before use.
Tip 3: Dosage and Preparation: Exact dosage and preparation methods vary depending on the specific herb and the individual’s condition. Consult with a qualified herbalist or naturopathic doctor for guidance on appropriate dosages and preparation techniques, such as teas, tinctures, or capsules.
Tip 4: Sourcing High-Quality Herbs: The quality and potency of botanical products can vary significantly. Obtain herbs from reputable sources that adhere to good manufacturing practices and provide detailed information regarding sourcing, processing, and quality control.
Tip 5: Monitoring for Adverse Effects: As with any treatment, it is important to monitor for any adverse effects or allergic reactions. Discontinue use and seek medical attention if any concerning symptoms arise. Certain herbs may interact with medications or have contraindications for specific health conditions.
Tip 6: Adjunctive Therapies: Consider incorporating adjunctive therapies that support the body’s natural defenses, such as a balanced diet, adequate hydration, stress management techniques, and probiotics to promote gut health. A strong immune system and healthy gut flora can aid in recovery.
Tip 7: Understanding Limitations: While botanical options may offer potential benefits, they may not be universally effective. If symptoms persist or worsen despite the botanical approach, conventional medical treatment should be pursued without delay.
Successfully integrating botanicals into a giardiasis management plan requires a comprehensive understanding of the individual’s health status, the specific properties of the herbs, and the potential for interactions. Working closely with healthcare providers ensures safe and effective care.
The subsequent sections will offer further details on specific botanicals, addressing mechanisms of action, safety profiles, and integration strategies in the overall management of giardiasis.
1. Berberine's antiparasitic action
Berberine, an isoquinoline alkaloid found in various plants such as goldenseal ( Hydrastis canadensis), barberry ( Berberis vulgaris), and Oregon grape ( Mahonia aquifolium), is studied for its potential role in managing giardiasis. Its antiparasitic action provides a rationale for its inclusion in some herbal protocols targeting Giardia duodenalis infections.
- Mechanism of Action
Berberine disrupts various cellular processes in Giardia, including interference with DNA replication, cell division, and energy metabolism. In vitro studies have demonstrated its ability to inhibit the growth and adherence of Giardia trophozoites to intestinal epithelial cells. This multifaceted impact contributes to its potential antiparasitic effect.
- Clinical Evidence
While preliminary in vitro and animal studies suggest berberine’s efficacy against Giardia, human clinical trials are limited. Some small-scale studies have shown promising results in reducing Giardia cyst excretion and alleviating symptoms of giardiasis. However, larger, well-controlled trials are needed to confirm these findings and establish optimal dosing regimens.
- Bioavailability and Formulation
Berberine’s bioavailability is relatively low, which can limit its effectiveness when administered orally. Some formulations aim to enhance bioavailability by combining berberine with agents that inhibit its metabolism or promote its absorption. The choice of formulation can influence the clinical outcome.
- Safety and Interactions
Berberine is generally considered safe when taken at recommended doses for short periods. However, it can cause gastrointestinal side effects, such as nausea, diarrhea, and abdominal cramping, in some individuals. Berberine can also interact with certain medications, including anticoagulants, antiplatelet drugs, and some antibiotics. Careful consideration of potential drug interactions is essential.
The exploration of berberine’s role in managing giardiasis requires a balanced approach, considering both its potential benefits and limitations. Further research is needed to fully elucidate its efficacy, optimize its formulation, and establish definitive guidelines for its safe and effective use as part of botanical strategies. Consultation with knowledgeable healthcare professionals is paramount.
2. Garlic's Allicin Component
The potential role of allicin, the primary bioactive component of garlic ( Allium sativum), in addressing Giardia duodenalis infections, positions it within the scope of botanical approaches to giardiasis. Its purported antiparasitic properties necessitate a closer examination of its mechanisms and clinical relevance.
- Mechanism of Action Against Giardia
Allicin’s antiparasitic activity is attributed to its ability to generate reactive oxygen species and disrupt thiol-containing enzymes within Giardia trophozoites. This oxidative stress can lead to damage to cellular components, inhibiting the parasite’s growth and survival. In vitro studies suggest that allicin can inhibit Giardia’s adherence to intestinal epithelial cells, thereby reducing its ability to colonize the gut.
- Evidence from Laboratory Studies
Numerous in vitro studies have demonstrated allicin’s efficacy against Giardia. These investigations typically involve exposing Giardia trophozoites to varying concentrations of allicin and assessing the impact on their viability and morphology. Several studies reported that allicin can eradicate Giardia at concentrations achievable through dietary intake or supplementation.
- Clinical Translation and Challenges
Despite the promising in vitro findings, clinical evidence supporting allicin’s effectiveness in treating human giardiasis remains limited. Several factors contribute to this translational challenge, including allicin’s instability, rapid metabolism, and potential for degradation in the gastrointestinal tract. Moreover, the variability in allicin content in different garlic preparations makes standardization challenging.
- Considerations for Therapeutic Use
When considering the therapeutic use of garlic or allicin supplements for giardiasis, it is essential to select standardized preparations with a defined allicin content. The method of garlic processing and preparation can significantly influence the amount of allicin available. Raw garlic, crushed just before consumption, tends to have the highest allicin content. Encapsulated allicin supplements may offer a more convenient and standardized alternative, though their bioavailability needs to be considered. Dosage must be carefully considered due to allicin’s potential to cause gastrointestinal distress at high doses.
While allicin holds promise as a potential adjunct in botanical approaches to giardiasis, its clinical utility necessitates further investigation through well-designed human trials. The challenges associated with allicin’s stability and bioavailability need to be addressed through innovative formulations and delivery methods. Responsible integration of garlic and allicin into a giardiasis management plan requires collaboration with qualified healthcare practitioners to ensure safe and effective implementation.
3. Wormwood's artemisinin content
Artemisinin, a sesquiterpene lactone derived from Artemisia annua (Wormwood), is recognized for its antimalarial properties and is under investigation for potential application in treating other parasitic infections, including giardiasis. Its inclusion in discussions surrounding botanical interventions for Giardia duodenalis stems from its demonstrated activity against certain protozoan parasites.
- Mechanism of Action
Artemisinin’s mechanism of action against parasites involves the generation of free radicals upon interaction with iron. These free radicals cause oxidative stress, damaging parasitic proteins and membranes. While the precise mechanism against Giardia is still under investigation, it is hypothesized to follow a similar pathway, disrupting the parasite’s cellular processes and viability.
- In Vitro and In Vivo Studies
In vitro studies have shown that artemisinin can inhibit the growth of Giardia duodenalis trophozoites. Some in vivo studies, primarily conducted on animal models, suggest that artemisinin or wormwood extracts can reduce Giardia cyst excretion and alleviate symptoms of giardiasis. However, the results are not uniformly consistent, and further research is required to confirm these findings.
- Bioavailability and Formulation
Artemisinin has limited bioavailability, which can impact its efficacy when administered orally. Different formulations, such as artemisinin combined with piperaquine or other agents, have been developed to enhance its absorption and prolong its half-life. The choice of formulation may influence the clinical outcome in treating giardiasis.
- Safety and Tolerability
Artemisinin is generally considered safe at recommended doses, but it can cause side effects such as nausea, vomiting, and abdominal pain in some individuals. High doses or prolonged use may lead to more serious adverse effects, including neurotoxicity. Concurrent use of artemisinin with certain medications may result in drug interactions, requiring careful monitoring.
The integration of wormwood and artemisinin into a holistic approach to managing giardiasis warrants careful consideration. Further studies are needed to determine optimal dosages, treatment durations, and the most effective formulations. Consultation with healthcare professionals is necessary to assess potential risks and benefits, especially in individuals with pre-existing health conditions or those taking other medications. Responsible use of wormwood requires adherence to established safety guidelines and monitoring for adverse effects.
4. Quality, source verification
The pursuit of botanical interventions for giardiasis necessitates rigorous attention to quality and source verification. The inherent variability in plant composition, coupled with potential adulteration, contamination, and misidentification, pose significant challenges to ensuring consistent and reliable therapeutic outcomes. The following points delineate critical facets of quality and source verification in the context of botanical approaches to Giardia duodenalis infections.
- Botanical Identification and Authentication
Accurate identification of the plant species is paramount. Misidentification can lead to the use of ineffective or even harmful substitutes. Reputable suppliers utilize botanical experts and analytical techniques, such as macroscopic and microscopic examination, as well as DNA barcoding, to authenticate plant materials. Certificates of Analysis should confirm the correct botanical identity.
- Cultivation and Harvesting Practices
The conditions under which plants are cultivated and harvested significantly impact their chemical composition and purity. Sustainable and ethical sourcing practices, including adherence to Good Agricultural and Collection Practices (GACP), minimize the risk of contamination with pesticides, heavy metals, and other environmental pollutants. GACP guidelines ensure proper soil management, water quality, and harvesting techniques.
- Manufacturing and Processing Standards
The manufacturing and processing of herbal products must adhere to stringent quality control measures. Good Manufacturing Practices (GMP) ensure that products are consistently produced and controlled according to quality standards. GMP guidelines address aspects such as raw material testing, process validation, equipment calibration, and finished product testing. Reputable manufacturers provide detailed information regarding their quality control procedures.
- Third-Party Testing and Certification
Independent third-party testing provides an additional layer of assurance regarding the quality and purity of herbal products. Organizations such as the U.S. Pharmacopeia (USP), NSF International, and ConsumerLab.com offer certification programs that verify products meet specified quality standards. Products bearing these certifications have undergone rigorous testing for identity, potency, and contaminants.
The integration of botanical interventions for giardiasis requires a commitment to quality and transparency throughout the supply chain. Healthcare practitioners and individuals seeking such treatments should prioritize products from suppliers who provide comprehensive documentation regarding botanical identification, sourcing practices, manufacturing processes, and third-party testing. Diligence in these matters enhances the likelihood of obtaining safe and effective botanical remedies.
5. Dosage, preparation accuracy
The effectiveness and safety of botanical approaches to managing Giardia duodenalis infections are inextricably linked to precise dosage and accurate preparation methods. Variations in these elements can significantly impact therapeutic outcomes, potentially leading to treatment failure or adverse effects. Understanding the intricacies of dosage and preparation is therefore essential for responsible implementation.
- Standardization of Herbal Extracts
The concentration of active compounds within a given herb can vary significantly based on factors such as growing conditions, harvesting time, and extraction techniques. Standardization aims to ensure a consistent level of bioactive constituents in each dose. Herbal extracts labeled with a specific percentage of a marker compound (e.g., berberine in goldenseal) provide a more reliable measure of potency than non-standardized preparations.
- Appropriate Dosage Forms and Delivery Methods
The choice of dosage form (e.g., capsules, tinctures, teas) and delivery method can affect the bioavailability and absorption of active compounds. Some compounds may be better absorbed when taken in a lipid-based carrier, while others may be degraded by stomach acid. Consulting with a knowledgeable herbalist or naturopathic doctor can help determine the most appropriate dosage form and delivery method for a given herb and individual.
- Preparation Techniques and Extraction Methods
The method used to prepare an herbal remedy can influence the extraction of active compounds. Decoctions (boiling herbs in water) are suitable for extracting water-soluble compounds, while tinctures (soaking herbs in alcohol) are better for extracting resinous or oil-soluble constituents. Proper preparation techniques ensure that the desired compounds are effectively extracted and preserved.
- Individualization of Dosage Regimens
Dosage requirements can vary significantly among individuals based on factors such as age, weight, metabolism, and the severity of the infection. A one-size-fits-all approach is rarely appropriate. Healthcare practitioners consider individual factors when determining the optimal dosage regimen. Careful monitoring of symptoms and potential side effects is essential to adjust the dosage as needed.
Ultimately, the successful application of botanical interventions for giardiasis hinges on meticulous attention to dosage and preparation accuracy. Precise standardization, appropriate dosage forms, careful preparation techniques, and individualized dosage regimens are all critical components of a responsible and effective approach. Collaboration with qualified healthcare professionals is paramount to ensure safe and optimal outcomes.
6. Safety, interaction monitoring
The administration of botanical interventions for Giardia duodenalis infections necessitates meticulous safety protocols and diligent monitoring for potential interactions. The inherently complex chemical composition of herbal remedies presents inherent risks, including adverse reactions and the potential for pharmacological interactions with concurrently administered medications or pre-existing health conditions. Neglecting these aspects can significantly compromise patient well-being.
The clinical application of botanical treatments requires a comprehensive understanding of the specific herb’s safety profile. This includes known contraindications, potential side effects, and documented drug interactions. For instance, berberine-containing herbs, frequently considered for their antiparasitic properties, can interfere with the metabolism of certain pharmaceuticals, potentially altering their efficacy or increasing the risk of adverse effects. Similarly, wormwood, with its artemisinin content, may exhibit neurotoxic effects at elevated doses or during prolonged use. Prior to initiating herbal therapy, a thorough patient history, including a detailed review of all medications and pre-existing conditions, is essential. Ongoing monitoring for adverse effects, such as gastrointestinal distress, allergic reactions, or neurological symptoms, is crucial throughout the treatment course. Liver and kidney function tests may be warranted in certain cases to assess the potential for organ toxicity.
In summation, prioritizing patient safety and diligently monitoring for potential interactions are indispensable components of botanical approaches to giardiasis. Responsible integration of herbal remedies into a treatment plan necessitates a thorough understanding of their pharmacological properties, potential risks, and interaction profiles. Collaboration between patients and qualified healthcare providers is paramount to ensure safe and effective outcomes, safeguarding against potential harm and maximizing the therapeutic benefits of botanical interventions. The complexity and potential pitfalls highlight the imperative for well-informed decision-making and rigorous clinical oversight.
7. Adjunctive support necessity
Adjunctive support is not merely supplemental; it is an integral component of any comprehensive protocol addressing Giardia duodenalis infections, irrespective of whether the primary intervention involves conventional pharmaceuticals or botanical treatments. The necessity stems from the multifaceted nature of giardiasis and the limitations of relying solely on direct antiparasitic effects.
- Gut Microbiome Restoration
Giardia infections disrupt the balance of the gut microbiome, often leading to dysbiosis. Probiotic supplementation, featuring strains such as Lactobacillus and Bifidobacterium, can aid in restoring a healthy microbial balance, enhancing competitive exclusion of Giardia, and improving overall gut health. Fermented foods, such as yogurt or kefir, may also contribute to microbiome diversity, although their Giardia-specific effects are less directly studied.
- Immune System Modulation
A robust immune response is critical for clearing Giardia infections and preventing recurrence. Nutrients like vitamin D, vitamin C, and zinc play essential roles in immune function. Dietary strategies focused on consuming nutrient-dense foods and addressing any underlying deficiencies can bolster the body’s natural defenses. Certain herbal adaptogens, like Echinacea, are sometimes used to support immune function, although their efficacy in the context of giardiasis requires further investigation.
- Intestinal Barrier Integrity
Giardia can damage the intestinal lining, increasing permeability and contributing to inflammation. Compounds like L-glutamine, an amino acid that serves as a primary fuel source for intestinal cells, can aid in repairing and maintaining the integrity of the intestinal barrier. Dietary interventions that reduce inflammation, such as limiting processed foods and refined sugars, are also crucial.
- Hydration and Electrolyte Balance
Diarrhea, a common symptom of giardiasis, can lead to dehydration and electrolyte imbalances. Adequate fluid intake, particularly with oral rehydration solutions containing electrolytes like sodium, potassium, and chloride, is essential for maintaining physiological function and preventing complications. Herbal teas, such as chamomile or ginger, may provide additional soothing and anti-inflammatory benefits.
In conclusion, while botanical treatments may offer direct antiparasitic activity, the resolution of giardiasis extends beyond pathogen eradication. Addressing the downstream effects of the infection, such as gut dysbiosis, immune dysfunction, and intestinal damage, through targeted adjunctive support is vital for promoting complete recovery and preventing relapse. A holistic approach that integrates both direct antiparasitic interventions and comprehensive supportive measures maximizes the potential for successful outcomes in managing Giardia duodenalis infections.
Frequently Asked Questions
This section addresses common inquiries regarding the use of plant-derived remedies in the context of managing Giardia infections. These responses aim to provide factual information and should not substitute consultation with qualified healthcare professionals.
Question 1: Are botanical options a complete substitute for conventional medical treatment for giardiasis?
No, botanical options may not serve as a direct replacement for conventional medical treatment in all cases of giardiasis. The severity of infection, individual health status, and potential for complications influence treatment decisions. A healthcare provider can assess the suitability of botanical remedies, either as a primary or adjunctive therapy, based on a comprehensive evaluation.
Question 2: What evidence supports the efficacy of botanicals against Giardia?
Evidence supporting the efficacy of botanicals against Giardia primarily stems from in vitro studies and animal models. Human clinical trials are limited, and findings vary across studies. While some botanicals demonstrate antiparasitic activity in laboratory settings, the translation of these effects to clinical outcomes in humans requires further investigation.
Question 3: How can the quality of herbal products be assured?
Assuring the quality of herbal products necessitates scrutiny of sourcing, manufacturing processes, and third-party testing. Reputable suppliers provide detailed information regarding botanical identification, cultivation practices, and quality control procedures. Certifications from independent organizations, such as USP or NSF, offer an additional layer of assurance.
Question 4: Are there risks associated with using botanical treatments for giardiasis?
Yes, risks accompany the use of botanical treatments for giardiasis. These risks include potential allergic reactions, gastrointestinal side effects, and interactions with concurrently administered medications. Certain herbs may be contraindicated for individuals with specific health conditions, such as liver or kidney disease.
Question 5: How are botanical dosages determined for Giardia infections?
Botanical dosages are determined based on factors such as the specific herb, the severity of the infection, and individual patient characteristics. Dosage recommendations typically derive from traditional use, pharmacological studies, and clinical experience. Consultation with a qualified herbalist or naturopathic doctor is advisable to establish appropriate dosages.
Question 6: Is adjunctive support necessary when using botanicals for giardiasis?
Adjunctive support often plays a critical role in the successful management of giardiasis, regardless of the primary treatment approach. Addressing gut dysbiosis, modulating immune function, and supporting intestinal barrier integrity can enhance therapeutic outcomes and prevent recurrence. Dietary modifications and probiotic supplementation represent common adjunctive strategies.
In summary, while botanical interventions may offer potential benefits in the context of giardiasis, a cautious and informed approach is essential. Consultation with qualified healthcare professionals, rigorous quality control, and diligent monitoring for adverse effects are paramount to ensure patient safety and optimize therapeutic outcomes.
The subsequent sections will delve into specific botanicals, addressing mechanisms of action, safety profiles, and integration strategies in the overall management of giardiasis.
Conclusion
The preceding exploration of “giardia herbal treatment” has illuminated both the potential and limitations inherent in employing botanical interventions for Giardia duodenalis infections. Key points emphasized include the necessity of rigorous quality control, the importance of understanding individual herb pharmacology, the critical role of adjunctive therapies in supporting gut health and immune function, and the imperative for professional medical oversight. While preliminary research and traditional use suggest promise for certain botanicals, conclusive evidence from large-scale human clinical trials remains limited. The complexity of herbal remedies and the potential for adverse effects and drug interactions necessitate a cautious and informed approach.
The ongoing investigation into botanical options for giardiasis warrants continued scientific inquiry, with a focus on standardization, bioavailability enhancement, and rigorous clinical validation. Until such evidence is available, the integration of plant-derived remedies should occur within a framework of shared decision-making between patients and qualified healthcare providers, prioritizing patient safety and optimizing treatment outcomes. A commitment to evidence-based practice and a discerning approach to anecdotal claims are essential to advancing the responsible use of botanicals in the management of Giardia infections.