Botanical remedies utilized to alleviate respiratory distress associated with bronchial inflammation and resulting expectoration are the focus of this discussion. These interventions, often drawn from traditional medicine systems, aim to mitigate the symptoms of constricted airways and persistent, forceful expulsion of air from the lungs. A common example includes the use of extracts from plants known for their anti-inflammatory or bronchodilatory properties to ease breathing and reduce the urge to clear the throat.
The exploration of plant-derived therapies for respiratory ailments stems from a long history of traditional healing practices across various cultures. The appeal lies in their perceived natural origin and, for some, a belief in fewer adverse effects compared to synthetic pharmaceuticals. Historically, these remedies played a significant role in managing chronic respiratory conditions before the advent of modern medicine, and continue to be investigated for their potential synergistic benefits alongside conventional treatments.
The following sections will delve into specific botanical agents commonly employed for respiratory relief, examining their purported mechanisms of action, exploring existing scientific evidence regarding their efficacy, and discussing important considerations for their safe and responsible use within an integrated approach to managing respiratory health.
Guidance on Botanical Approaches for Respiratory Discomfort
The following guidance addresses the use of plant-derived substances to potentially ease respiratory distress associated with bronchial inflammation and resulting expectoration. These tips are for informational purposes only and do not constitute medical advice. Consultation with a qualified healthcare professional is essential before initiating any new treatment regimen, particularly for a chronic condition such as this.
Tip 1: Prioritize Professional Medical Evaluation: A definitive diagnosis from a physician is paramount. Respiratory symptoms may stem from various underlying causes, and self-treating without accurate identification of the condition can be detrimental.
Tip 2: Research Specific Botanical Agents Thoroughly: Investigate the purported mechanisms of action, potential side effects, and known drug interactions of any plant-derived substance considered for use. Reputable scientific literature should be consulted to evaluate the available evidence.
Tip 3: Source High-Quality Botanical Products: Ensure that any purchased herbal products are obtained from reputable suppliers with demonstrable quality control measures. Adulteration and contamination are potential risks in unregulated markets.
Tip 4: Adhere to Recommended Dosages: Strictly follow the dosage guidelines provided by a qualified herbalist or healthcare professional. Exceeding recommended dosages can increase the risk of adverse effects.
Tip 5: Monitor for Allergic Reactions: Introduce new botanical agents gradually and carefully monitor for any signs of allergic reaction, such as skin rash, itching, swelling, or difficulty breathing. Discontinue use immediately if any adverse reaction occurs.
Tip 6: Consider Potential Interactions with Conventional Medications: Botanical agents can interact with prescription medications, potentially altering their efficacy or increasing the risk of side effects. A pharmacist or physician should be consulted to assess potential interactions.
Tip 7: Maintain a Comprehensive Health Record: Document all botanical agents used, including dosage, frequency, and any observed effects (both positive and negative). This information can be valuable for healthcare providers.
In summary, while plant-derived substances may offer potential benefits for alleviating respiratory discomfort, their use requires careful consideration, thorough research, and professional guidance. Safety and efficacy cannot be assumed, and a collaborative approach with healthcare providers is essential.
The subsequent sections will explore additional facets of managing respiratory health and integrating complementary therapies under medical supervision.
1. Botanical Identification
Accurate botanical identification forms the bedrock of safe and effective herbal interventions for cough associated with bronchial inflammation. Misidentification can lead to the use of ineffective or even harmful plants, undermining treatment goals and potentially endangering patient health. The complexity of plant nomenclature and the variations within species necessitate rigorous attention to detail.
- Taxonomic Accuracy
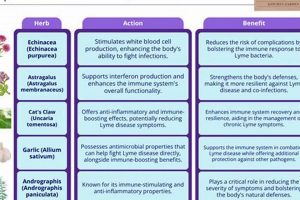
Correctly identifying the genus, species, and, where relevant, subspecies or variety of a plant is the initial and most critical step. The therapeutic properties of plants are often specific to particular taxa. For instance, different species within the Eucalyptus genus possess varying concentrations of active compounds like cineole, which influences their effectiveness in addressing respiratory ailments. Using an incorrect species could lead to inadequate therapeutic effect or unexpected adverse reactions.
- Morphological Authentication
Morphological characteristics, such as leaf shape, flower structure, and stem anatomy, serve as primary identifiers. Experienced herbalists and botanists utilize these features to confirm the identity of a plant specimen. However, morphological traits can vary due to environmental factors, presenting challenges. Detailed field guides and reference specimens are essential tools in this process. For example, distinguishing between different species of Plantago requires careful examination of leaf venation and seed capsule characteristics.
- Chemotyping Analysis
Chemotyping involves analyzing the chemical composition of a plant to confirm its identity and determine the concentration of active constituents. This method is particularly useful when morphological features are ambiguous or when variations in chemical profile influence therapeutic efficacy. Techniques like chromatography and mass spectrometry are employed. For example, variations in the concentration of thymol and carvacrol in different chemotypes of Thymus vulgaris impact its antimicrobial and expectorant properties.
- Source Verification
Tracing the source of herbal material back to its origin is crucial for ensuring authenticity and quality. This involves verifying the supplier’s identification procedures and the growing conditions of the plant. Adulteration and substitution are prevalent issues in the herbal market, necessitating vigilance. For example, confirming that Glycyrrhiza glabra (licorice) is sourced from a reputable supplier who adheres to good agricultural practices is essential to avoid contamination with similar-looking but less effective species.
These interconnected facets highlight the importance of meticulous botanical identification in the context of employing plant-derived substances for cough associated with bronchial inflammation. Accurate identification directly impacts the safety and efficacy of the treatment, underscoring the need for expertise and rigorous quality control throughout the sourcing and preparation process.
2. Pharmacological Actions
Pharmacological actions form the mechanistic foundation of plant-derived interventions used to address cough stemming from bronchial inflammation. The efficacy of a given botanical agent rests upon its ability to interact with the body’s physiological systems in a manner that mitigates the underlying causes or symptoms. For instance, compounds exhibiting bronchodilatory properties can relax constricted airway muscles, easing airflow. Similarly, agents with mucolytic effects can break down excessive mucus, facilitating its expulsion. The absence of relevant pharmacological actions renders a particular herb ineffective for addressing the specific pathophysiology of cough.
Understanding the specific pharmacological actions associated with different botanical compounds allows for a more targeted and rational approach to treatment. For example, Glycyrrhiza glabra (licorice) possesses anti-inflammatory properties attributed to glycyrrhizin, which inhibits the metabolism of cortisol. This action may help reduce airway inflammation, a common trigger for cough. Similarly, Hedera helix (ivy leaf) contains saponins that exhibit secretolytic effects, stimulating the production of thinner mucus that is easier to clear. Without knowledge of these pharmacological mechanisms, the selection and application of herbal remedies would be reduced to guesswork.
In summation, a thorough comprehension of pharmacological actions is indispensable for the appropriate and effective employment of plant-derived substances in managing cough. This knowledge informs the selection of specific herbs, guides dosage considerations, and facilitates the integration of herbal interventions with conventional treatments, ultimately promoting improved patient outcomes. Challenges remain in fully elucidating the complex interplay of multiple compounds within a single plant extract and their interactions with the human body. However, ongoing research continues to refine understanding in this crucial area.
3. Efficacy Evidence
The assessment of efficacy represents a critical juncture in evaluating the appropriateness of plant-derived interventions for managing cough associated with bronchial inflammation. Rigorous scientific investigation is required to substantiate claims of therapeutic benefit and to differentiate between genuine pharmacological effects and placebo responses. The presence or absence of robust efficacy evidence directly influences clinical decision-making and patient safety.
- Randomized Controlled Trials (RCTs)
RCTs are considered the gold standard for evaluating the efficacy of medical interventions. These trials involve randomly assigning participants to either a treatment group (receiving the herbal intervention) or a control group (receiving a placebo or standard treatment). The outcomes are then compared between the groups to determine if the herbal intervention demonstrates a statistically significant benefit. For example, an RCT might evaluate the effect of Eucalyptus globulus oil inhalation on cough frequency and severity in individuals with asthma. The methodological rigor of RCTs minimizes bias and strengthens the validity of the findings.
- Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analyses
Systematic reviews comprehensively synthesize the findings of multiple RCTs addressing the same research question. Meta-analyses, a type of systematic review, statistically combine the data from these trials to provide a more precise estimate of the treatment effect. These analyses offer a higher level of evidence than individual trials by increasing statistical power and reducing the impact of small sample sizes. For example, a meta-analysis might examine the collective evidence from multiple trials assessing the effect of Andrographis paniculata on upper respiratory tract infections, which can often trigger cough.
- Observational Studies
Observational studies, such as cohort studies and case-control studies, can provide valuable insights into the long-term effects and real-world effectiveness of herbal interventions. While these studies are more susceptible to bias than RCTs, they can capture data on diverse populations and settings. For example, a cohort study might follow a group of individuals with chronic bronchitis who regularly use Pelargonium sidoides extract to assess its impact on the frequency of cough exacerbations.
- Traditional Use and Ethnopharmacological Data
Traditional use and ethnopharmacological data can provide initial clues regarding the potential efficacy of herbal interventions. Centuries of empirical observation within traditional medicine systems may identify plants with apparent therapeutic benefits. However, this data requires careful interpretation and validation through modern scientific methods. For example, the traditional use of Inula racemosa in Ayurvedic medicine for respiratory ailments warrants further investigation through controlled clinical trials to determine its actual efficacy and safety.
The convergence of evidence from RCTs, systematic reviews, observational studies, and traditional use provides a more comprehensive assessment of the efficacy of plant-derived interventions for cough associated with bronchial inflammation. It underscores the importance of not relying solely on anecdotal evidence or traditional claims but rather seeking robust scientific validation to ensure patient safety and informed clinical decision-making.
4. Safety Profiles
The establishment of comprehensive safety profiles is paramount when considering plant-derived interventions for the management of cough associated with bronchial inflammation. A thorough understanding of potential adverse effects, contraindications, and drug interactions is essential to mitigate risks and ensure patient well-being. The absence of rigorous safety data necessitates a cautious approach, particularly given the potential for chronic use and the vulnerability of individuals with underlying respiratory conditions.
- Adverse Event Monitoring
Systematic monitoring for adverse events is crucial in establishing the safety profile of any herbal treatment. This involves actively collecting and analyzing data on potential side effects reported by individuals using the intervention. Adverse events can range from mild gastrointestinal upset to more severe reactions such as allergic responses or hepatotoxicity. Detailed documentation of the type, severity, and frequency of adverse events is essential for identifying potential safety concerns and informing appropriate risk mitigation strategies. For instance, certain herbs known to affect blood clotting could pose a risk for individuals on anticoagulant medications.
- Contraindication Identification
Identifying contraindications, situations in which the use of a particular herbal treatment is inadvisable or potentially harmful, is a critical component of establishing a safety profile. Certain herbs may be contraindicated in individuals with specific medical conditions, such as pregnancy, breastfeeding, or liver disease. For example, some herbs with emmenagogue properties are contraindicated during pregnancy due to the potential to induce uterine contractions. Similarly, herbs metabolized by the liver may be contraindicated in individuals with impaired liver function. Thorough research and careful consideration of individual patient factors are essential for identifying and avoiding contraindications.
- Drug Interaction Assessment
Herbal treatments can interact with conventional medications, potentially altering their efficacy or increasing the risk of adverse effects. Assessing the potential for drug interactions is therefore a crucial aspect of safety profiling. Some herbs may inhibit or induce the activity of drug-metabolizing enzymes, leading to altered drug concentrations in the body. For example, St. John’s Wort is known to induce CYP3A4, an enzyme that metabolizes numerous medications, potentially reducing their effectiveness. Thorough investigation of potential drug interactions is essential for preventing adverse outcomes and ensuring the safe co-administration of herbal and conventional treatments.
- Quality Control Assurance
The safety profile of an herbal treatment is inextricably linked to the quality of the raw materials and the manufacturing processes employed. Contamination with heavy metals, pesticides, or other adulterants can pose significant health risks. Similarly, variations in the concentration of active constituents can lead to inconsistent therapeutic effects and potential toxicity. Implementing rigorous quality control measures, including botanical identification, chemical analysis, and adherence to good manufacturing practices, is essential for ensuring the safety and consistency of herbal products. Third-party certification can provide additional assurance of product quality and safety.
These facets collectively emphasize the importance of a comprehensive and systematic approach to establishing safety profiles for plant-derived interventions used in managing cough associated with bronchial inflammation. A lack of rigorous safety data can compromise patient well-being and undermine the responsible use of herbal medicine. Ongoing research and vigilant monitoring are essential for refining our understanding of the safety of herbal treatments and for optimizing their integration into clinical practice.
5. Dosage Protocols
Establishing appropriate dosage protocols is of paramount importance when utilizing plant-derived interventions for cough associated with bronchial inflammation. The efficacy and safety of herbal treatments are intrinsically linked to the administered dose, necessitating a careful consideration of factors influencing optimal therapeutic levels. Deviation from established protocols can lead to sub-therapeutic effects or, conversely, adverse reactions, thereby undermining the intended benefits and potentially jeopardizing patient health.
- Weight and Age Considerations
Body weight and age exert a significant influence on drug metabolism and distribution. Pediatric and geriatric populations, in particular, often require adjusted dosages to account for differences in physiological function and metabolic capacity. Standard adult dosages may be inappropriate and potentially harmful in these vulnerable groups. For example, the dosage of Glycyrrhiza glabra (licorice) for a child with cough should be significantly lower than that for an adult, due to the increased sensitivity to its potential effects on blood pressure. Healthcare practitioners must carefully consider these factors when determining appropriate dosages for individual patients.
- Severity of Symptoms
The severity of cough symptoms can influence the required dosage of herbal treatment. Individuals with mild, infrequent cough may require lower doses than those experiencing severe, persistent cough. A graded approach to dosage adjustment, based on symptom intensity, allows for a more personalized and responsive treatment strategy. For instance, the frequency of Thymus vulgaris (thyme) syrup administration may be increased during periods of acute cough exacerbation and reduced as symptoms subside. Close monitoring of symptom response is essential for optimizing dosage levels.
- Standardization of Herbal Extracts
The concentration of active constituents can vary significantly between different batches of herbal extracts. Standardization, the process of ensuring a consistent level of key compounds, is crucial for achieving predictable and reproducible therapeutic effects. Dosage protocols should be based on the standardized concentration of active constituents, rather than solely on the weight of the crude herb. For example, the dosage of Hedera helix (ivy leaf) extract should be based on the standardized content of hederacoside C, its primary active compound. This approach minimizes variability and improves the reliability of treatment outcomes.
- Frequency and Duration of Administration
The frequency and duration of herbal treatment administration are important considerations in dosage protocols. Some herbs may require frequent dosing to maintain therapeutic levels, while others may have longer-lasting effects. The duration of treatment should be tailored to the individual’s response and the underlying cause of the cough. Prolonged use of certain herbs, such as Glycyrrhiza glabra (licorice), may increase the risk of adverse effects, necessitating careful monitoring and periodic assessment of treatment efficacy and safety. Intermittent dosing schedules may be appropriate for managing chronic cough, with periods of active treatment followed by periods of observation.
In conclusion, dosage protocols represent a critical determinant of the success and safety of plant-derived interventions in addressing cough associated with bronchial inflammation. Factors such as weight, age, symptom severity, extract standardization, and administration schedules must be carefully considered to optimize treatment outcomes and minimize potential risks. A personalized and adaptive approach to dosage adjustment, guided by close monitoring and expert clinical judgment, is essential for harnessing the full therapeutic potential of herbal medicine in a responsible and effective manner.
6. Formulation Methods
The preparation of plant-derived substances significantly impacts the efficacy and safety profiles of herbal treatments for bronchial inflammation. Formulation methods directly influence the extraction of active compounds, their bioavailability, and their stability, thereby affecting the therapeutic outcome. The selection of an appropriate formulation method is not arbitrary; it is guided by the chemical properties of the target compounds, the desired route of administration, and the specific needs of the individual patient. For instance, compounds that are poorly soluble in water may require extraction using alcoholic solvents or encapsulation in liposomes to enhance their absorption. Similarly, volatile compounds, such as those found in essential oils, may be best administered via inhalation or topical application. Incorrect formulation methods can result in sub-therapeutic doses or, conversely, the concentration of undesirable compounds, leading to adverse effects.
The practical significance of understanding formulation methods is evident in the preparation of herbal cough syrups. Traditional cough syrups often involve decoction, a process of boiling plant material in water to extract water-soluble compounds. However, decoction may not be suitable for extracting compounds that are heat-sensitive or poorly soluble in water. In such cases, a tincture, prepared by soaking plant material in alcohol, may be a more effective formulation. Furthermore, the addition of honey or other demulcents to the syrup can enhance its soothing effect on the throat. The specific ingredients and preparation techniques employed in a cough syrup formulation can significantly impact its ability to alleviate cough symptoms and promote bronchial health. Standardized manufacturing processes are essential to ensure consistency and minimize variability in the final product. Failure to adhere to proper formulation methods can compromise the quality and effectiveness of the herbal treatment.
In summation, formulation methods constitute a critical and often overlooked aspect of herbal treatments for bronchial inflammation. The choice of formulation method directly impacts the extraction, bioavailability, and stability of active compounds, thereby influencing the therapeutic outcome. A thorough understanding of the chemical properties of the target compounds, the desired route of administration, and the needs of the individual patient is essential for selecting an appropriate formulation method. Challenges remain in standardizing formulation methods and ensuring consistent product quality. However, ongoing research and advancements in extraction and delivery technologies are continually improving the efficacy and safety of herbal treatments for cough.
7. Interaction Potential
The concurrent use of plant-derived substances with conventional asthma medications introduces a complex interplay with potential ramifications for therapeutic outcomes. Understanding the interaction potential between these modalities is crucial, as botanical agents may alter the pharmacokinetics or pharmacodynamics of synthetic drugs, leading to either reduced efficacy or increased toxicity. For example, an individual using inhaled corticosteroids for asthma control may simultaneously consume an herbal supplement containing Glycyrrhiza glabra (licorice). Glycyrrhizin, a compound found in licorice, can potentiate the effects of corticosteroids by inhibiting their metabolism, potentially increasing the risk of adverse effects such as elevated blood pressure or fluid retention. Conversely, certain herbal constituents may induce drug-metabolizing enzymes, accelerating the clearance of asthma medications and diminishing their therapeutic effects.
The clinical significance of interaction potential extends beyond theoretical considerations, impacting real-world patient management. Individuals with poorly controlled asthma, despite adhering to their prescribed medication regimen, may unknowingly be experiencing reduced drug efficacy due to herbal supplement use. Healthcare providers must proactively inquire about the concurrent use of herbal products to accurately assess treatment response and adjust medication dosages accordingly. Furthermore, the availability of comprehensive drug interaction databases specific to herbal medicines is limited, necessitating a cautious and individualized approach to patient care. Educational resources that inform both patients and providers about potential interactions are essential for promoting safe and effective asthma management.
In summary, the interaction potential between herbal treatments and conventional asthma medications represents a critical consideration in respiratory healthcare. Clinicians must be vigilant in assessing herbal supplement use, and patients must be educated about the potential risks and benefits. Ongoing research to identify and characterize specific interactions is warranted to inform evidence-based clinical guidelines. Failure to adequately address interaction potential can compromise treatment efficacy and patient safety, highlighting the importance of a holistic and integrated approach to asthma management.
Frequently Asked Questions
The subsequent questions and answers address common inquiries and concerns regarding the utilization of plant-derived substances in the management of cough associated with bronchial inflammation. The information presented is intended for educational purposes and does not constitute medical advice. Consultation with a qualified healthcare professional is essential before initiating any new treatment regimen.
Question 1: Are botanical remedies a substitute for conventional asthma medications?
Botanical remedies are not a substitute for conventional asthma medications, particularly in cases of acute exacerbations or severe, persistent asthma. Conventional medications, such as inhaled corticosteroids and bronchodilators, are the cornerstone of asthma management, supported by extensive clinical evidence. Botanical remedies may be considered as complementary therapies under medical supervision, but should never replace essential prescription medications.
Question 2: What are the potential risks associated with using herbal treatments for cough?
Potential risks include allergic reactions, adverse interactions with conventional medications, and the use of adulterated or misidentified herbal products. Certain botanical agents may also be contraindicated in individuals with specific medical conditions, such as pregnancy or liver disease. Rigorous quality control and informed medical guidance are essential to mitigate these risks.
Question 3: How can product quality be ensured when purchasing herbal supplements?
To ensure product quality, it is advisable to purchase herbal supplements from reputable suppliers with demonstrable quality control measures. Look for products that have been independently tested and certified by third-party organizations. Verify the botanical identification of the plant material and review the product label for information on standardization and potential contaminants.
Question 4: What scientific evidence supports the efficacy of herbal treatments for cough?
The scientific evidence supporting the efficacy of herbal treatments for cough varies depending on the specific botanical agent. Some herbs, such as Hedera helix (ivy leaf) and Pelargonium sidoides, have been studied in clinical trials and shown to provide symptomatic relief. However, further research is needed to confirm the efficacy of many other herbal remedies and to elucidate their mechanisms of action.
Question 5: Can herbal treatments be used safely in children with asthma-related cough?
The use of herbal treatments in children with asthma-related cough requires extreme caution and should only be undertaken under the direct supervision of a qualified healthcare professional. Children are more susceptible to the adverse effects of herbal remedies, and dosage adjustments may be necessary. Certain herbs are contraindicated in children due to potential toxicity or lack of safety data.
Question 6: Where can reliable information be obtained regarding the safe and effective use of herbal treatments?
Reliable information can be obtained from qualified healthcare professionals, such as physicians, pharmacists, and registered herbalists. Reputable scientific databases and peer-reviewed journals provide access to research findings on herbal medicine. Government health agencies and professional organizations also offer evidence-based information on the safety and efficacy of herbal treatments.
In summary, the use of plant-derived interventions for cough and bronchial inflammation should be approached with caution and informed medical guidance. The information presented in these FAQs serves to highlight the potential benefits and risks associated with herbal treatments, emphasizing the importance of evidence-based decision-making and individualized patient care.
The subsequent section will offer guidance on integrating herbal treatments into a comprehensive asthma management plan.
Conclusion
This exploration has elucidated critical facets surrounding herbal treatment for asthma cough, encompassing botanical identification, pharmacological actions, efficacy evidence, safety profiles, dosage protocols, formulation methods, and interaction potential. It underscores the necessity for rigorous scientific evaluation and cautious clinical application, given the inherent complexities and potential risks associated with plant-derived interventions.
The judicious and informed utilization of these therapies, under the guidance of qualified healthcare professionals, may offer adjunctive benefits in select cases. However, continuous research and stringent regulatory oversight remain imperative to ensure patient safety and to establish definitive evidence-based recommendations for herbal treatment for asthma cough within comprehensive asthma management strategies.