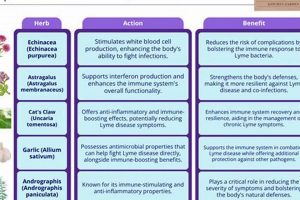
The utilization of plant-derived substances to manage the symptoms and inflammation associated with ulcerative colitis represents a complementary approach to conventional medical interventions. This involves employing herbs and botanical formulations believed to possess anti-inflammatory, immunomodulatory, or gut-healing properties, with the intention of alleviating discomfort and potentially promoting remission in individuals affected by the condition.
Historically, diverse cultures have incorporated botanical remedies into their traditional healing practices for gastrointestinal ailments. The appeal of these approaches often lies in the perception of naturalness and a desire for gentler alternatives to pharmaceutical drugs. Benefits potentially include reduced reliance on conventional medications and the mitigation of associated side effects. However, it is important to acknowledge that scientific validation of efficacy and safety remains crucial.
The subsequent discussion will explore specific herbal options frequently considered for ulcerative colitis management, alongside a critical examination of the available evidence and essential considerations for informed decision-making regarding their use. It’s vital to understand the current state of research and potential risks before incorporating any of these methods into a comprehensive treatment plan.
Considerations for Botanical Interventions in Ulcerative Colitis
The following guidelines offer crucial considerations for individuals exploring plant-based strategies as a component of managing ulcerative colitis. These tips emphasize informed decision-making and collaborative care with medical professionals.
Tip 1: Consultation with a Healthcare Provider: Initiate any regimen with a thorough discussion with a gastroenterologist or qualified medical professional. This ensures integration with existing treatments and monitors for potential interactions.
Tip 2: Rigorous Product Sourcing: Obtain herbal remedies from reputable manufacturers adhering to stringent quality control standards. Third-party certifications can provide assurance of purity and accurate ingredient labeling.
Tip 3: Gradual Introduction and Monitoring: Introduce new botanical treatments incrementally, allowing observation for adverse reactions or symptom exacerbation. Maintain a detailed record of dosage, timing, and any experienced effects.
Tip 4: Awareness of Potential Interactions: Many herbs can interact with prescription medications, potentially altering their efficacy or increasing side effects. Inform healthcare providers of all ingested substances, including herbal supplements.
Tip 5: Understanding Evidence-Based Research: Scrutinize available scientific literature regarding the specific herbs being considered. Acknowledge that evidence may be limited and that individual responses can vary significantly.
Tip 6: Consideration of Individual Sensitivities: Individuals with allergies or sensitivities to specific plants or botanical families should exercise caution and avoid related herbal remedies. Start with minimal doses and closely monitor for allergic reactions.
Tip 7: Long-Term Sustainability: Implement these strategies as part of a holistic approach, which integrates alongside with prescribed medications or a diet and regular exercise that promotes physical health.
Adherence to these recommendations facilitates a cautious and informed approach to integrating botanical remedies into the management of ulcerative colitis. It reinforces the importance of individualized care and ongoing communication with healthcare providers.
The subsequent section will delve into the legal considerations associated with this treatment to emphasize the need for safety and awareness.
1. Anti-inflammatory properties
The anti-inflammatory capacity of certain herbs is a central consideration within the context of botanical interventions for ulcerative colitis. Chronic inflammation is a hallmark of this inflammatory bowel disease, driving its symptoms and contributing to disease progression. Consequently, herbal remedies possessing demonstrated anti-inflammatory effects are investigated for their potential to mitigate this inflammatory cascade within the gastrointestinal tract.
- Inhibition of Pro-inflammatory Cytokines
Many herbs are believed to exert their anti-inflammatory effects by inhibiting the production or activity of pro-inflammatory cytokines, such as TNF-alpha, IL-1beta, and IL-6. These cytokines play a crucial role in the inflammatory response characteristic of ulcerative colitis. For example, compounds within turmeric (curcuminoids) have demonstrated the ability to suppress TNF-alpha production in vitro and in vivo, suggesting a potential mechanism for reducing inflammation within the colon.
- Modulation of Inflammatory Signaling Pathways
Herbs may also influence inflammatory processes by modulating signaling pathways that regulate inflammation, such as the NF-kB pathway. Activation of NF-kB leads to the transcription of genes involved in inflammation, and some herbal compounds can inhibit this pathway, thereby reducing the production of inflammatory mediators. This targeted modulation of signaling pathways represents a refined approach to controlling inflammation at the cellular level.
- Antioxidant Activity and Reduction of Oxidative Stress
Oxidative stress, resulting from an imbalance between the production of reactive oxygen species (ROS) and the body’s ability to neutralize them, contributes to inflammation in ulcerative colitis. Certain herbs possess antioxidant properties, enabling them to scavenge ROS and reduce oxidative damage. This reduction in oxidative stress can indirectly dampen the inflammatory response within the colonic mucosa. Examples include herbs rich in polyphenols, which act as free radical scavengers.
- Influence on Immune Cell Function
The anti-inflammatory effects of herbs can extend to influencing the function of immune cells involved in the pathogenesis of ulcerative colitis. Certain herbs may modulate the activity of T cells, macrophages, and neutrophils, which contribute to the inflammatory cascade in the gut. This modulation can involve suppressing the activation of these cells or promoting the production of anti-inflammatory mediators. For example, some herbs have been shown to promote the differentiation of regulatory T cells, which play a role in suppressing excessive immune responses.
The multifaceted anti-inflammatory properties of these herbs highlight their potential role in managing ulcerative colitis. However, it is crucial to acknowledge that the extent and mechanisms of these effects are often complex and require further rigorous investigation. The clinical efficacy and safety of such herbal treatments necessitate evaluation through well-designed clinical trials to determine their true value in alleviating inflammation and improving outcomes for individuals with ulcerative colitis.
2. Gut microbiome modulation
The intricate relationship between the gut microbiome and ulcerative colitis is increasingly recognized as a critical factor in disease pathogenesis and potential therapeutic interventions. Modulation of this microbial ecosystem, through various means including herbal treatments, represents a promising avenue for managing the condition.
- Prebiotic Effects and Beneficial Bacteria Growth
Certain herbs can act as prebiotics, providing nourishment for beneficial gut bacteria and promoting their growth. This selective stimulation of beneficial species, such as Lactobacillus and Bifidobacterium, can lead to a more balanced and resilient gut microbiome. For example, herbs containing soluble fibers may enhance the proliferation of these bacteria, which, in turn, produce short-chain fatty acids (SCFAs) like butyrate. Butyrate is a primary energy source for colonocytes and possesses anti-inflammatory properties, contributing to improved gut health in individuals with ulcerative colitis.
- Reduction of Pathogenic Bacteria
Conversely, some herbal compounds exhibit antimicrobial properties that can selectively reduce the population of harmful bacteria within the gut. An overabundance of pathogenic bacteria is often implicated in the inflammatory processes characteristic of ulcerative colitis. Herbs containing compounds such as berberine have demonstrated inhibitory effects on certain pathogenic strains, potentially reducing the inflammatory burden in the colon. However, caution is necessary to ensure that such interventions do not indiscriminately eliminate beneficial bacteria as well.
- Enhancement of Microbial Diversity
A diverse gut microbiome is generally associated with better health outcomes, including improved immune regulation and resilience to disease. Some herbal treatments may promote microbial diversity by providing a wider range of substrates for bacterial metabolism or by directly influencing the composition of the microbial community. A more diverse microbiome is thought to be better equipped to resist colonization by pathogens and to maintain a stable and balanced ecosystem. Herbs with a wide spectrum of bioactive compounds may contribute to this enhancement of microbial diversity.
- Impact on Gut Barrier Function
The integrity of the gut barrier is crucial in preventing the translocation of bacteria and their products into the bloodstream, which can trigger systemic inflammation. Certain herbs can influence gut barrier function by promoting the production of mucus, strengthening tight junctions between epithelial cells, or reducing inflammation that can compromise barrier integrity. By improving gut barrier function, these herbs can help to prevent the leakage of inflammatory substances into the circulation, thereby reducing systemic inflammation and improving outcomes in ulcerative colitis.
The modulation of the gut microbiome through herbal treatments offers a multifaceted approach to managing ulcerative colitis. The precise mechanisms and efficacy of individual herbs vary, emphasizing the need for personalized treatment strategies and careful monitoring. Clinical trials are essential to validate the potential benefits and ensure the safety of these interventions, taking into account the complex interplay between herbal compounds, the gut microbiome, and the host immune system.
3. Symptom relief potential
Symptom relief represents a primary objective in the therapeutic management of ulcerative colitis. Herbal interventions are frequently explored for their capacity to alleviate common manifestations of the condition, including abdominal pain, diarrhea, rectal bleeding, and urgency. The rationale behind this approach centers on the hypothesis that specific botanical compounds possess properties capable of directly addressing these symptoms or indirectly mitigating their underlying causes. For instance, herbs with purported anti-spasmodic effects may reduce abdominal cramping, while those exhibiting astringent qualities might help control diarrhea and bleeding. The perceived gentler nature of certain herbal remedies, compared to conventional pharmaceutical options, can also contribute to their appeal among individuals seeking symptom control.
The actual efficacy of symptom relief afforded by herbal treatment, however, remains a subject of ongoing investigation. While anecdotal evidence and traditional use suggest potential benefits, rigorous scientific validation through controlled clinical trials is essential. The variable composition of herbal products, coupled with individual differences in response, introduce complexities in accurately assessing their therapeutic value. It is imperative to recognize that symptom improvement alone does not necessarily equate to disease modification or resolution. Relief from discomfort should not be misconstrued as a cure, and the underlying inflammatory processes of ulcerative colitis necessitate continuous monitoring and appropriate medical management, irrespective of perceived symptom control achieved through herbal means.
In summary, the potential for symptom relief is a key driver in the utilization of herbal treatments for ulcerative colitis. Nevertheless, a balanced perspective, grounded in scientific evidence and guided by professional medical advice, is crucial. The pursuit of symptom alleviation should not overshadow the importance of comprehensive disease management strategies, including conventional therapies, lifestyle modifications, and regular monitoring, to optimize long-term outcomes and prevent disease progression.
4. Evidence-based research
Evidence-based research forms the cornerstone of informed decision-making in the realm of ulcerative colitis herbal treatment. It serves as the critical link between traditional practices and scientifically validated efficacy, ensuring patient safety and therapeutic effectiveness. The application of rigorous research methodologies is essential to discern genuine benefits from anecdotal claims or placebo effects.
- Randomized Controlled Trials (RCTs)
RCTs represent the gold standard for evaluating the efficacy of any medical intervention, including herbal treatments for ulcerative colitis. These trials involve randomly assigning participants to either a treatment group receiving the herbal remedy or a control group receiving a placebo or standard treatment. By comparing outcomes between these groups, researchers can determine whether the herbal remedy has a statistically significant effect on disease activity, symptom severity, or quality of life. The scarcity of well-designed RCTs for many herbal treatments underscores the need for further investigation in this area. For example, a properly designed RCT would help differentiate curcumin’s anti-inflammatory effects from a placebo response in UC patients.
- Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analyses
Systematic reviews and meta-analyses synthesize the findings of multiple studies on a particular topic, providing a comprehensive overview of the available evidence. These analyses can identify trends, assess the consistency of results across studies, and estimate the overall effect size of an intervention. In the context of ulcerative colitis herbal treatment, systematic reviews can help determine which herbal remedies have the strongest evidence supporting their use and identify gaps in the existing research. For instance, a meta-analysis might evaluate the collective data from several RCTs assessing the effectiveness of a specific herbal formulation in inducing or maintaining remission in UC.
- Dosage and Standardization Studies
Herbal products often lack standardized formulations, making it difficult to determine the optimal dosage and ensure consistent therapeutic effects. Research focusing on dosage and standardization is crucial to address this issue. These studies aim to identify the active compounds within an herbal remedy, determine their concentration, and establish appropriate dosing regimens. Standardizing herbal products can improve their reproducibility and predictability, enhancing their reliability as a treatment option. This is crucial in order to ascertain that patients can experience the same relief under identical circumstances to ensure herbal treatment effectiveness.
- Safety and Toxicity Assessments
Before any herbal treatment can be widely recommended for ulcerative colitis, its safety profile must be thoroughly evaluated. This includes assessing potential side effects, drug interactions, and contraindications. Toxicity studies, conducted in vitro and in vivo, can help identify potential risks associated with herbal remedies and determine safe dosage ranges. Furthermore, post-market surveillance is essential to monitor for adverse events and identify any long-term health consequences. The absence of comprehensive safety data for many herbal treatments highlights the importance of caution and the need for further research in this area.
The facets of evidence-based research discussed above are crucial for the responsible integration of herbal treatments into the management of ulcerative colitis. While traditional knowledge and anecdotal experiences may offer valuable insights, they must be complemented by rigorous scientific investigation to ensure patient safety and maximize therapeutic benefits. Continued research efforts are needed to expand the evidence base and guide clinical decision-making in this evolving field.
5. Safety and interactions
The intersection of safety and interactions represents a critical domain in the context of ulcerative colitis herbal treatment. The integration of botanical remedies alongside conventional medical approaches necessitates a thorough understanding of potential risks and synergistic or antagonistic effects.
- Potential for Adverse Effects
Herbal remedies, despite their natural origins, are not inherently devoid of potential adverse effects. Some individuals may experience allergic reactions, gastrointestinal distress, or other unwanted symptoms following the ingestion of specific herbs. For example, certain herbal preparations can cause liver damage or exacerbate existing kidney conditions. Therefore, a cautious and individualized approach is essential, beginning with low doses and close monitoring for any adverse reactions.
- Herb-Drug Interactions
Many herbs can interact with prescription medications, potentially altering their efficacy or increasing the risk of side effects. For instance, St. John’s Wort, a common herbal antidepressant, can interfere with the metabolism of numerous drugs, including immunosuppressants used in the treatment of ulcerative colitis, leading to decreased drug levels and treatment failure. Similarly, herbs with anticoagulant properties, such as garlic or ginger, can increase the risk of bleeding in patients taking blood-thinning medications. Thoroughly reviewing all medications and herbal supplements with a healthcare provider is crucial to avoid harmful interactions.
- Variability in Product Quality and Standardization
The quality and composition of herbal products can vary significantly depending on the manufacturer, source, and processing methods. Lack of standardization can result in inconsistent dosages of active compounds, making it difficult to predict therapeutic effects and increasing the risk of adverse reactions. Contamination with heavy metals, pesticides, or other adulterants is also a concern. Choosing reputable brands that adhere to stringent quality control standards and undergo third-party testing is essential to ensure product safety and efficacy.
- Impact on Disease Monitoring
Certain herbal treatments may mask or alter the symptoms of ulcerative colitis, making it more difficult to monitor disease activity and assess the effectiveness of conventional therapies. For example, herbs with anti-inflammatory properties may temporarily reduce symptoms without addressing the underlying inflammation, potentially leading to a false sense of security and delaying necessary medical interventions. Regular communication with a healthcare provider and adherence to recommended monitoring schedules are crucial to accurately assess disease progression and adjust treatment plans accordingly.
These interwoven aspects emphasize the imperative of meticulous investigation and informed decision-making when considering herbal treatments for ulcerative colitis. Collaboration with healthcare professionals, careful product selection, and vigilance for potential adverse effects and interactions are paramount to ensure patient safety and optimize treatment outcomes.
6. Individualized approach
The administration of herbal treatments for ulcerative colitis necessitates a highly individualized strategy, primarily due to the heterogeneous nature of the disease itself and the variable responses individuals exhibit to botanical interventions. The manifestation of ulcerative colitis differs significantly among patients, with variations in disease severity, location of inflammation, and associated complications. These disparities necessitate customized treatment plans that consider each patient’s unique disease profile. Furthermore, genetic predispositions, gut microbiome composition, and lifestyle factors all influence an individual’s response to herbal therapies. A standardized “one-size-fits-all” approach is therefore unlikely to yield optimal outcomes and may potentially pose risks due to adverse reactions or interactions with existing medications.
The importance of an individualized approach extends beyond the initial selection of herbal remedies. Continuous monitoring and adjustment of treatment protocols are essential to optimize efficacy and minimize potential side effects. For instance, a patient with mild ulcerative colitis experiencing primarily rectal bleeding might benefit from a specific herbal formulation with astringent properties, while another patient with more extensive colonic inflammation and diarrhea might require a different combination of herbs targeting inflammation and gut motility. Regular assessment of symptoms, endoscopic evaluations, and laboratory tests are crucial to guide these adjustments and ensure that the treatment remains appropriate and effective over time. The integration of personalized dietary modifications and stress management techniques further enhances the individualized treatment strategy.
In summary, the successful integration of herbal treatments into the management of ulcerative colitis hinges on a meticulous and individualized approach. This strategy acknowledges the unique disease characteristics of each patient, considers their specific genetic and environmental factors, and incorporates continuous monitoring and adjustments to optimize therapeutic outcomes. A standardized protocol will rarely be sufficient; personalized attention, guided by scientific evidence and professional expertise, is paramount for achieving meaningful and sustained improvement in patient well-being. Moreover, it is essential to reiterate that herbal treatments should be considered within the context of a comprehensive medical management plan, under the guidance of qualified healthcare professionals.
7. Quality and sourcing
The efficacy and safety of herbal interventions in ulcerative colitis management are inextricably linked to the quality and sourcing of the botanical materials utilized. Unlike pharmaceutical drugs, herbal products often lack stringent regulatory oversight regarding manufacturing processes, quality control, and ingredient standardization. Consequently, significant variations can exist between different brands and even between batches of the same product. This variability directly impacts the therapeutic consistency and safety profile of herbal treatments, potentially leading to inconsistent symptom relief, adverse reactions, or even contamination with harmful substances.
The sourcing of herbal ingredients is equally critical. Geographic location, cultivation practices, and harvesting methods can all influence the chemical composition and potency of medicinal plants. For example, herbs grown in polluted environments may accumulate heavy metals or other toxins, rendering them unsuitable for therapeutic use. Furthermore, unethical harvesting practices can deplete endangered plant species and disrupt ecosystems. The selection of reputable suppliers who prioritize sustainable and ethical sourcing practices is therefore essential for ensuring the long-term availability and integrity of herbal remedies. Several organizations offer certifications or labels that indicate adherence to specific quality and sustainability standards, providing consumers with valuable information when making purchasing decisions. An example of a practical benefit in this field is the opportunity to implement a quality assurance department in the herbal treatment companies which can make it sustainable and safe.
In conclusion, the quality and sourcing of herbal products represent fundamental determinants of their therapeutic value and safety in ulcerative colitis management. The absence of rigorous quality control measures and the potential for unethical sourcing practices underscore the importance of exercising due diligence when selecting herbal remedies. By prioritizing reputable suppliers, seeking products with third-party certifications, and consulting with knowledgeable healthcare professionals, individuals can minimize the risks associated with herbal treatments and maximize their potential benefits within a comprehensive ulcerative colitis management plan.
Frequently Asked Questions
The following questions address common concerns and misconceptions regarding the use of herbal treatments for ulcerative colitis. The information provided is intended to be informative and should not substitute for professional medical advice.
Question 1: Are herbal treatments a cure for ulcerative colitis?
Herbal treatments are not a cure for ulcerative colitis. While some herbs may possess anti-inflammatory or immunomodulatory properties that can help manage symptoms, they do not address the underlying cause of the disease. Ulcerative colitis is a chronic condition requiring ongoing medical management.
Question 2: Are herbal treatments safe for everyone with ulcerative colitis?
Herbal treatments are not universally safe. Potential side effects, allergic reactions, and interactions with prescription medications exist. Individuals with pre-existing medical conditions or those taking other medications must consult with a healthcare provider before initiating herbal treatment.
Question 3: Is there scientific evidence to support the use of herbal treatments for ulcerative colitis?
The scientific evidence supporting the use of herbal treatments for ulcerative colitis varies. Some herbs have demonstrated potential benefits in clinical trials, while others lack sufficient evidence. Rigorous research is needed to validate the efficacy and safety of specific herbal remedies.
Question 4: Can herbal treatments replace conventional medical treatments for ulcerative colitis?
Herbal treatments should not replace conventional medical treatments for ulcerative colitis without the guidance of a healthcare provider. Ulcerative colitis can lead to serious complications if left unmanaged. Combining herbal treatments with conventional therapies may be appropriate in certain cases, but this decision should be made in consultation with a medical professional.
Question 5: How can individuals ensure the quality and safety of herbal products?
Ensuring the quality and safety of herbal products requires careful selection and sourcing. Purchase products from reputable manufacturers that adhere to quality control standards and undergo third-party testing. Be aware of potential contamination and adulteration issues and consult with a healthcare provider or herbalist for guidance.
Question 6: What are the potential risks of using herbal treatments for ulcerative colitis?
Potential risks of using herbal treatments for ulcerative colitis include allergic reactions, gastrointestinal side effects, interactions with medications, and contamination with harmful substances. Individuals should be aware of these risks and consult with a healthcare provider before initiating treatment.
Herbal treatments for ulcerative colitis can be potentially helpful, but there is no guarantee that the symptoms may be relieved. If symptoms persist, please seek professional help as soon as possible.
The subsequent discussion will explore the legal considerations associated with this treatment to emphasize the need for safety and awareness.
Conclusion
The preceding discussion has presented a multifaceted exploration of ulcerative colitis herbal treatment, encompassing potential benefits, limitations, and essential considerations. It underscores the complexity of integrating botanical remedies into the management of this chronic inflammatory bowel disease, emphasizing that while certain herbs may offer symptomatic relief or contribute to overall well-being, they are not a substitute for conventional medical care. The importance of evidence-based research, rigorous product sourcing, and individualized treatment strategies has been consistently highlighted.
Given the potential risks and the limitations of current scientific knowledge, individuals considering ulcerative colitis herbal treatment should proceed with caution and under the guidance of qualified healthcare professionals. Continued research is crucial to further elucidate the efficacy, safety, and optimal application of specific herbal remedies, paving the way for more informed and personalized treatment approaches in the future. The responsible integration of complementary therapies, alongside conventional medicine, offers the most promising path toward improved outcomes and enhanced quality of life for those affected by this challenging condition.