The management of human papillomavirus (HPV) infections, a prevalent sexually transmitted disease, often involves conventional medical approaches. However, some individuals explore alternative therapies utilizing botanical extracts and traditional remedies to potentially address the virus and associated symptoms. These complementary methods are based on the premise that certain plant-derived compounds possess antiviral, immunomodulatory, or anti-inflammatory properties. An example includes the topical application of specific herbal formulations to treat genital warts, a common manifestation of HPV infection.
The interest in employing natural substances stems from various factors, including a desire to minimize potential side effects associated with pharmaceutical interventions, a belief in holistic healthcare practices, and the accessibility of certain herbal remedies. Historically, various cultures have relied on plants for medicinal purposes, and the potential of these traditional practices is now being re-examined through scientific research. Benefits could encompass improved immune function and reduced inflammation. It’s important to recognize that the efficacy and safety of these alternative treatments are areas of ongoing investigation.
The subsequent sections will delve into the scientific basis, potential benefits, limitations, and safety considerations of integrating plant-based approaches into the overall management of HPV infections. It will discuss the need for robust clinical trials to validate claims of efficacy and the importance of consulting with healthcare professionals to ensure that any chosen strategy aligns with individual health needs and established medical guidelines.
Considerations for Investigating Plant-Based Approaches for HPV Management
The following points offer guidance for those researching complementary strategies using botanicals in conjunction with conventional treatments for human papillomavirus (HPV) infections.
Tip 1: Research Reputable Sources: Conduct thorough research utilizing peer-reviewed scientific publications and recognized medical databases. Prioritize information from institutions known for rigorous scientific inquiry and objectivity.
Tip 2: Understand Mechanism of Action: Investigate the proposed mechanisms by which specific herbal compounds might affect HPV. Focus on whether the compound exhibits antiviral activity, modulates the immune response, or possesses anti-inflammatory properties.
Tip 3: Assess Clinical Evidence: Critically evaluate the available clinical trial data related to the specific herbal treatment. Determine the size and quality of the studies, the populations studied, and the reported outcomes. Scrutinize the studies for potential biases or limitations.
Tip 4: Consult a Healthcare Professional: Prioritize consultation with a qualified healthcare provider, such as a physician or a registered herbalist experienced in working with HPV. Discuss the potential benefits, risks, and interactions of any herbal treatments with existing medications or health conditions. Avoid self-treating based solely on anecdotal evidence or promotional claims.
Tip 5: Verify Product Quality: If considering the use of a specific herbal product, research the manufacturer’s quality control standards and third-party testing procedures. Ensure that the product is standardized for active ingredients and free from contaminants. Exercise caution with products that make unsubstantiated claims or lack clear labeling.
Tip 6: Monitor for Adverse Effects: Be vigilant for any adverse effects or allergic reactions while using herbal treatments. Discontinue use immediately if any unexpected symptoms arise and seek medical attention.
Tip 7: Manage Expectations: Approach plant-based treatments as a complementary, rather than a replacement, for conventional medical care. Understand that herbal therapies may not eliminate HPV infection and may only provide symptomatic relief.
Adherence to these guidelines promotes informed decision-making when exploring complementary approaches, helping to weigh potential benefits against potential risks.
By adhering to the aforementioned advice, individuals can make informed decisions regarding the integration of herbal remedies into their overall strategy for managing HPV infection, ideally in consultation with their healthcare provider.
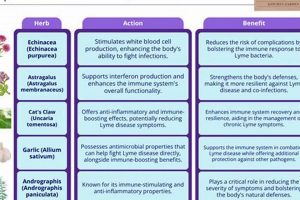
The presence of antiviral constituents is a critical determinant of a plant’s potential efficacy in the context of botanical treatments for human papillomavirus (HPV) infections. Specific compounds within certain herbs may directly inhibit viral replication, reduce viral load, or interfere with the virus’s ability to infect new cells. The effectiveness of any herbal approach is fundamentally predicated on the identification and concentration of these active antiviral compounds. An example is epigallocatechin gallate (EGCG), a component of green tea, which has demonstrated in vitro antiviral activity against HPV. The presence and concentration of EGCG directly influence green tea’s potential as a therapeutic agent. Without such constituents, an herbal intervention’s impact on the viral infection is severely limited.
Clinical studies investigating herbal treatments for HPV often focus on identifying the specific antiviral compounds responsible for observed effects. The presence of these compounds is not merely correlational but causative. For instance, research on Andrographis paniculata explores the antiviral activity of andrographolide, its primary constituent, on various viruses. When considering botanical options, the knowledge of these antiviral agents is crucial for choosing treatments. Understanding the mechanisms by which these compounds exert their antiviral effectswhether by inhibiting viral enzymes, preventing viral entry into cells, or disrupting viral assemblyis equally vital for optimizing treatment strategies. Proper extraction and preparation techniques can further enhance the concentration and bioavailability of these antiviral agents, thereby increasing the likelihood of a therapeutic outcome.
The pursuit of effective botanical treatments hinges on a thorough understanding of the antiviral constituents present within specific herbs. Challenges exist in standardizing preparations, ensuring consistent concentrations of active compounds, and conducting robust clinical trials to validate antiviral activity in vivo. Nevertheless, focusing on these constituents facilitates a targeted approach to identifying and developing plant-based remedies with the potential to complement conventional medical interventions for managing HPV infections. Prioritization of constituents and efficacy is vital to responsible herbal treatment plans.
2. Immunomodulatory effects
The modulation of the immune system constitutes a significant component of certain plant-based approaches to managing human papillomavirus (HPV) infections. The body’s inherent ability to identify and eliminate HPV-infected cells is often suppressed, leading to persistent infection and the development of associated lesions. Certain herbal remedies are purported to possess immunomodulatory properties that can enhance or restore this natural immune response.
- Enhancement of Natural Killer (NK) Cell Activity
Natural killer cells are crucial components of the innate immune system, responsible for identifying and destroying virally infected cells. Some herbal extracts are believed to stimulate NK cell activity, thereby increasing the body’s ability to target and eliminate HPV-infected cells. For example, certain mushroom extracts, such as those derived from Ganoderma lucidum (Reishi), have demonstrated in vitro and in vivo immunomodulatory effects, including enhanced NK cell cytotoxicity. The magnitude and duration of this enhancement, however, require further investigation in controlled clinical trials.
- Cytokine Modulation
Cytokines are signaling molecules that regulate immune responses. Certain herbal compounds may influence the production and balance of various cytokines, promoting an anti-viral immune environment. For instance, some studies suggest that Echinacea may modulate the production of cytokines like interferon-gamma (IFN-), which plays a critical role in antiviral immunity. Balancing cytokine production is essential, as excessive inflammation can be detrimental. The complexity of cytokine networks necessitates careful consideration of the potential downstream effects of herbal interventions.
- Activation of Dendritic Cells (DCs)
Dendritic cells are antigen-presenting cells that initiate adaptive immune responses. Activation of DCs by herbal compounds can enhance the presentation of HPV antigens to T cells, leading to a more effective T cell-mediated immune response. Some research suggests that specific polysaccharides derived from medicinal plants may activate DCs, promoting T cell priming and viral clearance. The specific mechanisms by which these polysaccharides interact with DC receptors remain an area of active investigation.
- Regulation of T Cell Responses
T cells are central to adaptive immunity, directly killing infected cells (cytotoxic T cells) and coordinating the immune response (helper T cells). Certain herbal extracts may influence the differentiation, proliferation, and function of T cell subsets. For example, some studies suggest that specific herbal formulations may enhance the activity of cytotoxic T cells, improving their ability to eliminate HPV-infected cells. Careful monitoring of T cell responses is necessary to ensure that herbal interventions promote effective antiviral immunity without inducing autoimmunity.
The modulation of the immune response represents a promising avenue in the development of plant-based strategies for HPV management. However, further rigorous scientific investigation is required to elucidate the specific mechanisms of action, determine optimal dosages and formulations, and assess the long-term efficacy and safety of these interventions. The complexity of the immune system underscores the need for a cautious and evidence-based approach to integrating immunomodulatory herbs into conventional medical care.
3. Clinical trial evidence
The rigorous evaluation of herbal treatments for human papillomavirus (HPV) infection necessitates the examination of clinical trial evidence. Such evidence serves as the foundation for determining the efficacy, safety, and appropriate application of botanical interventions in a medical context. The absence of robust clinical trial data renders claims regarding the therapeutic benefits of plant-based remedies largely unsubstantiated.
- Randomized Controlled Trials (RCTs)
Randomized controlled trials represent the gold standard for evaluating medical interventions. In the context of herbal treatments for HPV, RCTs involve randomly assigning participants with HPV infection to either a treatment group receiving the herbal intervention or a control group receiving a placebo or standard medical care. The outcomes in each group are then compared to determine whether the herbal treatment demonstrates a statistically significant benefit. For example, an RCT might compare the clearance rate of genital warts in participants treated with a specific herbal cream versus a placebo cream. The presence of well-designed RCTs is essential for establishing the clinical effectiveness of any herbal treatment.
- Study Design and Methodology
Beyond the presence of RCTs, the quality of the study design and methodology is paramount. Factors such as sample size, blinding, and control for confounding variables influence the reliability of the study findings. A study with a small sample size may lack the statistical power to detect a true effect of the herbal treatment. Blinding ensures that neither the participants nor the researchers know who is receiving the active treatment, minimizing bias. Control for confounding variables, such as age, smoking status, and other risk factors for HPV infection, is necessary to isolate the effect of the herbal treatment. Rigorous methodology is imperative for ensuring the validity of clinical trial evidence.
- Adverse Event Monitoring
Clinical trials also play a crucial role in identifying and monitoring adverse events associated with herbal treatments. Adverse events can range from mild side effects, such as skin irritation, to more serious complications, such as allergic reactions or drug interactions. A well-designed clinical trial will include systematic monitoring for adverse events, allowing researchers to assess the safety profile of the herbal treatment. For example, a clinical trial of an oral herbal supplement for HPV infection might monitor participants for liver toxicity or gastrointestinal disturbances. Comprehensive adverse event monitoring is essential for determining the safety and tolerability of herbal interventions.
- Standardization of Herbal Preparations
The standardization of herbal preparations is a critical consideration in clinical trials. Herbal products can vary widely in their composition and potency, depending on factors such as plant species, growing conditions, and extraction methods. To ensure the reproducibility of clinical trial results, it is essential that the herbal preparation used in the study is standardized to contain a consistent level of active constituents. For example, a clinical trial of green tea extract for HPV infection should specify the concentration of epigallocatechin gallate (EGCG) in the extract. Standardization of herbal preparations is necessary for ensuring the reliability and generalizability of clinical trial findings.
In summation, the availability of well-designed and rigorously conducted clinical trials is essential for evaluating the efficacy and safety of herbal treatments for human papillomavirus infection. The presence of RCTs, sound study methodology, systematic adverse event monitoring, and standardized herbal preparations are all critical components of robust clinical trial evidence. The absence of such evidence should prompt caution and skepticism regarding claims of therapeutic benefit.
4. Preparation standardization
The consistent and reliable application of herbal treatments for human papillomavirus (HPV) is fundamentally dependent upon preparation standardization. Inconsistency in herbal product composition directly undermines the potential for reproducible therapeutic effects. Because botanical materials naturally exhibit variability due to factors such as growing conditions, harvesting techniques, and extraction processes, the active compounds within a non-standardized preparation can fluctuate significantly. This variability introduces uncertainty into treatment outcomes, hindering the ability to determine true efficacy. For instance, a preparation of Hypericum perforatum (St. John’s Wort) used to modulate mood, if not properly standardized for its hypericin content, may yield varying levels of clinical effectiveness, rendering it unreliable for consistent therapeutic results. Similarly, without standardized preparation of herbal HPV treatments, the potential for therapeutic benefit remains unpredictable.
The standardization process typically involves identifying key active constituents within the herb and ensuring a consistent concentration of these compounds in the final product. This may involve using specific extraction techniques, analytical testing to quantify the active compounds, and adjusting the preparation to meet pre-defined quality control standards. Standardized preparations allow for more accurate dosing, reducing the risk of both ineffectiveness and adverse effects. For example, a standardized extract of Camellia sinensis (green tea), with a specified concentration of epigallocatechin gallate (EGCG), used as a topical application for genital warts ensures that each application delivers a consistent amount of the antiviral compound. The standardized concentration provides a basis for correlating dosage to therapeutic outcome through clinical trials.
In conclusion, the link between preparation standardization and the effective implementation of herbal treatments for HPV virus is inextricable. Variability in herbal product composition directly undermines the potential for reproducible therapeutic effects. The establishment and adherence to rigorous standardization protocols is not merely a quality control measure but a foundational element necessary for evidence-based utilization of herbal medicine in the context of HPV management. Challenges remain in developing standardized preparations for all relevant herbs and conducting large-scale clinical trials to validate their efficacy, however it is an essential direction for future botanical treatment options.
5. Professional guidance
The incorporation of botanical remedies into the management of human papillomavirus (HPV) necessitates qualified healthcare professional guidance. The selection, dosage, and administration of herbal treatments are not without potential risks or contraindications, particularly in conjunction with conventional medical therapies. Professional oversight helps to ensure patient safety and optimize treatment strategies based on individual health profiles and HPV infection characteristics. Examples include patients using prescription medications which interact with herbal supplements.
A trained healthcare provider, possessing expertise in both conventional medicine and herbal therapies, can assess the suitability of plant-based approaches, taking into account factors such as the patient’s medical history, current medications, allergy status, and the specific type and severity of HPV infection. Such professionals can also monitor patients for adverse reactions or potential interactions between herbal treatments and conventional pharmaceutical interventions. Furthermore, professional counsel informs patients about realistic expectations regarding herbal treatments, helping to avoid the misconception that these remedies are standalone cures for HPV infection. For instance, an herbalist working alongside a gynecologist can integrate topical herbal preparations to treat HPV-related cervical dysplasia, while simultaneously monitoring the patient’s response to conventional treatments like LEEP procedures.
Ultimately, the integration of herbal therapies within an HPV management plan, conducted in the absence of professional guidance, carries potential risk and may compromise patient outcomes. Professional oversight fosters informed decision-making, minimizes the likelihood of adverse events, and ensures that botanical approaches are employed as complementary tools within a comprehensive medical strategy. The coordinated care approach improves the likelihood of successful HPV management and promotes patient well-being. Any patient using an herbal treatment without qualified and specific guidance is likely at risk of not achieving a positive outcome.
Frequently Asked Questions
The following questions and answers address common concerns and misconceptions surrounding the use of herbal treatments for human papillomavirus (HPV) infections. The information presented is intended to provide a factual overview and should not be construed as medical advice.
Question 1: Are herbal treatments proven to cure HPV infections?
The claim that herbal treatments definitively cure HPV infections lacks sufficient scientific substantiation. While some plant-derived compounds exhibit antiviral or immunomodulatory properties in laboratory studies, clinical trial evidence supporting their effectiveness in eliminating HPV infection in humans is limited. Herbal therapies may offer symptomatic relief or support immune function, but they should not be considered a replacement for conventional medical care.
Question 2: Can herbal remedies prevent the transmission of HPV?
There is no conclusive scientific evidence to suggest that herbal remedies can prevent the transmission of HPV. Safe sexual practices, such as the use of condoms, and vaccination against HPV remain the most effective strategies for reducing the risk of HPV transmission.
Question 3: Are herbal treatments for HPV safe?
The safety of herbal treatments for HPV can vary depending on the specific herbs used, the dosage, and individual patient factors. Some herbal remedies may interact with conventional medications or cause adverse side effects. It is crucial to consult with a qualified healthcare professional before using any herbal treatment, particularly if one has pre-existing medical conditions or is taking other medications.
Question 4: How can one assess the quality of herbal products marketed for HPV?
Assessing the quality of herbal products requires careful consideration. Look for products manufactured by reputable companies that adhere to Good Manufacturing Practices (GMP) and undergo third-party testing for purity and potency. Standardized herbal extracts, which contain a consistent concentration of active compounds, are generally preferred over non-standardized preparations. However, it’s important to remember that standardization alone does not guarantee efficacy.
Question 5: What are the potential risks of self-treating HPV with herbal remedies?
Self-treating HPV with herbal remedies carries several potential risks. Inaccurate self-diagnosis, delayed access to appropriate medical care, adverse drug interactions, and the use of ineffective or contaminated herbal products are all concerns. Professional oversight is essential to ensure patient safety and optimize treatment outcomes.
Question 6: Where can reliable information about herbal treatments for HPV be found?
Reliable information about herbal treatments for HPV can be obtained from peer-reviewed scientific publications, reputable medical databases, and qualified healthcare professionals. It is important to critically evaluate information from internet sources and avoid relying on anecdotal evidence or unsubstantiated claims.
In summary, while certain herbal remedies may offer potential benefits in the management of HPV infections, there is a need for further research to validate their efficacy and safety. Consultation with a qualified healthcare professional is paramount to making informed decisions about HPV treatment options.
The subsequent section will delve into the role of conventional medical interventions in the management of HPV infections.
Conclusion
This exploration has illuminated the complexities surrounding the application of hpv virus herbal treatment. It has revealed the potential for certain botanical compounds to exhibit antiviral or immunomodulatory effects, as suggested by in vitro studies and preliminary clinical investigations. The necessity of rigorous preparation standardization, accompanied by comprehensive clinical trial validation, has been underscored. Furthermore, the critical role of qualified healthcare professionals in guiding patients toward safe and effective integration of botanical strategies within conventional medical paradigms has been emphasized.
The field of hpv virus herbal treatment remains an area requiring continued scrutiny and rigorous scientific inquiry. As research progresses, a clearer understanding of the efficacy, safety, and optimal utilization of plant-based remedies in the context of HPV infection may emerge. Until such evidence solidifies, informed decision-making, in collaboration with experienced medical professionals, remains paramount for responsible and effective HPV management. Further investigation and high-quality scientific evidence are essential to definitively establish the role of botanical interventions in combating HPV infection.