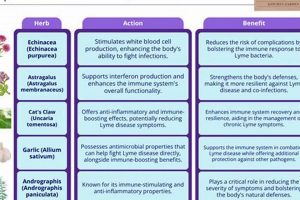
The employment of botanical remedies to alleviate fluid retention within body tissues characterizes a specific approach to managing edema. This approach encompasses the utilization of various plants and their extracts, prepared in different forms such as teas, tinctures, or topical applications, with the intention of promoting fluid balance and reducing swelling. For example, dandelion root, known for its diuretic properties, is sometimes incorporated into such remedies.
Addressing edema is crucial for maintaining overall health and comfort, as persistent swelling can impair mobility, cause discomfort, and potentially indicate underlying medical conditions. Historically, many cultures have relied on plant-based substances to manage fluid imbalances. The benefits potentially include a more natural approach to symptom management and a focus on supporting the body’s inherent regulatory mechanisms. However, thorough evaluation is necessary to ensure both safety and efficacy.
Subsequent sections will explore specific botanical options frequently discussed in connection with managing edema, their purported mechanisms of action, and considerations regarding their usage, including potential interactions with conventional medications and the importance of professional medical consultation.
Guidance on the Utilization of Botanical Remedies for Edema
The following recommendations aim to provide informative guidance for individuals considering the incorporation of plant-derived substances into their edema management strategy. These points are intended for educational purposes and should not substitute professional medical advice.
Tip 1: Prioritize Consultation with a Healthcare Professional. Before commencing any new treatment regimen, particularly one involving botanical preparations, a thorough consultation with a qualified medical practitioner is paramount. This ensures the identification of underlying causes of the edema and the assessment of potential interactions with existing medications or conditions.
Tip 2: Emphasize Identifying the Root Cause. Edema is frequently a symptom of an underlying medical condition, such as heart failure, kidney disease, or lymphatic dysfunction. Determining and addressing the primary cause is critical for effective long-term management, and relying solely on botanical remedies may delay appropriate medical intervention.
Tip 3: Exercise Caution with Diuretic Herbs. Certain botanicals possess diuretic properties, potentially increasing urine output. While this may temporarily reduce fluid accumulation, it can also lead to electrolyte imbalances and dehydration if not carefully monitored. Examples include dandelion, parsley, and juniper.
Tip 4: Understand Potential Interactions. Plant-derived substances can interact with prescription and over-the-counter medications. For instance, certain herbs may enhance or diminish the effects of blood thinners or diuretics, leading to adverse consequences. Comprehensive disclosure of all medications and supplements to a healthcare provider is crucial.
Tip 5: Source Products from Reputable Suppliers. The quality and purity of botanical products can vary significantly. Selecting products from reputable manufacturers who adhere to stringent quality control standards is essential to minimize the risk of contamination or adulteration. Look for third-party certifications where available.
Tip 6: Monitor for Adverse Reactions. Carefully observe for any adverse reactions, such as skin rashes, gastrointestinal upset, or allergic reactions, following the introduction of a new botanical preparation. Discontinue use and seek medical attention if any concerning symptoms arise.
Tip 7: Consider Lifestyle Modifications. Lifestyle adjustments, such as reducing sodium intake, elevating affected limbs, and wearing compression stockings, can complement the utilization of botanical remedies and contribute to a more comprehensive edema management plan.
These guidelines emphasize the importance of informed decision-making, professional guidance, and a holistic approach to managing edema. The responsible and evidence-based application of botanical remedies, in conjunction with conventional medical care, may contribute to improved symptom control and overall well-being.
The subsequent conclusion will summarize the key considerations discussed and reiterate the necessity of prioritizing professional medical advice in the management of edema.
1. Diuretic Properties
The presence of diuretic properties in certain plants constitutes a primary reason for their historical and contemporary use in managing edema. This characteristic, referring to the capacity of a substance to increase urine production, is central to the perceived efficacy of many botanical remedies for fluid retention.
- Mechanism of Action
Botanical diuretics exert their effect through various mechanisms, including inhibiting sodium reabsorption in the kidneys, thereby promoting water excretion. Compounds such as flavonoids, found in plants like parsley and hawthorn, are thought to contribute to this action by influencing renal tubular function. This increased urine output assists in reducing fluid volume in the extracellular spaces, alleviating edema.
- Variability in Efficacy
The diuretic potency of different plants varies considerably. While some, like furosemide, produce a pronounced and rapid effect, botanical diuretics generally exhibit a milder action. The effectiveness is further influenced by factors such as the plant species, part used (e.g., root, leaf), preparation method (e.g., infusion, extract), and individual patient factors including kidney function and concurrent medications. This variability necessitates careful monitoring and cautious use.
- Electrolyte Imbalances
Increased urine production can lead to electrolyte imbalances, particularly reductions in potassium, sodium, and magnesium levels. These imbalances can result in adverse effects, including muscle cramps, cardiac arrhythmias, and general weakness. Individuals using botanical diuretics should be monitored for electrolyte disturbances, particularly if they are also taking conventional diuretics or have underlying cardiac or renal conditions. Dietary supplementation or electrolyte monitoring may be necessary.
- Interactions and Contraindications
Botanical diuretics can interact with various medications, including antihypertensives, antiarrhythmics, and non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs). For example, using a botanical diuretic with a potassium-sparing diuretic drug could lead to hyperkalemia. Specific conditions, such as kidney disease or heart failure, may be contraindications for certain botanical diuretics. Healthcare professionals must be informed about all medications and supplements a patient is taking to avoid potentially dangerous interactions.
These facets highlight the intricate relationship between diuretic properties and their application in botanical approaches to edema management. While the promotion of fluid excretion is a desirable outcome, careful consideration of the potential risks and individual patient characteristics is essential to ensure safe and effective use. The integration of botanical diuretics should be conducted under the supervision of a qualified healthcare provider, with appropriate monitoring and adjustments as needed.
2. Underlying Condition Assessment
The effectiveness and safety of any approach to managing edema, including those involving botanical remedies, are inextricably linked to a thorough assessment of potential underlying medical conditions. Edema frequently manifests as a symptom indicative of a deeper physiological imbalance, rather than being a primary disease entity. Attempting to alleviate edema with botanical substances without identifying and addressing the root cause may provide temporary relief but fails to resolve the fundamental health issue and could potentially mask a serious, progressive condition. For instance, edema in the lower extremities might signal chronic venous insufficiency, congestive heart failure, or renal dysfunction. The administration of a diuretic herb, while reducing fluid volume, does not address the underlying circulatory or organ pathology.
A comprehensive assessment typically involves a detailed medical history, physical examination, and relevant diagnostic testing. The medical history should encompass inquiries about pre-existing conditions, medication use, dietary habits, and lifestyle factors. The physical examination includes evaluating the distribution and severity of edema, assessing vital signs, and auscultating heart and lung sounds. Diagnostic testing may involve blood tests to evaluate kidney and liver function, electrolyte levels, and cardiac biomarkers; urine analysis to assess renal protein excretion; and imaging studies such as echocardiography or Doppler ultrasound to evaluate cardiac function or venous insufficiency. Correctly identifying conditions such as deep vein thrombosis, which requires immediate medical intervention, is essential before considering any treatment regimen.
In summary, an accurate assessment of the underlying cause of edema is paramount for guiding treatment decisions and ensuring patient safety. While botanical remedies may offer symptomatic relief, they should not be employed as a substitute for addressing the primary medical condition. An integrative approach, combining conventional diagnostic methods with evidence-based botanical interventions under the supervision of a qualified healthcare professional, represents the most responsible and effective strategy for managing edema.
3. Potential Drug Interactions
The co-administration of plant-derived substances and conventional pharmaceuticals presents a risk of interactions that can significantly alter drug efficacy and safety profiles. This consideration is particularly relevant in the context of utilizing botanical remedies for edema, as individuals experiencing fluid retention may concurrently be managing underlying medical conditions with prescription medications. The mechanisms underlying these interactions are multifaceted, including alterations in drug absorption, distribution, metabolism, and excretion. For example, certain herbal constituents can inhibit or induce cytochrome P450 enzymes in the liver, which are responsible for metabolizing numerous drugs. This can lead to either increased drug levels, potentially causing toxicity, or decreased drug levels, resulting in therapeutic failure. Specific instances include interactions between warfarin, an anticoagulant, and herbs such as ginger or garlic, which possess antiplatelet effects. The combination may increase the risk of bleeding events. Similarly, concurrent use of diuretics, both conventional and botanical, can lead to additive effects, resulting in excessive electrolyte depletion and dehydration.
Understanding the potential for these interactions requires a thorough assessment of all medications and supplements a patient is taking. Healthcare professionals must inquire about botanical remedies, even if patients do not consider them “medications”. Pharmacokinetic studies investigating the effects of specific herbs on drug metabolism are often limited, creating uncertainty in predicting the magnitude and clinical significance of interactions. Resources such as drug interaction databases can provide valuable information, but clinical judgment remains essential. Monitoring for adverse effects and therapeutic response is crucial when botanical remedies are used concurrently with conventional medications. Adjustments to drug dosages may be necessary to mitigate the risk of interactions. Furthermore, patient education regarding potential symptoms of drug interactions is paramount to ensure prompt recognition and reporting of adverse events.
In summary, the potential for drug interactions represents a critical consideration when integrating herbal treatment for edema into a patient’s care plan. A comprehensive assessment of medication history, awareness of interaction mechanisms, vigilant monitoring, and patient education are essential to minimize risks and optimize therapeutic outcomes. The responsible utilization of botanical remedies necessitates a collaborative approach between patients and healthcare providers, prioritizing patient safety and evidence-based decision-making.
4. Dosage and Formulation
The therapeutic efficacy and safety of plant-derived substances in managing edema are fundamentally dependent on appropriate dosage and formulation. Deviation from established guidelines or a lack of standardized preparation methods can render a botanical remedy ineffective or, conversely, increase the risk of adverse effects. Precise attention to these factors is therefore indispensable for responsible use.
- Standardization of Extracts
The concentration of active compounds can vary significantly between different batches of the same plant species, influenced by factors such as growing conditions, harvesting methods, and processing techniques. Standardization aims to ensure consistency by quantifying the level of specific marker compounds in an extract. For instance, a hawthorn extract might be standardized to a certain percentage of flavonoids, ensuring a consistent dose of the purported active components with each administration. This reduces variability and improves the predictability of therapeutic effects.
- Appropriate Dosage Regimens
Determining the optimal dose of a botanical remedy for edema requires careful consideration of individual patient factors, including age, weight, kidney function, and concurrent medications. Dosing recommendations are often derived from traditional use, animal studies, or limited clinical trials. However, these sources may not always provide precise guidance for all patients. Initiating treatment with a lower dose and gradually increasing it until the desired effect is achieved, while monitoring for adverse reactions, represents a cautious approach. Excessive dosage can lead to electrolyte imbalances or other adverse effects, whereas insufficient dosage may result in therapeutic failure.
- Formulation and Bioavailability
The formulation of a botanical remedy significantly influences its bioavailability, which is the extent to which the active compounds are absorbed into the bloodstream and become available to exert their effects. Different formulations, such as teas, tinctures, capsules, or topical applications, exhibit varying degrees of bioavailability. For example, lipophilic compounds may be better absorbed when formulated in an oil-based extract. The particle size of a powdered herb can also affect its absorption rate. Selecting the appropriate formulation for a specific botanical and patient is crucial for optimizing therapeutic outcomes.
- Considerations for Combination Products
Many botanical remedies for edema consist of multiple herbs combined in a single product. While this approach may offer synergistic effects, it also complicates the determination of appropriate dosage and increases the risk of interactions. Each herb in the combination contributes its own set of active compounds, and their combined effects may be difficult to predict. Careful evaluation of the individual components and their potential interactions is essential when using combination products. It is prudent to start with lower doses and monitor closely for adverse reactions.
In conclusion, the selection of appropriate dosage and formulation represents a critical step in the responsible utilization of botanical substances for managing edema. Standardization of extracts, careful consideration of individual patient factors, appropriate formulation to optimize bioavailability, and cautious use of combination products are all essential elements. A collaborative approach between patients and healthcare providers, emphasizing evidence-based decision-making and vigilant monitoring, is paramount to ensure therapeutic efficacy and minimize potential risks.
5. Quality Control Standards
The efficacy and safety of herbal treatments for edema are intrinsically linked to rigorous quality control standards. Herbal remedies, derived from natural sources, are susceptible to variations in composition and contamination, necessitating stringent measures to ensure consistent product quality. The absence of such standards introduces significant risks, potentially leading to ineffective treatments or adverse health outcomes. For instance, the concentration of active compounds in a batch of dandelion extract intended to alleviate fluid retention could vary greatly depending on the plant’s growing conditions, harvest time, and extraction process. Without proper quality control, the product may contain insufficient amounts of the intended diuretic, rendering it ineffective. Conversely, the presence of heavy metals or pesticides due to inadequate sourcing or processing could pose serious health risks.
Adherence to established quality control protocols involves multiple stages, beginning with the selection of raw materials. This includes verifying the botanical identity of the plant, ensuring it is free from adulterants or contaminants, and assessing its purity. Subsequent processing steps, such as extraction, drying, and encapsulation, must also adhere to standardized procedures to maintain product integrity. Manufacturers often employ techniques such as High-Performance Liquid Chromatography (HPLC) to quantify the levels of active compounds and ensure batch-to-batch consistency. Furthermore, testing for microbial contamination, heavy metals, and pesticide residues is crucial to guarantee product safety. Real-world examples of quality control failures in the herbal supplement industry highlight the potential consequences of neglecting these standards. Instances of products being adulterated with prescription drugs or containing undisclosed allergens underscore the need for robust oversight and regulatory enforcement.
In conclusion, quality control standards are not merely an adjunct to herbal treatments for edema, but a fundamental prerequisite for their safe and effective use. These standards encompass meticulous sourcing, processing, and testing procedures designed to ensure product consistency, purity, and safety. While challenges remain in harmonizing quality control standards globally and ensuring consistent enforcement, the commitment to these principles is essential for protecting consumers and fostering confidence in the potential benefits of herbal medicine. The integration of evidence-based research with rigorous quality control practices represents a crucial step toward realizing the full potential of herbal treatments for edema while mitigating potential risks.
Frequently Asked Questions Regarding Herbal Treatment for Edema
The following addresses common inquiries and misconceptions surrounding the utilization of plant-derived substances in the management of fluid retention. The information presented is intended for educational purposes and should not substitute professional medical advice.
Question 1: Are botanical remedies a substitute for conventional medical treatment of edema?
No. Botanical remedies may offer adjunctive support in managing edema symptoms, but they are not a replacement for conventional medical evaluation and treatment. Edema often indicates an underlying medical condition requiring diagnosis and management by a qualified healthcare professional.
Question 2: What specific botanical substances are commonly associated with edema management?
Certain plants, such as dandelion (Taraxacum officinale), parsley (Petroselinum crispum), and hawthorn (Crataegus species), are traditionally used for their diuretic properties. However, their efficacy and safety vary, and their use should be guided by a healthcare provider.
Question 3: Are there potential risks associated with using herbal diuretics?
Yes. Botanical diuretics can lead to electrolyte imbalances, dehydration, and interactions with prescription medications. Monitoring by a healthcare professional is essential to mitigate these risks.
Question 4: How can the quality and purity of herbal products be assured?
Selecting products from reputable manufacturers who adhere to stringent quality control standards is crucial. Look for third-party certifications and standardized extracts to ensure consistent potency and purity.
Question 5: Can herbal remedies interact with prescription medications?
Yes. Many botanical substances can interact with prescription medications, potentially altering their efficacy or increasing the risk of adverse effects. A healthcare provider should be informed of all medications and supplements being used.
Question 6: How long does it typically take to see results from herbal treatment for edema?
The timeframe for experiencing therapeutic effects varies depending on the underlying cause of the edema, the specific botanical remedy used, and individual patient factors. Consistent monitoring and communication with a healthcare provider are essential to assess efficacy and adjust treatment as needed.
These responses emphasize the importance of responsible decision-making, professional guidance, and a comprehensive approach to managing edema. The safe and effective utilization of botanical remedies requires a collaborative effort between patients and healthcare providers, prioritizing patient safety and evidence-based care.
The following section will provide a concluding summary of key considerations and reiterate the necessity of seeking professional medical advice for edema management.
Conclusion
The preceding analysis has explored various facets of incorporating botanical remedies into the management of fluid retention. Key considerations include the potential diuretic properties of certain plants, the critical importance of assessing underlying medical conditions, the risk of drug interactions, the necessity of appropriate dosage and formulation, and the imperative for rigorous quality control standards. These factors underscore the complexities involved in utilizing plant-derived substances to address edema and highlight the need for informed decision-making.
Given the potential risks and the variability in efficacy associated with herbal treatment for edema, it is essential to emphasize the critical role of professional medical consultation. While botanical remedies may offer adjunctive support in managing edema symptoms, they should not be viewed as a substitute for conventional medical care. Individuals experiencing persistent or unexplained fluid retention are strongly advised to seek evaluation and guidance from a qualified healthcare provider to ensure accurate diagnosis and appropriate management strategies. The responsible integration of botanical approaches requires a collaborative effort between patients and healthcare professionals, prioritizing patient safety and evidence-based practices.