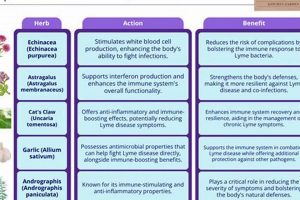
The practice involves utilizing plants and their extracts to alleviate elevated body temperatures. Specific herbs are selected for their potential antipyretic, anti-inflammatory, and immune-supporting properties. An example includes the use of willow bark, a natural source of salicin, to reduce discomfort associated with elevated temperatures.
Historically, botanical remedies have been a primary method for managing febrile conditions across diverse cultures. The benefits lie in their potential to address the underlying causes while supporting the body’s natural healing mechanisms. Their continued relevance stems from a holistic approach that considers the interconnectedness of physiological systems.
The following sections will examine specific herbal approaches, considerations for safe usage, and the importance of consulting with qualified healthcare professionals regarding their application in managing elevated temperatures.
Guidance on Botanical Approaches for Managing Elevated Temperatures
The effective utilization of botanical therapies requires careful consideration and adherence to established guidelines. This section presents key points to consider when exploring such interventions.
Tip 1: Identify the Root Cause: Elevated temperatures are often a symptom of an underlying condition. Accurately diagnosing the cause is critical before initiating any intervention, including botanical remedies.
Tip 2: Consult with a Qualified Practitioner: Seek guidance from a healthcare professional experienced in botanical medicine. This ensures appropriate selection of herbs and dosage based on individual needs and medical history.
Tip 3: Prioritize Safety and Quality: Utilize herbs sourced from reputable suppliers and thoroughly research potential interactions with existing medications or pre-existing conditions.
Tip 4: Adhere to Recommended Dosages: Strictly follow the recommended dosages provided by a qualified practitioner or as indicated on product labels. Exceeding recommended dosages can lead to adverse effects.
Tip 5: Monitor for Allergic Reactions: Be vigilant for signs of allergic reactions, such as skin rashes, itching, or difficulty breathing. Discontinue use immediately and seek medical attention if such symptoms occur.
Tip 6: Consider Age and Physiological State: The suitability of specific botanicals varies based on age, pregnancy status, and underlying health conditions. Exercise extreme caution when administering to children, pregnant women, or individuals with compromised immune systems.
Tip 7: Employ a Holistic Approach: Integrate botanical therapies with other supportive measures, such as adequate hydration, rest, and appropriate nutrition, to promote overall well-being.
The informed application of these guidelines can enhance the potential benefits while minimizing the risks associated with botanical approaches to managing elevated temperatures.
The subsequent sections will explore the scientific evidence supporting the use of specific botanicals and further considerations for their integration into comprehensive care plans.
1. Antipyretic properties identification
The identification of antipyretic properties within plant-based substances is fundamental to the rational application of botanical medicine for managing elevated body temperatures. Rigorous evaluation is required to determine the efficacy and safety of herbal treatments intended to reduce fever.
- Pharmacological Screening
Pharmacological screening involves laboratory analysis to identify compounds within plants that inhibit pyrogen-induced increases in body temperature. This often includes in vitro assays to assess the inhibition of prostaglandin synthesis, a key mechanism in fever development. For instance, assays might quantify the ability of plant extracts to inhibit cyclooxygenase (COX) enzymes, which are crucial for prostaglandin production.
- Clinical Trials
Clinical trials are essential to validate the antipyretic effects observed in vitro. These trials involve administering the herbal treatment to human subjects experiencing fever and monitoring changes in body temperature. Rigorous trial designs, including placebo controls and double-blinding, are necessary to minimize bias and establish the treatment’s true efficacy. Dosage optimization and safety monitoring are also critical components of clinical trial protocols.
- Traditional Knowledge Validation
Traditional knowledge often provides a starting point for identifying plants with potential antipyretic properties. Ethnobotanical studies document the historical use of plants for fever management in various cultures. Scientific investigation can then validate these traditional uses through pharmacological and clinical research, potentially uncovering novel therapeutic agents.
- Mechanism of Action Elucidation
Understanding the specific mechanisms by which a plant exerts its antipyretic effect is crucial. This includes identifying the active compounds responsible for the fever-reducing activity and elucidating their interactions with the body’s physiological systems. Knowing the mechanism of action allows for more targeted and rational application of the herbal treatment.
The accurate identification of antipyretic properties is not merely an academic exercise; it directly impacts the safety and effectiveness of botanical approaches. Failing to rigorously assess these properties can lead to the use of ineffective or even harmful treatments for individuals experiencing elevated body temperatures. Combining traditional knowledge with modern scientific techniques strengthens the validity of applying fever herbal treatment.
2. Dosage considerations critical
The determination of appropriate dosages is a critical facet of employing botanical remedies for elevated body temperatures. Inadequate dosages may render the treatment ineffective, while excessive amounts can induce adverse effects. Precise dosage considerations are therefore essential for ensuring both therapeutic efficacy and patient safety.
- Variability in Potency
The inherent variability in the concentration of active compounds within plant materials necessitates careful dose adjustments. Factors such as growing conditions, harvesting methods, and processing techniques can significantly influence the potency of herbal preparations. For instance, the concentration of salicin in willow bark extracts can vary widely, requiring standardized extracts and precise dosage calculations to achieve consistent antipyretic effects.
- Individual Physiological Factors
Individual physiological factors, including age, weight, metabolic rate, and hepatic and renal function, influence the pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics of herbal constituents. Pediatric and geriatric populations, in particular, require tailored dosage regimens to account for their unique physiological characteristics. For example, a smaller dose of an herbal antipyretic may be appropriate for a child compared to an adult due to differences in body weight and metabolic capacity.
- Herb-Drug Interactions
Potential interactions between herbal remedies and conventional medications necessitate careful dosage adjustments. Some herbs can inhibit or induce drug-metabolizing enzymes, altering the plasma concentrations and effects of concurrently administered drugs. For example, St. John’s Wort, known to induce CYP3A4 enzymes, could reduce the effectiveness of certain antipyretic medications if co-administered. Healthcare professionals must assess the patient’s medication profile to avoid adverse interactions.
- Route of Administration
The route of administration affects the bioavailability and onset of action of herbal antipyretics. Oral administration typically results in slower absorption and lower bioavailability compared to intravenous administration, necessitating higher dosages to achieve the desired therapeutic effect. Different preparations, such as teas, tinctures, or capsules, may also have varying bioavailability, requiring adjustments in dosage protocols.
These considerations highlight the complexity of dosage determination when employing botanical interventions for elevated temperatures. While traditional usage may offer guidance, the integration of scientific principles and individualized patient assessments is crucial for ensuring optimal outcomes and minimizing the potential for harm. Prioritizing careful dose selection ensures the overall safety and effectiveness of the intervention.
3. Herb-drug interactions awareness
The confluence of botanical remedies and conventional pharmaceuticals necessitates a heightened awareness of potential interactions, particularly when addressing elevated body temperatures. Such interactions can compromise the efficacy of either treatment modality or, more critically, induce adverse physiological responses.
- Cytochrome P450 Modulation
Many herbal constituents possess the capacity to modulate the activity of cytochrome P450 (CYP) enzymes, a critical enzyme family involved in the metabolism of numerous drugs. For example, certain compounds in feverfew, historically employed for fever reduction, can inhibit CYP3A4. This inhibition can elevate the plasma concentrations of concurrently administered drugs metabolized by CYP3A4, potentially leading to toxicity. Conversely, other herbs may induce CYP enzymes, reducing drug efficacy.
- Pharmacodynamic Synergism or Antagonism
Herbal remedies and conventional drugs may exhibit synergism or antagonism at the pharmacodynamic level. For instance, combining willow bark (containing salicin, a precursor to aspirin) with nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) could potentiate the risk of gastrointestinal bleeding due to their shared mechanism of action. Conversely, an herbal antipyretic with anti-inflammatory properties might antagonize the effects of certain immunosuppressant drugs.
- Altered Drug Absorption and Distribution
Certain herbal components can influence the absorption, distribution, metabolism, and excretion (ADME) of conventional drugs. For example, mucilaginous herbs, often used to soothe irritated tissues, can impede the absorption of orally administered medications by forming a physical barrier in the gastrointestinal tract. Similarly, some herbal constituents may compete with drugs for binding sites on plasma proteins, altering their distribution and bioavailability.
- Impact on Coagulation Pathways
Several herbs traditionally used for fever management, such as ginger and garlic, exhibit antiplatelet activity. Concurrent use of these herbs with anticoagulant or antiplatelet medications, such as warfarin or aspirin, significantly increases the risk of bleeding complications. Careful monitoring of coagulation parameters is essential in individuals receiving both herbal and conventional antithrombotic therapies.
These examples underscore the importance of thorough medication reconciliation and professional oversight when integrating botanical approaches into fever management. A comprehensive understanding of potential herb-drug interactions minimizes the risk of adverse events and ensures the safe and effective utilization of both herbal and conventional treatments.
4. Safety profile evaluation
A comprehensive safety profile evaluation is an indispensable component of employing botanical remedies for fever management. This evaluation mitigates potential risks associated with herbal interventions, ensuring that therapeutic benefits outweigh potential adverse effects. Prioritizing safety involves scrutinizing various aspects of the herbal product and its application.
- Toxicity Assessment
Toxicity assessment entails identifying potential adverse effects associated with a specific herb. This encompasses evaluating both acute and chronic toxicity through in vitro and in vivo studies. For example, certain plants traditionally used for fever may contain compounds that, in excessive doses, can induce hepatotoxicity or nephrotoxicity. Determining the lethal dose (LD50) in animal models provides critical data for establishing safe dosage ranges in humans. Thorough toxicity testing is paramount, particularly when considering vulnerable populations such as children or individuals with pre-existing hepatic or renal impairment.
- Allergenicity Testing
Allergenicity testing is crucial for identifying potential allergic reactions to herbal products. Some individuals may exhibit hypersensitivity to specific plant constituents, leading to symptoms ranging from mild skin rashes to severe anaphylaxis. Patch testing and in vitro assays can help identify potential allergens. Clear labeling regarding allergenic potential is essential to inform consumers and healthcare providers, enabling them to make informed decisions. For instance, individuals with ragweed allergies may exhibit cross-reactivity to chamomile, a commonly used herb for reducing fever-related discomfort.
- Contaminant Screening
Contaminant screening involves assessing herbal products for the presence of heavy metals, pesticides, microbial pathogens, and other contaminants. These contaminants can pose significant health risks, especially in individuals with compromised immune systems. Analytical techniques such as gas chromatography-mass spectrometry (GC-MS) and inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry (ICP-MS) are employed to detect and quantify these contaminants. Adherence to Good Manufacturing Practices (GMP) and rigorous quality control procedures minimizes the risk of contamination. Herbal products sourced from regions with lax environmental regulations may be at a higher risk of contamination, necessitating stringent screening protocols.
- Adulteration Detection
Adulteration detection focuses on identifying the presence of undeclared substances in herbal products. This includes the intentional addition of synthetic drugs or the unintentional substitution of one herb for another. Adulteration compromises the safety and efficacy of herbal remedies and can have serious health consequences. Techniques such as high-performance liquid chromatography (HPLC) and DNA barcoding are utilized to verify the authenticity and purity of herbal ingredients. Vigilant monitoring and regulatory enforcement are essential to combat the adulteration of herbal products and protect consumer safety. For example, a product labeled as containing a specific fever-reducing herb might be adulterated with a synthetic antipyretic drug, posing risks of unexpected adverse effects and masking the underlying condition.
The meticulous execution of these safety evaluations is integral to the responsible application of botanical treatments for elevated temperatures. It ensures that the benefits of herbal intervention are maximized while the potential for harm is minimized, providing healthcare professionals and patients with the assurance needed for informed decision-making. Combining both traditional knowledge and modern evaluation techniques provides the best route for integrating fever herbal treatments.
5. Professional guidance essential
The safe and effective utilization of botanical remedies for elevated body temperatures mandates professional oversight. The complexities inherent in plant-based medicine, coupled with individual physiological variations and potential interactions, necessitate the expertise of qualified healthcare practitioners.
- Accurate Diagnosis and Etiology Identification
Elevated temperatures are symptomatic, not definitive. A fever may arise from viral, bacterial, or parasitic infections, inflammatory conditions, or even malignancies. A qualified practitioner can conduct a thorough assessment to ascertain the underlying etiology, ensuring that any botanical intervention is appropriately targeted. Self-treating with botanicals without a proper diagnosis risks masking a serious condition or delaying necessary conventional medical care. For example, attempting to manage a fever stemming from a bacterial infection with solely herbal remedies, rather than antibiotics, can lead to disease progression and potentially life-threatening complications.
- Herb-Drug Interaction Mitigation
The potential for interactions between herbal remedies and prescription or over-the-counter medications necessitates careful scrutiny. A trained healthcare professional possesses the knowledge to identify and mitigate these interactions, preventing adverse effects and ensuring the safe concurrent use of different treatment modalities. For instance, an individual taking warfarin (an anticoagulant) and simultaneously consuming herbs with antiplatelet properties could experience a significantly increased risk of bleeding. A practitioner can assess these risks and recommend appropriate dosage adjustments or alternative treatment strategies.
- Dosage Optimization and Individualization
Dosage considerations for botanical remedies are not standardized and require individualized adjustments based on age, weight, physiological state, and the severity of the condition. A healthcare provider experienced in botanical medicine can tailor the dosage regimen to optimize therapeutic efficacy while minimizing the risk of adverse effects. The active compounds in plant materials vary in concentration depending on environmental factors and preparation methods, adding another layer of complexity. A professional is equipped to navigate these complexities and provide precise dosing instructions.
- Safety Monitoring and Adverse Event Management
While botanical remedies are often perceived as safe, they are not devoid of potential adverse effects. A healthcare practitioner can monitor for signs of allergic reactions, toxicity, or other adverse events and implement appropriate management strategies. This includes assessing liver and kidney function, evaluating for drug interactions, and providing supportive care. In the event of a serious adverse reaction, a professional can administer conventional medical interventions and coordinate care with other healthcare providers, ensuring patient safety.
Therefore, the application of fever herbal treatments should be undertaken with the guidance of a qualified healthcare practitioner. This ensures accurate diagnosis, appropriate treatment selection, dosage optimization, monitoring for adverse effects, and coordination of care with conventional medical approaches. This collaborative approach maximizes the potential benefits of botanical medicine while safeguarding patient well-being.
Frequently Asked Questions
This section addresses common inquiries regarding the use of botanical remedies for managing elevated body temperatures. The information presented aims to provide clarity and promote informed decision-making.
Question 1: Are botanical remedies a suitable substitute for conventional fever-reducing medications?
Botanical remedies may offer supportive care for mild to moderate elevated temperatures. However, they are not always a direct substitute for conventional medications, especially in cases of high fever or underlying serious conditions. A healthcare professional should be consulted to determine the most appropriate course of treatment.
Question 2: How can one ascertain the quality and safety of fever herbal treatment products?
The quality and safety of herbal products can be verified by seeking products from reputable manufacturers that adhere to Good Manufacturing Practices (GMP). Look for third-party certifications and ensure the product is free from contaminants and adulterants. Consult with a qualified herbalist or healthcare provider for recommendations on trusted brands.
Question 3: What are the potential risks associated with utilizing fever herbal treatment?
Potential risks include allergic reactions, herb-drug interactions, and the possibility of using ineffective treatments, delaying appropriate medical care. Certain herbs may be contraindicated for individuals with specific health conditions or those taking certain medications. Pregnant and breastfeeding women should exercise particular caution.
Question 4: How does fever herbal treatment interact with conventional medical treatments?
Interactions can occur at both the pharmacokinetic and pharmacodynamic levels. Some herbs can alter the absorption, metabolism, or excretion of conventional drugs, while others can potentiate or antagonize their effects. It is crucial to inform a healthcare provider about all herbal remedies being used to avoid adverse interactions.
Question 5: Are there specific age groups for whom fever herbal treatment is not recommended?
Certain herbal remedies may not be suitable for infants, young children, or the elderly due to their increased susceptibility to adverse effects. Dosage adjustments are often necessary, and close monitoring is essential. It is advisable to consult with a pediatrician or geriatrician before administering herbal treatments to these populations.
Question 6: How long should one use a fever herbal treatment before seeking professional medical attention?
If fever persists for more than 24-48 hours, is accompanied by severe symptoms (e.g., stiff neck, difficulty breathing, confusion), or worsens despite herbal treatment, professional medical attention should be sought immediately. Herbal remedies should not delay or replace necessary conventional medical interventions.
The judicious use of botanical remedies for managing elevated body temperatures requires a thorough understanding of their potential benefits, risks, and interactions. Collaboration with qualified healthcare providers is essential for ensuring safe and effective treatment.
The subsequent section will delve into practical considerations for integrating fever herbal treatments within a comprehensive healthcare plan.
Fever Herbal Treatment
The preceding discussion has explored various facets of botanical interventions for elevated body temperatures. Key points include the necessity of accurate antipyretic property identification, critical dosage considerations, meticulous herb-drug interaction awareness, comprehensive safety profile evaluation, and the absolute essentiality of professional guidance. These elements collectively contribute to the responsible and judicious application of plant-based remedies for fever management. The information has illuminated the complexities associated with integrating fever herbal treatments, moving beyond simplistic assumptions and emphasizing the need for informed decision-making.
Given the potential for both benefit and harm, a cautious and evidence-informed approach is paramount. Continued research, rigorous quality control standards, and collaborative dialogue between healthcare professionals and patients are crucial for optimizing the role of botanical medicine in fever management. The pursuit of knowledge and adherence to ethical practices will ensure that fever herbal treatment is implemented responsibly, ultimately contributing to enhanced patient well-being.