The application of botanical remedies to alleviate the symptoms and potentially aid in the recovery process associated with compromised nerve function constitutes a distinct approach within complementary medicine. This encompasses the utilization of plant-derived substances, often in the form of extracts, tinctures, or topical applications, with the intention of modulating inflammation, promoting nerve regeneration, and reducing neuropathic pain. An example is the use of Hypericum perforatum (St. John’s Wort) in some traditional practices for addressing nerve-related discomfort.
Historically, various cultures have integrated plant-based therapies into their healthcare systems for managing conditions involving neurological compromise. The potential advantages of employing such remedies include accessibility in certain regions, perceived lower risk of adverse effects compared to some pharmaceutical interventions (though interactions are possible and should be carefully considered), and a holistic perspective that acknowledges the interconnectedness of bodily systems. The exploration of these treatments offers a potential avenue for individuals seeking adjunct or alternative options for managing nerve-related conditions.
Subsequent sections will delve into specific botanicals frequently cited in relation to nerve health, scrutinize available scientific evidence regarding their efficacy, discuss potential mechanisms of action, and underscore the importance of consulting with qualified healthcare professionals prior to initiating any new therapeutic regimen, particularly those involving botanical substances with potential pharmacological activity.
Guidance on Botanical Approaches for Nerve Damage
The following constitutes informed guidance related to the potential use of botanical interventions for individuals experiencing nerve damage. This information is intended to augment, not replace, professional medical advice.
Tip 1: Comprehensive Medical Evaluation: Prior to considering any botanical intervention, a thorough evaluation by a qualified medical professional is paramount. Accurate diagnosis of the underlying cause of the nerve damage is crucial for effective management. Self-treating can mask symptoms and delay appropriate care.
Tip 2: Consult with a Qualified Herbalist: Seek guidance from a certified herbalist or naturopathic doctor experienced in treating neurological conditions. Such practitioners possess specialized knowledge of botanical pharmacology, potential interactions, and appropriate dosages. They can tailor recommendations to individual needs and circumstances.
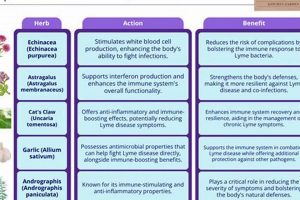
Tip 3: Research Specific Botanicals: Investigate the scientific literature pertaining to specific herbs proposed for nerve damage. PubMed, Google Scholar, and reputable botanical databases offer access to research articles and reviews. Focus on studies evaluating efficacy, safety, and potential mechanisms of action. For example, research Curcuma longa (Turmeric) for its anti-inflammatory properties.
Tip 4: Prioritize Quality and Source: Opt for high-quality botanical products from reputable sources. Third-party testing for purity, potency, and contaminants is essential. Adulteration and misidentification of herbal products are common issues. Select standardized extracts when available to ensure consistent levels of active compounds.
Tip 5: Start Low and Go Slow: Initiate botanical interventions at low doses and gradually increase as tolerated, under the guidance of a healthcare professional. This minimizes the risk of adverse reactions. Monitor symptoms closely and report any concerning changes to a healthcare provider immediately.
Tip 6: Be Mindful of Interactions: Many botanicals can interact with prescription medications, over-the-counter drugs, and other herbal supplements. Provide a complete list of all medications and supplements to healthcare providers, including herbalists. For example, Hypericum perforatum (St. John’s Wort) is known to interact with numerous medications.
Tip 7: Consider Topical Applications: Certain botanical preparations may be applied topically to address localized nerve pain. Capsaicin cream, derived from chili peppers, can provide temporary pain relief by desensitizing nerve fibers. Always perform a patch test before applying to larger areas to assess for skin sensitivity.
Tip 8: Lifestyle Modifications: Augment botanical interventions with lifestyle modifications that promote nerve health. These include maintaining a balanced diet rich in antioxidants, engaging in regular exercise, managing stress through techniques such as meditation, and avoiding neurotoxic substances such as alcohol and tobacco.
The key takeaway is that while some botanicals may offer potential benefits for managing nerve damage, their use should be approached with caution, informed by scientific evidence, and integrated within a comprehensive treatment plan supervised by qualified healthcare professionals. Potential benefits include reduced inflammation, improved nerve function, and pain relief.
The following section explores potential risks associated with pursuing unproven treatments for nerve damage.
1. Identification
Accurate identification of the specific plant species used in botanical treatments is foundational to any discussion of herbal interventions for nerve damage. Misidentification can lead to ineffective treatment at best, and toxic reactions at worst. The chemical composition, and therefore the potential therapeutic effect, varies significantly even between closely related species. For example, while several members of the Hypericum genus exist, only Hypericum perforatum (St. John’s Wort) is typically associated with nerve-related applications. Substituting a different Hypericum species could yield unpredictable, potentially harmful, results.
The importance of precise identification extends beyond the genus level. Chemotypes, which are distinct chemical varieties within the same species, can exhibit varying therapeutic properties. Consider Rosmarinus officinalis (Rosemary); different chemotypes produce essential oils with differing concentrations of active compounds like camphor, cineole, and verbenone. The selection of a rosemary chemotype for nerve regeneration, if that were the intended application, would necessitate careful consideration of its specific chemical profile. Furthermore, the stage of plant development, geographical origin, and cultivation practices can all influence the concentration of active constituents.
In summary, reliable identification of botanical remedies is not merely a technical detail; it is a critical determinant of safety and efficacy. The inherent variability within the plant kingdom necessitates rigorous quality control measures, including macroscopic and microscopic examination, chemical fingerprinting, and DNA barcoding, to ensure that the correct species and chemotype are consistently used. Ignoring the nuances of botanical identification undermines the entire premise of employing herbal treatments for nerve damage.
2. Mechanism
Understanding the mechanism of action of any therapeutic intervention is crucial, and this principle applies equally to botanical remedies targeting nerve damage. Without a reasonable hypothesis regarding how a specific herb exerts its effects, its use is largely empirical and potentially unreliable. Identifying the underlying biological pathways affected by an herb provides a rational basis for its application and allows for prediction of potential benefits and risks. For example, if an herb is believed to reduce nerve inflammation, understanding the specific inflammatory mediators it targets (e.g., cytokines, prostaglandins) is essential. If an herb is purported to enhance nerve regeneration, the relevant growth factors and signaling cascades involved in neuronal repair must be considered. The lack of mechanistic clarity poses a considerable challenge to the rational application of botanical medicine.
The challenge of elucidating mechanisms is further complicated by the multi-component nature of most herbal extracts. Unlike single-molecule pharmaceuticals, herbal preparations contain numerous compounds that may act synergistically, antagonistically, or independently. Identifying the key active constituents responsible for the observed effects, and how they interact with biological systems, requires sophisticated analytical techniques and pharmacological studies. For instance, if Curcuma longa (Turmeric) is used for its purported neuroprotective effects, it is important to determine whether curcumin, or other curcuminoids, are the primary drivers of this effect, and which specific molecular targets they engage. Similarly, when using Ginkgo biloba to improve cerebral circulation, one must understand the contribution of flavonoids, terpenoids, and other constituents to its overall effect on blood vessel tone and neuronal function.
In conclusion, while traditional use and anecdotal evidence may suggest potential benefits of herbal treatments for nerve damage, a thorough understanding of their mechanisms of action is indispensable for responsible and effective application. Future research should prioritize elucidating the molecular targets and signaling pathways affected by specific herbs, using rigorous scientific methods to validate their purported benefits. This mechanistic understanding is not only academically important but also crucial for translating traditional knowledge into evidence-based clinical practice.
3. Dosage
Dosage is a critical determinant of both the safety and efficacy of any herbal treatment, especially when addressing nerve damage. It represents the quantity of an herbal preparation administered over a specific period, influencing the therapeutic response and the potential for adverse effects. Precise dosage considerations are paramount due to the complex chemical composition of herbs and individual variations in physiological response.
- Variability in Potency
Herbal products exhibit inherent variability in the concentration of active constituents. Factors such as plant genetics, growing conditions, harvesting methods, and processing techniques all contribute to this variability. Therefore, a standardized dosage based solely on weight or volume may not accurately reflect the amount of active compounds delivered. For instance, two different preparations of Hypericum perforatum (St. John’s Wort) might contain vastly different concentrations of hypericin, the compound believed to be responsible for its antidepressant and nerve-supporting effects. Failure to account for this variability can lead to subtherapeutic doses or, conversely, doses that induce adverse reactions.
- Individual Physiological Factors
Individual factors such as age, weight, metabolism, liver and kidney function, and concurrent medications significantly influence how the body processes and responds to herbal remedies. The same dose of an herb may have profoundly different effects in different individuals. For example, an elderly individual with impaired liver function may metabolize an herb more slowly, leading to higher blood concentrations and an increased risk of adverse effects. Similarly, individuals taking medications that interact with specific herbal compounds may require dosage adjustments to avoid harmful interactions. Therefore, a one-size-fits-all dosage approach is generally inappropriate.
- Acute vs. Chronic Conditions
Dosage requirements often differ depending on whether the herbal treatment is intended for acute or chronic nerve damage. In acute situations, higher doses may be necessary to rapidly address inflammation or pain. However, long-term use of high doses can increase the risk of adverse effects. Conversely, chronic conditions may require lower, sustained doses to support nerve regeneration and reduce long-term symptoms. For example, in the acute phase of nerve compression, higher doses of anti-inflammatory herbs like Curcuma longa (Turmeric) might be used, whereas lower maintenance doses may be appropriate for long-term nerve support. Careful consideration of the duration of treatment is therefore crucial.
- Route of Administration
The route of administration (e.g., oral, topical, intravenous) influences the bioavailability of herbal constituents and therefore the effective dosage. Oral administration is the most common route, but it subjects the herb to first-pass metabolism in the liver, which can reduce its bioavailability. Topical applications bypass the liver but may have limited penetration into deeper tissues. Intravenous administration, while less common, offers the highest bioavailability but carries a greater risk of adverse reactions. The selection of the appropriate route of administration is therefore critical for optimizing dosage and minimizing potential side effects. For example, a topical cream containing capsaicin derived from Capsicum might be used to manage localized nerve pain, whereas an oral formulation of Ginkgo biloba might be chosen to improve cerebral circulation related to nerve function.
In conclusion, dosage is a nuanced and critical aspect of herbal treatment for nerve damage, demanding careful consideration of variability in potency, individual physiological factors, the acute or chronic nature of the condition, and the route of administration. Consultation with a qualified healthcare professional, preferably one with expertise in botanical medicine, is essential to determine the appropriate dosage and monitor for potential adverse effects. Accurate dosing ensures that the herbal intervention is both safe and effective, maximizing the potential for positive outcomes while minimizing risks.
4. Interactions
The potential for interactions between herbal treatments and conventional medications represents a significant concern in the context of nerve damage management. Herbal remedies are not inherently benign simply because they are derived from natural sources. They contain bioactive compounds that can interfere with the absorption, metabolism, distribution, and excretion of pharmaceutical drugs. This interference can lead to either reduced efficacy of prescribed medications or an increased risk of adverse effects. Consider, for example, an individual taking warfarin, an anticoagulant medication, to prevent blood clots associated with nerve damage complications. Concomitant use of Ginkgo biloba, which also possesses anticoagulant properties, could potentiate the effects of warfarin, leading to an increased risk of bleeding. Conversely, Hypericum perforatum (St. John’s Wort) is a known inducer of cytochrome P450 enzymes, which are responsible for metabolizing numerous drugs. Co-administration with certain anticonvulsants used to manage neuropathic pain could accelerate their metabolism, reducing their therapeutic effect.
Furthermore, herb-herb interactions are also possible. Combining different herbal remedies without a thorough understanding of their pharmacological profiles can lead to unpredictable and potentially harmful consequences. For example, combining herbs with sedative properties, such as valerian and chamomile, could result in excessive drowsiness or respiratory depression, particularly in individuals already taking medications that depress the central nervous system. The complexity of these interactions underscores the importance of comprehensive medication reconciliation, including a detailed assessment of all herbal supplements and over-the-counter drugs, before initiating any herbal treatment for nerve damage. Moreover, individuals should be advised to inform all healthcare providers involved in their care about their use of herbal remedies to ensure coordinated and safe management.
In conclusion, the potential for interactions between herbal treatments and conventional medications is a critical consideration in the management of nerve damage. A thorough understanding of the pharmacological properties of herbal remedies and their potential to interact with prescription drugs is essential to minimize risks and optimize therapeutic outcomes. Healthcare providers should proactively inquire about herbal supplement use and provide evidence-based guidance to patients to ensure safe and effective integrated care. The absence of such precautions can compromise patient safety and undermine the benefits of both conventional and complementary therapies. This highlights the importance of an interdisciplinary approach, involving physicians, pharmacists, and qualified herbalists, to manage nerve damage effectively and safely.
5. Efficacy
The evaluation of efficacy stands as a central pillar in determining the viability of botanical interventions for nerve damage. Efficacy, in this context, refers to the capacity of an herbal treatment to produce a measurable and beneficial outcome in individuals experiencing nerve-related dysfunction. Establishing efficacy necessitates rigorous scientific investigation, moving beyond anecdotal reports or traditional usage claims. Without demonstrable efficacy, the application of herbal treatments remains speculative and potentially detrimental, as it may delay or supplant evidence-based medical care. A purported benefit lacking empirical validation cannot be ethically promoted as a reliable treatment option.
The determination of efficacy involves various research methodologies, including randomized controlled trials (RCTs), which are considered the gold standard for evaluating therapeutic interventions. These trials compare the outcomes of individuals receiving the herbal treatment with those receiving a placebo or a standard medical treatment. Outcome measures may include pain reduction, improved nerve conduction velocity, enhanced motor function, or histological evidence of nerve regeneration. For example, clinical trials investigating the efficacy of Alpha-lipoic acid, while technically a supplement and not strictly an herb, in treating diabetic neuropathy have shown promising results in some studies, demonstrating significant reductions in neuropathic pain compared to placebo. Conversely, other herbs traditionally used for nerve conditions may lack such robust evidence, highlighting the critical need for continued research. The absence of well-designed RCTs makes it difficult to definitively assess the efficacy of many herbal remedies for nerve damage.
In conclusion, the assessment of efficacy is indispensable for determining the value of herbal treatments for nerve damage. While traditional knowledge and preliminary studies may provide a basis for investigation, rigorous scientific evidence from well-designed clinical trials is essential to establish whether a particular herb offers genuine therapeutic benefits. The commitment to evidence-based practice requires a cautious approach, emphasizing the importance of research to validate claims and ensure that patients receive safe and effective care. The responsible use of herbal treatments for nerve damage hinges on the ongoing pursuit of knowledge and the critical evaluation of scientific data.
6. Safety
Safety is a paramount concern when considering herbal treatments for nerve damage. The potential for adverse effects, drug interactions, and variations in product quality necessitates a cautious and informed approach. Nerve damage itself can compromise sensory perception, potentially masking early signs of adverse reactions to herbal remedies. Therefore, individuals with nerve damage may be particularly vulnerable to the risks associated with poorly regulated or inappropriately used herbal products. Examples of safety concerns include allergic reactions to specific herbs, hepatotoxicity resulting from certain botanical constituents, and exacerbation of existing medical conditions due to interactions between herbs and conventional medications. The complexity of these interactions highlights the need for meticulous evaluation of each individual’s medical history and current medication regimen before initiating any herbal treatment. Without this diligent assessment, the potential benefits of herbal remedies may be outweighed by unacceptable safety risks.
Furthermore, the inconsistent quality control standards within the herbal supplement industry pose a substantial challenge to ensuring safety. Products may be adulterated with undeclared pharmaceuticals, contaminated with heavy metals or pesticides, or misidentified, leading to unpredictable and potentially harmful effects. The absence of stringent regulatory oversight necessitates that consumers exercise caution when selecting herbal products, opting for reputable brands that subject their products to third-party testing for purity and potency. Standardized extracts, which contain a consistent concentration of active compounds, are generally preferable to crude herbal preparations, as they allow for more precise dosing and reduce the risk of variability. Despite these precautions, the potential for adverse reactions remains, underscoring the importance of close monitoring by a qualified healthcare professional.
In conclusion, safety is an indispensable component of any discussion regarding herbal treatment for nerve damage. The inherent risks associated with herbal products, including adverse effects, drug interactions, and quality control issues, necessitate a cautious and evidence-based approach. Prioritizing safety requires thorough evaluation, careful product selection, and close monitoring by a healthcare professional. The responsible use of herbal remedies for nerve damage depends on a commitment to minimizing risks and ensuring that potential benefits are not overshadowed by unacceptable safety concerns.
7. Quality
The quality of herbal products intended for nerve damage treatment directly influences their safety and efficacy. Substandard quality can arise from various factors, including improper cultivation, inadequate processing, misidentification of plant species, contamination, and the presence of adulterants. Each of these factors can compromise the therapeutic potential of the herbal remedy, potentially exacerbating the underlying nerve damage or causing adverse health outcomes. For example, an herbal product contaminated with heavy metals could introduce neurotoxic substances into the body, directly counteracting the intended therapeutic effect. Similarly, the use of an incorrect plant species, even within the same genus, can result in the absence of desired active compounds or the presence of unintended, potentially harmful constituents. The absence of rigorous quality control measures can effectively render an herbal treatment not only ineffective but also a potential health hazard.
The importance of quality extends to all stages of herbal product development, from sourcing raw materials to manufacturing and distribution. Good Agricultural and Collection Practices (GACP) are essential to ensure that plants are cultivated and harvested under conditions that optimize the concentration of active constituents and minimize the risk of contamination. Manufacturing processes should adhere to Good Manufacturing Practices (GMP) to prevent adulteration and ensure consistent product quality. Third-party testing for identity, purity, potency, and the absence of contaminants is a critical step in verifying product quality and providing consumers with confidence in the safety and efficacy of the herbal remedy. An example of the significance of these practices is the standardized extraction of Ginkgo biloba, where controlled processes ensure a consistent concentration of ginkgo flavone glycosides and terpenoids, compounds believed to contribute to its neuroprotective effects. Without such quality control, the therapeutic benefits of Ginkgo biloba could be significantly diminished.
In conclusion, quality is not merely a desirable attribute but a prerequisite for the safe and effective use of herbal treatments for nerve damage. The implementation of rigorous quality control measures throughout the entire production chain is essential to mitigate the risks associated with substandard products and ensure that consumers receive herbal remedies that are both safe and capable of delivering the intended therapeutic benefits. The practical significance of this understanding lies in empowering healthcare professionals and consumers to make informed choices about herbal products, prioritizing quality and safety to optimize treatment outcomes and minimize the potential for harm. The challenges surrounding herbal product quality underscore the need for greater regulatory oversight and increased investment in research to establish evidence-based quality standards.
Frequently Asked Questions Regarding Herbal Treatment for Nerve Damage
This section addresses common inquiries and clarifies misconceptions surrounding the use of botanical remedies for nerve damage. The information presented is intended to supplement, not replace, professional medical advice.
Question 1: Are herbal treatments a proven cure for nerve damage?
Herbal treatments are not currently recognized as a definitive cure for nerve damage. While some botanicals may offer symptomatic relief or support nerve regeneration, their efficacy varies, and they do not address the underlying cause of all forms of nerve damage. Conventional medical treatments remain the primary approach for managing many nerve-related conditions.
Question 2: Can herbal remedies completely replace conventional medical treatments for nerve damage?
The substitution of conventional medical treatments with herbal remedies is generally not advisable without the guidance of a qualified healthcare professional. Many cases of nerve damage require interventions such as medication, physical therapy, or surgery. Herbal treatments may be used as complementary therapies, but they should not be considered a replacement for standard medical care.
Question 3: Are all herbal treatments for nerve damage safe?
Not all herbal treatments are inherently safe. Some herbs can cause adverse effects, interact with medications, or be contaminated with toxins. It is essential to source herbal products from reputable suppliers and consult with a qualified herbalist or healthcare provider before using them. Individuals with pre-existing medical conditions or those taking prescription medications should exercise particular caution.
Question 4: How can the quality of herbal products be ensured?
Ensuring the quality of herbal products requires careful attention to sourcing, manufacturing processes, and third-party testing. Look for products that have been certified by independent organizations and that provide detailed information about their ingredients and manufacturing practices. Standardized extracts, which contain a consistent concentration of active compounds, are generally preferable to crude herbal preparations.
Question 5: What is the role of scientific evidence in evaluating herbal treatments for nerve damage?
Scientific evidence plays a crucial role in evaluating the efficacy and safety of herbal treatments. Randomized controlled trials (RCTs) are considered the gold standard for assessing therapeutic interventions. While some herbs have shown promising results in preclinical studies or small clinical trials, more rigorous research is often needed to confirm their benefits and identify potential risks. Evidence-based decision-making is essential when considering herbal treatments for nerve damage.
Question 6: What qualifications should a healthcare professional possess to provide guidance on herbal treatments for nerve damage?
Healthcare professionals who provide guidance on herbal treatments for nerve damage should possess expertise in both conventional medicine and botanical medicine. Qualified practitioners may include medical doctors with specialized training in integrative medicine, naturopathic doctors, or certified herbalists with extensive clinical experience. It is important to verify their credentials and ensure that they have a thorough understanding of both the potential benefits and risks of herbal remedies.
The information provided serves as a general guide and should not be interpreted as a definitive endorsement of any specific herbal treatment. Individual circumstances and medical conditions require personalized assessment and management.
The next section will present potential avenues for future research.
Conclusion
This exposition has explored the landscape of “herbal treatment for nerve damage,” examining its historical context, potential mechanisms of action, safety considerations, and the critical importance of rigorous scientific validation. The analysis underscores that while certain botanicals may offer promise in alleviating symptoms or supporting nerve regeneration, they are not universally effective, and their use necessitates careful evaluation by qualified healthcare professionals.
The field of herbal medicine remains a dynamic area of research, and continued investigation is essential to fully elucidate the potential benefits and risks associated with botanical interventions for nerve damage. A commitment to evidence-based practice, coupled with a cautious and informed approach, will be crucial in determining the role of herbal treatments in the comprehensive management of nerve-related conditions. Only through rigorous scientific inquiry can the true value of these traditional remedies be definitively established and integrated safely into contemporary healthcare practices.