The employment of botanical preparations to alleviate symptoms associated with a specific viral infection characterized by genital lesions represents an approach some individuals explore. These remedies are derived from plants and are often formulated into teas, ointments, or capsules for consumption or topical application. The intention is to reduce outbreak frequency, shorten lesion healing time, and manage discomfort stemming from the viral infection.
Throughout history, various cultures have utilized plants for their perceived medicinal properties. The potential advantages of these interventions include accessibility and perceived fewer side effects compared to conventional antiviral medications. However, it is crucial to recognize that rigorous scientific validation, in the form of randomized controlled trials, is often lacking for many of these therapies, making efficacy determination challenging. Furthermore, consistent formulation and quality control can be variable among different preparations.
Subsequent sections will delve into the specifics of several commonly cited botanical agents, examining the purported mechanisms of action, available scientific evidence, and potential risks or interactions associated with their use. This exploration seeks to provide a balanced perspective on the role of botanical remedies within the context of managing this specific viral infection.
Guidance on Botanical Approaches
The following guidance addresses the use of plant-derived substances in managing a specific viral infection. It is imperative to consult with a qualified healthcare professional before initiating any new treatment regimen.
Tip 1: Prioritize Consultation. Before initiating any botanical intervention, seek counsel from a physician or licensed herbalist. This consultation should encompass a comprehensive review of medical history, current medications, and potential contraindications.
Tip 2: Research Reputable Sources. If considering botanical preparations, procure products from reputable manufacturers that adhere to stringent quality control standards. Verify the source’s credibility and ensure proper labeling of ingredients and concentrations.
Tip 3: Adhere to Dosage Guidelines. Carefully follow the recommended dosage instructions provided by the manufacturer or healthcare practitioner. Exceeding the suggested dose may increase the risk of adverse effects.
Tip 4: Monitor for Adverse Reactions. Regularly monitor for any signs of adverse reactions, such as skin irritation, allergic responses, or gastrointestinal distress. Discontinue use immediately and seek medical attention if any concerning symptoms arise.
Tip 5: Understand Potential Interactions. Be aware that botanical agents can interact with prescription medications. Inform the healthcare provider of all supplements being taken to assess potential drug interactions.
Tip 6: Maintain a Holistic Approach. Integrate botanical approaches as part of a comprehensive management strategy that includes stress reduction techniques, immune-boosting nutrition, and antiviral medications as prescribed by a physician.
Tip 7: Document Progress. Keep a detailed record of symptoms, botanical preparations used, dosages, and any observed effects. This documentation can aid in evaluating the efficacy of the chosen approach and inform subsequent treatment decisions.
Adherence to these guidelines, in conjunction with professional medical advice, may contribute to a more informed and responsible approach to exploring plant-derived remedies. It is essential to maintain realistic expectations and prioritize evidence-based medical care.
The subsequent sections of this article will explore specific botanicals and evidence-based alternatives for this condition.
1. Symptom Management Alleviation
Symptom management alleviation, in the context of botanical interventions for a specific viral infection, focuses on employing natural compounds to mitigate the physical manifestations and associated discomforts of recurrent outbreaks. This facet encompasses a range of strategies aimed at reducing lesion severity, shortening healing duration, and easing pain.
- Pain Reduction
Certain botanical compounds possess analgesic properties that can provide localized pain relief during outbreaks. Topical applications, such as creams or ointments containing specific plant extracts, may reduce nerve sensitivity and inflammation, thereby diminishing discomfort associated with lesions. For example, preparations containing capsaicin, derived from chili peppers, may desensitize nerve endings, although caution is warranted due to potential irritation.
- Inflammation Modulation
Many botanical agents exhibit anti-inflammatory actions that can reduce swelling, redness, and heat surrounding lesions. Compounds such as flavonoids and polyphenols, found in various herbs and plants, can inhibit inflammatory pathways, potentially accelerating the resolution of outbreaks. Chamomile and calendula, for instance, are often used topically for their purported anti-inflammatory effects.
- Wound Healing Promotion
Some plants contain compounds that facilitate tissue repair and regeneration, promoting faster healing of lesions. These substances may stimulate collagen production, enhance blood flow to the affected area, or possess antimicrobial properties that prevent secondary infections. Aloe vera, known for its soothing and healing properties, is frequently applied topically to promote wound closure.
- Itch Relief
Pruritus, or itching, is a common symptom during outbreaks. Certain botanical agents can provide relief from itching by soothing irritated skin, reducing inflammation, or exerting mild anesthetic effects. Colloidal oatmeal, derived from finely ground oats, is often used in baths or creams to alleviate itchiness associated with various skin conditions, including those related to viral infections.
The integration of botanical agents for symptom management should be approached with careful consideration of individual sensitivities, potential drug interactions, and the need for rigorous scientific validation. While anecdotal evidence and traditional practices may support the use of certain plant-derived substances, consultation with a healthcare professional is essential to ensure safe and effective implementation alongside conventional antiviral therapies.
2. Immune System Modulation
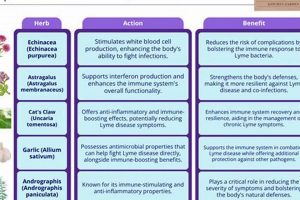
The interaction between botanical remedies and the immune system is a critical consideration within the context of managing a specific viral infection. A robust immune response is essential for controlling viral replication and reducing the frequency and severity of outbreaks. Certain botanical compounds are purported to possess immunomodulatory properties, meaning they can influence the activity of various immune cells and signaling pathways. For example, some herbs are believed to stimulate the production of interferon, a cytokine that inhibits viral replication. Others may enhance the activity of natural killer cells, which target and destroy virus-infected cells. However, it is crucial to recognize that the exact mechanisms and efficacy of these interventions are often not fully elucidated and require further investigation. The variable composition of herbal preparations and individual differences in immune function can influence the observed effects.
Real-world examples highlight the complexities of immune modulation. Echinacea, for instance, is commonly used to support immune function during upper respiratory infections. Some in vitro studies suggest that Echinacea extracts can stimulate the production of cytokines and enhance phagocytosis by macrophages. However, the effects of Echinacea on viral infections are less clear, and clinical trials have yielded mixed results. Similarly, Astragalus is a traditional Chinese medicine herb believed to possess immunostimulatory properties. Studies have shown that Astragalus can enhance the activity of T cells and natural killer cells, but the impact on viral infections requires further research. It’s necessary to underscore that stimulating the immune system indiscriminately can be detrimental; in certain cases, it can exacerbate inflammatory responses and potentially worsen symptoms.
In summary, while the concept of utilizing botanical agents to modulate the immune system in the context of managing a viral infection holds promise, a cautious and evidence-based approach is warranted. Rigorous scientific studies are necessary to determine the specific mechanisms of action, optimal dosages, and potential risks associated with these interventions. Moreover, a comprehensive management strategy should integrate conventional antiviral therapies, lifestyle modifications, and close monitoring by a healthcare professional to ensure optimal outcomes.
Antiviral properties research constitutes a foundational pillar in evaluating the potential efficacy of botanical interventions for herpes simplex virus type 2 (HSV-2) infection. The investigation into these properties seeks to identify and characterize plant-derived compounds that can directly inhibit viral replication, prevent viral entry into host cells, or disrupt other essential stages of the viral life cycle. This research is essential because anecdotal evidence or traditional use alone is insufficient to establish clinical effectiveness or safety. Without rigorous scientific investigation, the purported benefits of botanical remedies remain speculative.
The process typically begins with in vitro studies, where plant extracts or isolated compounds are tested against HSV-2 in cell cultures. Researchers assess parameters such as viral plaque formation, viral load reduction, and cell viability to determine the antiviral activity of the substance. If promising results are observed in vitro, the next step often involves in vivo studies, typically using animal models, to evaluate the compound’s effectiveness in a living organism. These studies consider factors such as bioavailability, toxicity, and the ability to reduce viral shedding or lesion severity. For instance, research on Melissa officinalis (lemon balm) has demonstrated antiviral activity against HSV-2 in vitro, and some clinical trials have suggested that topical application of lemon balm cream may reduce the duration and severity of herpes outbreaks. However, more extensive research is needed to confirm these findings and elucidate the underlying mechanisms.
Ultimately, the integration of rigorous antiviral properties research is crucial for translating traditional herbal practices into evidence-based therapeutic strategies. It provides a scientific basis for understanding how botanical remedies may impact HSV-2 infection and guides the development of safe and effective treatments. While botanical interventions may offer potential benefits, it is imperative to approach them with caution and prioritize evidence-based medical care. Further investigation is needed to clarify the role of botanical agents in the comprehensive management of HSV-2.
4. Safety Profile Assessment
A thorough safety profile assessment is paramount when considering botanical interventions for the management of herpes simplex virus type 2 (HSV-2). Given the potential for adverse effects and interactions with conventional treatments, a comprehensive understanding of the risks associated with these remedies is essential for informed decision-making.
- Potential for Adverse Reactions
Botanical preparations, while often perceived as natural and harmless, can elicit adverse reactions in some individuals. These reactions may range from mild skin irritation to severe allergic responses. For example, topical application of certain essential oils, such as tea tree oil, can cause contact dermatitis in sensitive individuals. Internal use of some herbs may lead to gastrointestinal distress, liver toxicity, or other systemic effects. The variability in the composition of botanical products, due to factors such as plant source, growing conditions, and manufacturing processes, further complicates the assessment of potential adverse reactions.
- Drug Interactions
Botanical remedies can interact with prescription medications, potentially altering their efficacy or increasing the risk of side effects. Some herbs can inhibit or induce cytochrome P450 enzymes, which are responsible for metabolizing many drugs. For instance, St. John’s Wort, a commonly used herb for depression, is known to interact with antiviral medications used to treat HSV-2, potentially reducing their effectiveness. Patients must disclose all herbal supplements to their healthcare providers to identify potential drug interactions and adjust treatment plans accordingly.
- Quality Control and Standardization
The lack of stringent quality control and standardization in the herbal product industry poses a significant challenge to safety assessment. Unlike pharmaceutical drugs, herbal remedies are often not subject to rigorous testing for purity, potency, and consistency. This can lead to variations in product composition and the presence of contaminants, such as heavy metals or pesticides. Consumers should seek products from reputable manufacturers that adhere to good manufacturing practices (GMP) and undergo third-party testing to ensure quality and safety.
- Contraindications and Special Populations
Certain botanical remedies may be contraindicated in specific populations, such as pregnant or breastfeeding women, children, and individuals with pre-existing medical conditions. For example, some herbs may have abortifacient effects or pose risks to fetal development. Individuals with liver or kidney disease may be more susceptible to adverse effects from herbal products. A healthcare professional can assess individual risk factors and provide guidance on the safe use of botanical remedies.
Integrating the elements of the safety profile assessment into the selection and use of botanical treatments for HSV-2 supports a more informed strategy. It emphasizes the significance of careful assessment, professional medical advice, and the selection of products from reliable sources to minimize risks and maximize potential benefits.
5. Drug Interaction Awareness
Drug interaction awareness represents a critical aspect of integrating botanical remedies into the management of herpes simplex virus type 2 (HSV-2) infection. The potential for interactions between herbal constituents and conventional antiviral medications poses a tangible risk to patient safety and treatment efficacy. A failure to recognize and address these interactions can lead to diminished therapeutic effects, increased adverse drug reactions, or unpredictable pharmacological outcomes. The complexity arises from the diverse chemical compounds present in herbal preparations and their capacity to influence various drug metabolism pathways.
One prominent mechanism of interaction involves the cytochrome P450 (CYP) enzyme system, a family of enzymes responsible for metabolizing a wide range of drugs. Certain herbal constituents can either inhibit or induce CYP enzymes, altering the rate at which antiviral medications are processed by the body. For instance, St. John’s Wort, a well-known herbal antidepressant, is a potent inducer of CYP3A4, an enzyme that metabolizes several antiviral drugs, including some used to treat HSV-2. This induction can lead to a reduction in the plasma concentration of the antiviral medication, potentially compromising its effectiveness. Conversely, other herbs may inhibit CYP enzymes, leading to elevated drug levels and an increased risk of toxicity. These interactions are not always predictable, as they can vary depending on individual factors, the specific herbal product used, and the dosage.
Consequently, a comprehensive assessment of potential drug interactions is essential before initiating any botanical intervention in individuals undergoing antiviral therapy for HSV-2. This assessment should involve a thorough review of all medications and supplements the patient is taking, followed by consultation with a healthcare professional or pharmacist with expertise in drug interactions. Implementing rigorous monitoring protocols and adjusting medication dosages as necessary can help mitigate the risks associated with these interactions and ensure the safe and effective use of both conventional and botanical treatments. Ultimately, patient safety and optimal therapeutic outcomes should be the guiding principles in integrating herbal remedies into HSV-2 management.
Frequently Asked Questions
The following section addresses common inquiries regarding the use of botanical remedies in the context of managing herpes simplex virus type 2 (HSV-2). The information presented is intended to provide a balanced perspective and should not be interpreted as medical advice. Consultation with a qualified healthcare professional is always recommended.
Question 1: Are botanical preparations a substitute for conventional antiviral medications in treating HSV-2?
Botanical preparations are generally not considered a substitute for conventional antiviral medications in the treatment of HSV-2. Antiviral medications, such as acyclovir, valacyclovir, and famciclovir, have undergone rigorous clinical trials and are proven effective in suppressing viral replication and reducing the frequency and severity of outbreaks. Botanical remedies may offer adjunctive support for symptom management, but their antiviral efficacy is often less well-established.
Question 2: What is the scientific evidence supporting the use of botanical remedies for HSV-2?
The scientific evidence supporting the use of botanical remedies for HSV-2 varies widely. Some herbs have demonstrated antiviral activity against HSV-2 in vitro, but these findings do not always translate to clinical efficacy in humans. Clinical trials evaluating the effectiveness of botanical remedies for HSV-2 are often limited in size, scope, and methodological rigor. Further research is needed to determine the specific mechanisms of action, optimal dosages, and potential risks associated with these interventions.
Question 3: Are botanical preparations safe to use alongside conventional antiviral medications?
The safety of using botanical preparations alongside conventional antiviral medications is a concern due to the potential for drug interactions. Some herbs can interfere with the metabolism or absorption of antiviral drugs, potentially altering their effectiveness or increasing the risk of side effects. Individuals considering combining botanical remedies with antiviral medications should consult with a healthcare professional to assess potential drug interactions and ensure safe use.
Question 4: How should botanical preparations be chosen and used for HSV-2?
The selection and use of botanical preparations for HSV-2 should be guided by evidence-based information and professional medical advice. Individuals should seek products from reputable manufacturers that adhere to good manufacturing practices (GMP) and undergo third-party testing to ensure quality and purity. It is essential to follow recommended dosage guidelines and monitor for any adverse reactions. Furthermore, communication with a healthcare provider about all supplements being taken is crucial to prevent potential drug interactions.
Question 5: What are the potential risks associated with botanical remedies for HSV-2?
The potential risks associated with botanical remedies for HSV-2 include allergic reactions, skin irritation, gastrointestinal distress, liver toxicity, and drug interactions. Some herbs may be contraindicated in certain populations, such as pregnant or breastfeeding women, children, and individuals with pre-existing medical conditions. The lack of standardization in herbal products can also lead to variations in potency and the presence of contaminants.
Question 6: Where can reliable information about botanical remedies for HSV-2 be found?
Reliable information about botanical remedies for HSV-2 can be found through reputable sources such as the National Center for Complementary and Integrative Health (NCCIH), the National Institutes of Health (NIH), and peer-reviewed scientific publications. Consultation with a healthcare professional or licensed herbalist can also provide valuable guidance.
In summary, while botanical remedies may offer potential benefits for symptom management in HSV-2, they are not a substitute for conventional antiviral medications. Thorough research, careful selection of products, and consultation with a healthcare professional are essential to ensure safe and effective use.
The next section will provide resources to find more about herbal medicine.
Conclusion
The utilization of botanical interventions for herpes simplex virus type 2 (HSV-2) necessitates careful consideration of evidence-based research, potential risks, and the limitations of current knowledge. While certain plant-derived substances may offer palliative effects, they should not be regarded as a replacement for conventional antiviral therapies. A thorough assessment of individual health conditions, potential drug interactions, and product quality is crucial before incorporating any botanical remedy into a treatment regimen. The current landscape of scientific evidence warrants caution, emphasizing the importance of informed decision-making in the management of this persistent viral infection.
Future research should prioritize rigorous clinical trials to elucidate the efficacy and safety of specific botanical compounds for HSV-2. Improved standardization and quality control measures are essential to ensure product consistency and minimize the risk of adverse events. Individuals seeking “herbal treatment for herpes 2” should engage in open communication with healthcare providers to develop a comprehensive management plan that integrates both conventional and complementary approaches, based on the best available evidence. A proactive and informed approach is paramount in navigating the complexities of managing this condition.