Onychomycosis, a fungal infection affecting the nail, is a common condition that can cause discoloration, thickening, and crumbling of the nail. Some individuals seek alternative approaches to manage this infection, exploring the potential of plant-derived remedies. These remedies encompass a range of botanical extracts and compounds believed to possess antifungal properties.
The appeal of utilizing botanicals lies in their perceived natural origin and, for some, a potential for fewer side effects compared to conventional pharmaceutical treatments. Throughout history, various cultures have incorporated plants into their healthcare practices. The exploration of botanicals for nail conditions aligns with a broader interest in complementary and alternative medicine. The benefit of this approach focuses on naturally and traditionally known process.
The subsequent sections will delve into specific herbal remedies commonly discussed for managing nail infections, examining available evidence regarding their efficacy, appropriate usage, and potential interactions or contraindications. Consideration will be given to the importance of consulting healthcare professionals before initiating any alternative treatment regimen.
Guidance on Botanical Approaches to Onychomycosis
The subsequent recommendations are presented to offer informational insights into the potential application of plant-derived substances for managing nail infections. Adherence to established medical protocols and consultation with qualified healthcare providers remain paramount.
Tip 1: Initial Consultation. Prior to initiating any botanical remedy, secure a definitive diagnosis of onychomycosis from a medical professional. Self-diagnosis may lead to inappropriate treatment and potential complications.
Tip 2: Rigorous Hygiene Practices. Maintain meticulous foot hygiene. This includes regular washing with soap and water, thorough drying, and frequent changes of socks, particularly in cases of excessive perspiration.
Tip 3: Diligent Application. When applying any topical botanical preparation, ensure the affected nail and surrounding skin are clean and dry. Follow the specific instructions provided by the product manufacturer or healthcare provider.
Tip 4: Consistent Treatment Duration. Botanical remedies may require extended periods of consistent application to achieve noticeable results. Adherence to the recommended treatment duration is crucial for assessing efficacy.
Tip 5: Monitoring for Adverse Reactions. Closely observe the treated area for any signs of adverse reactions, such as redness, irritation, or allergic responses. Discontinue use immediately and consult a healthcare professional if such reactions occur.
Tip 6: Addressing Underlying Conditions. Certain medical conditions, such as diabetes or peripheral vascular disease, can increase susceptibility to nail infections. Ensure appropriate management of any underlying health conditions.
Tip 7: Preventative Measures. Implement preventative measures to minimize the risk of recurrence, including wearing breathable footwear, avoiding prolonged exposure to moisture, and refraining from sharing personal grooming tools.
These guidelines are designed to promote informed decision-making regarding the potential use of botanical substances for nail infections. However, they are not intended to substitute for professional medical advice or treatment.
The concluding section will summarize key considerations and reiterate the importance of integrated medical management for onychomycosis.
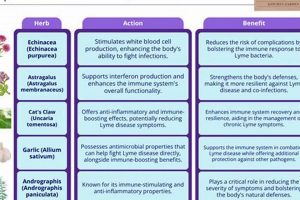
1. Antifungal Properties
The efficacy of plant-derived remedies for nail fungal infections, hinges fundamentally on their inherent antifungal properties. The presence of compounds exhibiting activity against dermatophytes, the primary causative agents of onychomycosis, is the core mechanism by which such botanicals exert their influence. Without demonstrable antifungal activity, the application of any herbal substance would be ineffective against the underlying infection. For example, tea tree oil, often cited in discussions of botanical treatments for nail fungus, contains terpinen-4-ol, a compound shown in some in vitro studies to inhibit the growth of certain fungi. This observed inhibition highlights the critical role of antifungal properties in the potential success of botanical interventions.
The concentration and bioavailability of these antifungal compounds are crucial determinants of their practical effectiveness. Even if a botanical extract possesses antifungal properties in laboratory settings, its ability to penetrate the nail plate and reach the site of infection in sufficient concentrations remains a challenge. Furthermore, the specific spectrum of activity is important; a compound effective against one species of dermatophyte may not be effective against another. The varied etiology of onychomycosis, involving multiple fungal species, underscores the need for a broad-spectrum antifungal agent or a combination of agents.
Ultimately, the significance of antifungal properties in botanical treatments for nail fungus resides in their potential to disrupt fungal growth and eradicate the infection. However, demonstrating this potential requires rigorous scientific validation through well-designed clinical trials. While anecdotal evidence and in vitro studies may suggest promise, definitive conclusions regarding efficacy necessitate robust data supporting the ability of these compounds to effectively combat nail fungal infections in real-world clinical scenarios. The challenge lies in translating observed antifungal activity into tangible clinical benefits.
2. Delivery Mechanisms
The effectiveness of botanical treatments for onychomycosis is significantly influenced by the chosen delivery mechanism. The nail plate presents a formidable barrier to topical applications, necessitating strategies that enhance penetration of antifungal compounds to the site of infection. Consequently, the selection and optimization of delivery methods are crucial for maximizing the therapeutic potential of plant-derived remedies. Inadequate penetration will render even potent antifungal substances ineffective, as they will fail to reach the fungal pathogens residing within the nail structure and bed. For instance, simply applying a botanical extract in its raw form may prove insufficient due to its limited ability to permeate the dense keratin matrix of the nail.
Various delivery mechanisms have been explored to improve the penetration of topical antifungal agents, including those derived from botanical sources. These methods include the use of penetration enhancers, such as urea or lactic acid, which can disrupt the nail structure and facilitate drug transport. Additionally, formulations incorporating liposomes or nanoparticles are being investigated for their potential to encapsulate and deliver antifungal compounds directly to the site of infection. Iontophoresis, a technique employing electrical current to enhance drug penetration, also represents a promising approach. The selection of an appropriate delivery mechanism should be based on the specific characteristics of the botanical extract, the severity of the infection, and individual patient factors. The choice of vehicle, whether an oil, cream, or lacquer, will also impact the amount of active ingredient delivered.
The development and refinement of effective delivery mechanisms remain a critical area of research in the field of botanical treatments for onychomycosis. Overcoming the barrier posed by the nail plate is essential to ensuring that antifungal compounds reach therapeutic concentrations at the site of infection. Future advances in nanotechnology and transdermal drug delivery may offer novel solutions for enhancing the penetration and efficacy of plant-derived remedies. However, further studies are needed to validate the clinical effectiveness of these advanced delivery systems and to determine their long-term safety and tolerability. The efficacy of “nail fungus herbal treatment” is therefore reliant not solely on the selection of an appropriate herb, but also on the method by which it is delivered.
3. Treatment Duration
Treatment duration represents a critical factor in the context of herbal remedies for onychomycosis. Unlike many conventional pharmaceutical treatments that offer relatively shorter courses, botanical approaches often necessitate prolonged and consistent application to achieve tangible results. This extended timeframe is inherently linked to the mechanisms of action and bioavailability of the active compounds within the herbal substances.
- Slower Mechanism of Action
Botanical remedies typically exhibit a slower mechanism of action compared to synthetic antifungal drugs. The active compounds in herbs often require a longer period to penetrate the nail plate, reach the site of infection, and exert their antifungal effects. This slower pace necessitates a sustained commitment to the treatment regimen. Examples include the gradual inhibition of fungal growth by tea tree oil or the slow disruption of fungal cell walls by constituents of garlic extract.
- Nail Growth Rate
The inherent growth rate of the nail is a significant determinant of treatment duration. Infected nail tissue must be gradually replaced by healthy, fungus-free nail growth. Since nails grow slowly, particularly toenails, even with effective antifungal treatment, the affected portion needs time to grow out completely. This process can take several months to over a year, regardless of the treatment modality employed, with herbal remedies being no exception.
- Lower Bioavailability
Herbal formulations often exhibit lower bioavailability compared to conventional drugs. The active compounds may not be as readily absorbed or reach therapeutic concentrations at the site of infection. To compensate for this lower bioavailability, prolonged and frequent application is typically required. The formulation itself, be it an oil, cream, or lacquer, also influences bioavailability and, consequently, the necessary treatment duration.
- Compliance Challenges
The extended treatment duration associated with many botanical approaches presents a significant challenge to patient compliance. Adherence to the prescribed regimen over several months can be difficult, and inconsistent application may compromise the efficacy of the treatment. Clear communication and realistic expectations are crucial to ensure patients remain committed to the treatment for the necessary duration. This also requires managing expectations about the speed and degree of improvement during the process.
In conclusion, treatment duration is an integral component of herbal management strategies for onychomycosis. The interplay between the slower mechanism of action, nail growth rate, potentially lower bioavailability, and challenges in patient compliance underscores the need for a realistic and long-term perspective when considering botanical remedies. Success relies heavily on patient education, meticulous application, and sustained commitment to the prescribed regimen.
4. Potential Interactions
The use of botanical remedies for onychomycosis necessitates careful consideration of potential interactions, both with concurrently administered medications and with pre-existing medical conditions. Such interactions can either diminish the efficacy of the herbal treatment, exacerbate its adverse effects, or interfere with the management of underlying health issues. Therefore, a comprehensive understanding of these potential interactions is paramount to ensuring patient safety and optimizing therapeutic outcomes. For instance, certain herbal supplements, such as St. John’s Wort, are known to induce hepatic enzymes, potentially reducing the effectiveness of antifungal medications prescribed for systemic fungal infections. Although St. John’s Wort is typically not used for topical nail fungus treatments, this illustrates a general risk: always consider the patient’s concurrent medications.
The constituents of herbal remedies can exhibit diverse pharmacological effects, some of which may directly counteract or amplify the effects of conventional medications. For example, garlic, often touted for its antifungal properties, also possesses anticoagulant effects. The concurrent use of garlic supplements with anticoagulant medications, such as warfarin, could increase the risk of bleeding. Similarly, individuals with diabetes who are using herbal remedies to treat nail fungus should be particularly vigilant for potential interactions with antidiabetic medications. Certain herbs may affect blood glucose levels, potentially requiring adjustments to insulin dosages or other diabetes management strategies. This highlights the importance of a thorough patient history and careful monitoring when integrating herbal therapies into existing treatment regimens. It’s not only other medication but the pre-existing conditions that could create interactions.
In summary, the potential for interactions represents a significant consideration when using herbal treatments for onychomycosis. Healthcare professionals must meticulously assess patients’ medication lists, pre-existing conditions, and allergy history to identify potential risks. Clear communication with patients regarding the importance of disclosing all medications and supplements is essential. While herbal remedies may offer a complementary approach to managing nail fungus, their use should be guided by evidence-based practices and integrated with a comprehensive understanding of potential interactions to ensure patient safety and optimize therapeutic outcomes. The consideration of potential interactions is not merely a precautionary step, but an indispensable component of responsible “nail fungus herbal treatment.”
5. Clinical Evidence
The domain of botanical remedies for onychomycosis is fundamentally contingent upon the availability and rigor of clinical evidence. This evidence, derived from well-designed and controlled studies, serves as the cornerstone for evaluating the efficacy and safety of plant-derived treatments. In its absence, the use of botanicals remains largely speculative, based on anecdotal reports or in vitro data that may not translate to real-world clinical settings. The presence of robust clinical data establishes a causal link between the herbal intervention and its purported effect on nail fungal infections, providing a scientifically sound rationale for its application. Without clinical proof, the effect of “nail fungus herbal treatment” is uncertain.
The importance of clinical evidence stems from the need to differentiate between genuine therapeutic effects and placebo responses or spontaneous remission. Rigorous clinical trials, employing methodologies such as randomized controlled trials (RCTs), are essential for minimizing bias and confounding factors. Such trials typically involve comparing the botanical treatment to a placebo or to a standard antifungal medication, assessing outcomes such as mycological cure rates, clinical improvement, and adverse effects. Real-life examples illustrate the consequences of relying on unsubstantiated claims. The promotion of certain herbal remedies without adequate clinical backing has, in some instances, led to patient disappointment, delayed access to effective treatments, and potential harm from adverse reactions. Conversely, research demonstrating efficacy in certain herbal compounds offers opportunities for evidence-based application. For example, some studies exploring the use of tea tree oil and certain other botanicals have shown the potential for efficacy; the practical significance being that this knowledge encourages further research and informs clinical decision-making, guiding patients towards options that have shown potential and away from those lacking proper evaluation.
In summary, the integration of clinical evidence into the realm of nail fungal infections is essential for establishing the credibility and utility of botanical approaches. The challenges lie in conducting high-quality research that meets stringent scientific standards, accounting for factors such as variations in herbal product formulations, diverse patient populations, and long-term follow-up. Moving forward, the pursuit of robust clinical evidence remains paramount for validating the therapeutic potential of botanical remedies and ensuring their responsible application in the management of onychomycosis, thereby contributing to the overall standard of care and the improvement of patient outcomes. As such, the value and impact of “nail fungus herbal treatment” are directly linked to the quality of available evidence.
Frequently Asked Questions Regarding Nail Fungus Herbal Treatment
The subsequent questions address common inquiries and misconceptions pertaining to botanical remedies for onychomycosis. These responses are intended to provide clear, evidence-based information to guide informed decision-making.
Question 1: Is nail fungus herbal treatment a definitive cure for onychomycosis?
Botanical remedies may offer potential benefits in managing onychomycosis, definitive cure rates can vary significantly. The efficacy often depends on factors such as the severity of the infection, the specific botanical agent used, and individual patient characteristics. Consultation with a healthcare professional is essential for accurate diagnosis and personalized treatment recommendations.
Question 2: How long does it typically take to see results with nail fungus herbal treatment?
Results with botanical treatments are often gradual, requiring consistent application over extended periods. The timeframe for noticeable improvement can range from several months to a year or more, contingent upon nail growth rate and the effectiveness of the chosen remedy. Patience and adherence to the prescribed regimen are crucial.
Question 3: Are there any potential side effects associated with nail fungus herbal treatment?
While generally considered safe, botanical remedies can cause side effects in some individuals. These may include skin irritation, allergic reactions, or interactions with other medications. A thorough review of potential risks with a qualified healthcare provider is essential before initiating treatment.
Question 4: Can nail fungus herbal treatment be used in conjunction with conventional antifungal medications?
The concurrent use of botanical remedies with conventional antifungal medications should be approached with caution and under the guidance of a healthcare professional. Potential interactions and contraindications must be carefully evaluated to ensure patient safety and optimize therapeutic outcomes.
Question 5: How does one ensure the quality and purity of nail fungus herbal treatment products?
The quality and purity of herbal products can vary significantly. It is recommended to purchase products from reputable manufacturers that adhere to stringent quality control standards. Look for certifications or third-party testing to ensure product authenticity and safety.
Question 6: Is nail fungus herbal treatment appropriate for all types of nail infections?
Botanical remedies may not be suitable for all types of nail infections. Certain fungal species may be more resistant to herbal treatments than others. A definitive diagnosis from a healthcare professional is essential to determine the most appropriate treatment approach.
The information provided here is intended for general knowledge and informational purposes only, and does not constitute medical advice. Consultation with a qualified healthcare professional is always recommended for personalized guidance and treatment recommendations.
The subsequent section will summarize the key considerations discussed within this article.
Conclusion
This exploration of “nail fungus herbal treatment” has underscored the complex interplay of factors influencing its potential efficacy. The presence of antifungal properties, the effectiveness of delivery mechanisms, the duration of treatment, potential interactions with other substances, and the underlying support of clinical evidence are all critical determinants. The application of plant-derived substances requires a meticulous and informed approach, grounded in scientific rigor and patient-specific considerations. Understanding that botanicals are not universally effective and are not a substitute for professional diagnosis is essential.
The judicious use of herbal remedies in managing onychomycosis demands ongoing research and critical evaluation. While certain botanical compounds may hold promise, their integration into mainstream treatment protocols necessitates a commitment to evidence-based practices and a clear understanding of their limitations. As research continues, healthcare professionals and patients alike must prioritize patient safety, realistic expectations, and informed decision-making when considering “nail fungus herbal treatment” as part of an integrated approach to care. Further exploration is needed to determine optimal formulations, delivery methods, and treatment durations, ensuring the safe and effective application of plant-derived remedies for onychomycosis.