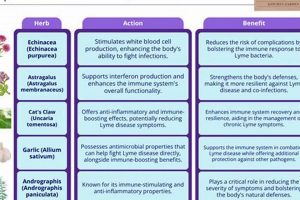
The utilization of botanical remedies to alleviate the discomfort associated with nerve damage affecting the extremities represents a growing area of interest. This approach focuses on leveraging the inherent properties of plants to potentially mitigate symptoms such as pain, numbness, and tingling. For example, specific plant-derived compounds may exhibit anti-inflammatory or analgesic effects, which could provide relief to individuals experiencing nerve-related discomfort in their hands and feet.
The appeal of this methodology lies in its potential to offer a more natural alternative to conventional pharmaceutical interventions. Throughout history, various cultures have incorporated plant-based medicines into their healing practices. The potential advantages include a reduced risk of adverse side effects compared to some prescription medications and the possibility of addressing the underlying causes of nerve dysfunction. This approach aims to support nerve regeneration and improve overall nerve health.
The subsequent sections will delve into specific botanicals commonly considered for this purpose, examining their proposed mechanisms of action and the available scientific evidence supporting their use. Further discussion will highlight critical considerations for individuals contemplating this approach, including potential interactions with other medications and the importance of consulting with qualified healthcare professionals to ensure safe and effective implementation.
Guidance on Botanical Approaches for Nerve Discomfort
The following recommendations are intended to provide information regarding the use of botanical remedies in the context of nerve-related discomfort. It is crucial to consult with qualified healthcare professionals before initiating any new treatment regimen.
Tip 1: Prioritize Professional Consultation: Before incorporating any herbal remedy, a thorough evaluation by a physician or qualified healthcare provider is essential to determine the underlying cause of nerve discomfort and to assess potential interactions with existing medications.
Tip 2: Research Reputable Sources: Gather information from reliable and evidence-based sources regarding the specific botanical under consideration. This includes understanding its purported mechanism of action, potential side effects, and any documented contraindications.
Tip 3: Understand Dosage and Preparation: Adhere strictly to recommended dosages and preparation methods. Herbal remedies can vary significantly in potency, and improper use may lead to adverse effects or reduced efficacy. Standardization is crucial.
Tip 4: Monitor for Adverse Reactions: Carefully observe for any signs of adverse reactions following the introduction of a botanical remedy. Discontinue use immediately and seek medical attention if any concerning symptoms arise.
Tip 5: Consider Potential Interactions: Be aware that herbal remedies can interact with prescription medications, over-the-counter drugs, and other supplements. A comprehensive review of all current medications and supplements is necessary.
Tip 6: Emphasize a Holistic Approach: Botanical remedies should be viewed as part of a broader, comprehensive treatment plan. This may include dietary modifications, physical therapy, and other supportive therapies.
Tip 7: Temper Expectations: While some individuals may experience benefits from botanical interventions, it is crucial to maintain realistic expectations. The efficacy of herbal remedies can vary widely, and results are not guaranteed.
This information aims to promote informed decision-making regarding the exploration of botanical options. It is not a substitute for professional medical advice, diagnosis, or treatment.
The subsequent discussion will explore particular botanical options and their supporting scientific evidence.
1. Anti-inflammatory properties
The reduction of inflammation represents a critical target in the management of nerve dysfunction. Nerve damage frequently triggers an inflammatory cascade, exacerbating pain and hindering nerve repair. Botanical remedies with demonstrable anti-inflammatory capabilities may offer a valuable strategy for mitigating these effects.
- Inhibition of Inflammatory Mediators
Certain botanicals contain compounds that directly inhibit the production of inflammatory mediators such as cytokines and prostaglandins. By reducing the levels of these substances, the inflammatory response within the affected nerves can be dampened, leading to decreased pain and improved nerve function. Examples include curcumin from turmeric, which has been shown to suppress the NF-B pathway, a key regulator of inflammation.
- Antioxidant Activity and Inflammation
Oxidative stress, often associated with inflammation, can further damage nerve cells. Botanical agents with antioxidant properties, such as those found in green tea or berries, can neutralize free radicals and reduce oxidative damage, indirectly contributing to the resolution of inflammation within the nerves. This dual action is important for long-term nerve health and symptom management.
- Modulation of Immune Response
In some cases, nerve damage can elicit an autoimmune response, where the body’s immune system attacks nerve tissue. Certain botanicals possess immunomodulatory effects, helping to regulate the immune response and prevent further damage to the nerves. Examples include Boswellia, which has been traditionally used to reduce inflammation and modulate immune responses.
- Microglial Cell Activity Regulation
Microglial cells in the central nervous system become activated in response to nerve injury, contributing to neuroinflammation. Specific botanical compounds can modulate the activity of these cells, shifting them from a pro-inflammatory to an anti-inflammatory state, thereby promoting nerve repair and reducing pain signaling. This is an emerging area of research with promising therapeutic potential.
These mechanisms underscore the potential for botanical interventions to address the inflammatory component of nerve dysfunction. By targeting various stages of the inflammatory process, these remedies may contribute to symptom relief and improved nerve health. However, it’s crucial to note that further research is needed to fully elucidate the efficacy and safety of these approaches in the context of nerve-related ailments, and any botanical treatment should be undertaken under the guidance of a qualified healthcare professional.
2. Pain reduction mechanisms
The alleviation of pain is a primary objective in managing nerve disorders. Botanical interventions are often explored for their potential to modulate pain pathways and reduce discomfort associated with nerve damage.
- Capsaicin-Mediated Analgesia
Capsaicin, derived from chili peppers, interacts with TRPV1 receptors on sensory neurons. Initial application may induce a burning sensation, but prolonged exposure leads to desensitization of these receptors, resulting in reduced pain signaling. Topical capsaicin creams are used for pain management in various conditions, including some forms of nerve disorders.
- Anti-Inflammatory Pain Relief
Inflammation exacerbates pain. Botanicals with anti-inflammatory properties, such as curcumin from turmeric and boswellic acids from Boswellia, can reduce inflammatory mediators, thereby alleviating pain. These substances inhibit the production of prostaglandins and leukotrienes, reducing the sensitization of pain receptors.
- Nerve Signal Modulation
Certain herbs may modulate nerve signal transmission, reducing the perception of pain. For example, some compounds interact with sodium channels on nerve cell membranes, dampening the transmission of pain signals to the brain. This mechanism is similar to that of some pharmaceutical pain medications.
- Endogenous Opioid System Activation
Some botanical compounds are hypothesized to indirectly activate the body’s endogenous opioid system, leading to pain relief. This system involves the release of endorphins and other natural pain-relieving substances. While research is ongoing, certain herbs may stimulate this system to provide analgesic effects.
The listed mechanisms illustrate diverse pathways through which botanicals may influence pain perception in the context of nerve dysfunction. It is essential to recognize that individual responses can vary and that the efficacy of these approaches is subject to ongoing investigation. Consultation with a qualified healthcare professional is crucial before employing any botanical remedy for pain management.
3. Nerve regeneration support
Nerve regeneration represents a critical factor in the recovery from nerve damage, the underlying cause of peripheral neuropathy. The ability of a botanical intervention to support nerve regeneration directly influences its effectiveness in addressing the root cause of the condition, rather than merely masking symptoms. This regenerative capacity distinguishes potentially restorative treatments from those offering only palliative relief.
Certain botanical compounds are theorized to stimulate nerve growth factor (NGF) production or enhance the survival and differentiation of Schwann cells, the cells responsible for myelin sheath formation around nerve fibers. For instance, compounds found in Lion’s Mane mushroom are under investigation for their potential to promote NGF synthesis. Similarly, research explores the role of other botanicals in improving nerve cell metabolism and reducing oxidative stress, creating a more favorable environment for nerve regeneration. The success of these approaches depends on various factors, including the severity of nerve damage, individual patient characteristics, and the specific mechanisms of action of the botanical agent.
The incorporation of nerve regeneration support into a peripheral neuropathy treatment strategy offers the prospect of long-term improvement in nerve function and reduced reliance on symptomatic management. While botanical interventions may not guarantee complete nerve regeneration, their potential to facilitate this process underscores their significance in a holistic approach to peripheral neuropathy management. Ongoing research continues to evaluate the efficacy and safety of these botanical agents in promoting nerve repair.
4. Blood flow enhancement
Compromised blood circulation frequently exacerbates nerve damage associated with peripheral neuropathy. Insufficient delivery of oxygen and nutrients to peripheral nerves impairs their function and regenerative capacity. Enhancement of blood flow, therefore, constitutes a crucial component of strategies addressing nerve disorders. Specific botanical agents are investigated for their potential to improve microcirculation and overall vascular function, thereby supporting nerve health.
For example, Ginkgo biloba is often cited for its purported ability to improve blood flow to the extremities. Components within Ginkgo may promote vasodilation, increasing blood vessel diameter and facilitating greater blood supply to nerve tissues. Similarly, other botanicals may exert effects on blood viscosity, reducing the resistance to flow within smaller blood vessels. The combination of improved blood flow and nutrient delivery creates a more conducive environment for nerve repair and function. Real-life examples include individuals with diabetic neuropathy who incorporate Ginkgo biloba into their treatment regimen, under medical supervision, and report improved sensation and reduced pain. However, such anecdotal evidence requires rigorous clinical validation. The practical significance of this understanding lies in the potential to augment existing treatments for nerve disorders by addressing a key underlying factor: inadequate blood supply to the nerves.
While blood flow enhancement through botanical interventions shows promise, challenges remain in establishing definitive evidence of efficacy and safety. The variability in botanical preparations and individual patient responses necessitates careful consideration. Furthermore, potential interactions with pharmaceutical medications require thorough assessment. In summary, optimizing blood flow represents a valuable adjunct to comprehensive strategies for managing peripheral neuropathy, with botanical agents offering a potential avenue for achieving this goal. Further research is crucial to elucidate the precise mechanisms and clinical benefits associated with these interventions.
5. Antioxidant protection
Oxidative stress, characterized by an imbalance between free radical production and antioxidant defense mechanisms, contributes significantly to nerve damage in peripheral neuropathy. Free radicals, unstable molecules, can damage cellular structures, including nerve cells, leading to inflammation and impaired nerve function. Antioxidant protection, therefore, becomes a critical component of strategies aimed at mitigating the progression and severity of peripheral neuropathy. Botanical interventions with antioxidant properties offer a potential avenue for neutralizing free radicals and reducing oxidative damage to peripheral nerves.
Certain herbal remedies contain compounds known for their antioxidant capacity. For instance, alpha-lipoic acid, found in various plants and available as a supplement, functions as a potent antioxidant, scavenging free radicals and supporting the regeneration of other antioxidants like glutathione. Similarly, curcumin, the active compound in turmeric, exhibits both antioxidant and anti-inflammatory properties, contributing to nerve protection. The practical application of this understanding lies in the integration of antioxidant-rich botanical agents into a comprehensive treatment plan for peripheral neuropathy. For example, individuals with diabetic neuropathy might incorporate alpha-lipoic acid supplementation, under medical supervision, to reduce oxidative stress and alleviate symptoms. However, the effectiveness and safety of such interventions require careful evaluation and personalized guidance.
In summary, antioxidant protection plays a vital role in safeguarding peripheral nerves from oxidative damage. Botanical interventions with demonstrable antioxidant properties offer a potential strategy for mitigating the progression of peripheral neuropathy. While further research is necessary to fully elucidate the efficacy and optimal application of these interventions, the principle of reducing oxidative stress remains a cornerstone of nerve health management. Challenges persist in standardizing botanical preparations and addressing individual variations in response. A holistic approach, integrating antioxidant-rich botanicals with other therapeutic modalities, holds the most promise for comprehensive management of peripheral neuropathy.
6. Individual variability responses
Individual variability in response to botanical interventions for nerve dysfunction underscores a fundamental challenge in peripheral neuropathy management. The efficacy of herbal treatments can vary widely among individuals, due to an array of genetic, physiological, and lifestyle factors. Therefore, understanding and accounting for this variability is crucial for optimizing treatment outcomes.
- Pharmacogenomic Factors
Genetic variations influence drug metabolism and receptor sensitivity. These variations can affect how individuals process and respond to botanical compounds. For instance, differences in cytochrome P450 enzyme activity may alter the rate at which herbal constituents are metabolized, leading to varying concentrations in the body and, consequently, disparate therapeutic effects. This genetic heterogeneity necessitates personalized treatment approaches based on individual metabolic profiles.
- Physiological Differences
Factors such as age, sex, body weight, and overall health status contribute to individual physiological differences. These factors impact drug absorption, distribution, metabolism, and excretion. For example, older adults may exhibit reduced kidney function, affecting the clearance of herbal compounds and potentially increasing the risk of adverse effects. Similarly, individuals with underlying liver conditions may metabolize certain botanicals differently, leading to altered efficacy and safety profiles.
- Lifestyle and Environmental Influences
Diet, smoking habits, alcohol consumption, and exposure to environmental toxins can significantly influence individual responses to botanical treatments. These factors can affect liver enzyme activity, gut microbiome composition, and overall immune function, all of which impact the bioavailability and efficacy of herbal remedies. Therefore, comprehensive patient assessments should consider lifestyle and environmental influences to tailor treatment plans appropriately.
- Variations in Gut Microbiome
The gut microbiome plays a crucial role in metabolizing and transforming many botanical compounds. Individual differences in gut microbiota composition can lead to varying levels of bioactive metabolites produced from herbal remedies. This variability in metabolite production can impact the therapeutic efficacy and potential toxicity of botanical treatments. Understanding an individual’s gut microbiome profile may provide valuable insights for predicting their response to specific herbal interventions.
The interplay of pharmacogenomic factors, physiological differences, lifestyle influences, and variations in the gut microbiome collectively shapes individual responses to botanical treatments for peripheral neuropathy. Recognizing and addressing these sources of variability is essential for optimizing therapeutic outcomes and minimizing the risk of adverse effects. Future research efforts should focus on identifying predictive biomarkers and developing personalized treatment strategies based on individual patient characteristics. As an added point, patient education regarding expectations is key since results are not uniform.
Frequently Asked Questions
The following section addresses common inquiries regarding the application of botanical remedies in the management of peripheral neuropathy. The information provided is intended for educational purposes and does not constitute medical advice. Consultation with a qualified healthcare professional is essential before initiating any new treatment regimen.
Question 1: What constitutes “herbal treatment” in the context of peripheral neuropathy?
The phrase “herbal treatment” refers to the utilization of plant-derived substances, either in their whole form or as extracted compounds, to potentially alleviate the symptoms or address the underlying causes of peripheral neuropathy. This approach is predicated on the premise that certain botanicals possess therapeutic properties, such as anti-inflammatory, analgesic, or neuroprotective effects. It is essential to distinguish between traditional use and scientifically validated efficacy.
Question 2: Is there scientific evidence to support the use of herbal treatments for peripheral neuropathy?
The level of scientific evidence supporting the use of various herbal treatments for peripheral neuropathy varies considerably. Some botanicals, such as alpha-lipoic acid, have demonstrated efficacy in clinical trials, while others lack robust scientific support. The quality of evidence also varies, with some studies exhibiting methodological limitations. A critical evaluation of available evidence is necessary to determine the potential benefits and risks of each specific herbal remedy.
Question 3: What are the potential risks associated with using herbal treatments for peripheral neuropathy?
Herbal treatments are not without potential risks. These risks may include allergic reactions, interactions with prescription medications, and adverse effects on liver or kidney function. Furthermore, the quality and purity of herbal products can vary, leading to inconsistent dosages and potential contamination. It is crucial to obtain herbal remedies from reputable sources and to inform healthcare providers of all supplements being taken.
Question 4: Can herbal treatments cure peripheral neuropathy?
The term “cure” implies the complete elimination of the underlying cause of a disease. While some herbal treatments may alleviate symptoms and potentially support nerve regeneration, there is currently no definitive evidence to suggest that they can cure peripheral neuropathy in all cases. Management often involves a multifaceted approach addressing the underlying cause and managing symptoms.
Question 5: How does herbal treatment compare to conventional medical treatment for peripheral neuropathy?
Conventional medical treatment for peripheral neuropathy typically involves medications to manage pain (e.g., antidepressants, anticonvulsants) and address underlying causes (e.g., blood sugar control in diabetes). Herbal treatments may offer a complementary approach, but should not be considered a replacement for conventional medical care, especially in cases of severe or rapidly progressing neuropathy. Combination therapy, integrating both approaches, may be appropriate in certain circumstances, under the guidance of a healthcare professional.
Question 6: What qualifications should a healthcare provider have to advise on herbal treatment for peripheral neuropathy?
A healthcare provider advising on herbal treatment for peripheral neuropathy should possess a strong understanding of both conventional medicine and herbal pharmacology. This may include physicians, naturopathic doctors, or other licensed healthcare professionals with specialized training in herbal medicine. It is crucial to ensure that the provider is knowledgeable about potential interactions between herbal remedies and conventional medications, as well as the appropriate dosages and safety considerations for each individual patient.
In summary, the use of herbal treatments for peripheral neuropathy requires careful consideration of potential benefits, risks, and individual patient factors. Consultation with a qualified healthcare professional is essential to ensure safe and effective integration of herbal remedies into a comprehensive treatment plan.
The following section will explore the considerations of incorporating alternative therapies.
Peripheral Neuropathy Herbal Treatment
This exploration into the realm of “peripheral neuropathy herbal treatment” reveals a complex landscape of potential benefits and inherent limitations. While certain botanical interventions demonstrate promise in mitigating symptoms such as pain and inflammation, and may even support nerve regeneration, the existing scientific evidence remains variable. Factors such as individual variability in response, potential interactions with conventional medications, and the quality control of herbal products necessitate a cautious and informed approach.
The information presented underscores the importance of consulting with qualified healthcare professionals prior to incorporating any herbal remedy into a treatment plan for peripheral neuropathy. Responsible exploration of these alternative approaches demands rigorous scientific scrutiny, standardized product quality, and personalized treatment strategies. Future research efforts should prioritize elucidating the mechanisms of action of specific botanicals and conducting well-designed clinical trials to definitively establish their efficacy and safety. Only through such diligent investigation can the true potential of herbal treatments for peripheral neuropathy be realized while ensuring patient safety and well-being.