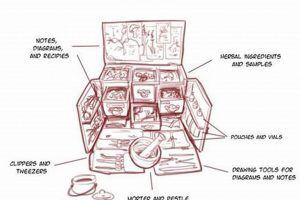
The convergence of botanical medicine and innovative delivery methods offers a sophisticated approach to mitigating kinetosis. This involves utilizing potent plant-derived compounds known for their anti-nausea and anti-vertigo properties, often formulated with enhanced absorption and targeted release mechanisms. For example, a liposomal ginger extract designed for sublingual administration represents such an advancement, bypassing the digestive system for faster relief.
This area of research is significant because it presents a potentially gentler alternative to conventional pharmaceuticals, often laden with side effects. Historically, various cultures have relied on herbs to manage motion-related discomfort. Modern science seeks to refine these traditional remedies, optimizing their efficacy and bioavailability through advanced technologies. This benefits individuals seeking natural preventative or therapeutic options, especially those sensitive to synthetic drugs.
The following article will delve into specific herbal remedies frequently used for motion sickness, the scientific evidence supporting their use, and the advancements in formulation and delivery systems that contribute to improved patient outcomes. This includes a discussion of dosage, potential interactions, and contraindications to ensure safe and effective application.
The following recommendations focus on utilizing plant-based solutions to alleviate motion sickness, incorporating advancements in herbal medicine for optimized results.
Tip 1: Prioritize Ginger Preparations. Ginger, known for its antiemetic properties, exhibits enhanced efficacy when processed using advanced extraction techniques to concentrate active compounds such as gingerol and shogaol. Consider standardized ginger extracts formulated for rapid absorption.
Tip 2: Explore Scopolamine Alternatives. While traditional scopolamine patches are effective, investigate herbal formulations containing belladonna alkaloids in carefully calibrated, lower doses to minimize potential side effects. Consult with a qualified healthcare professional regarding appropriate dosage.
Tip 3: Consider Peppermint Oil Inhalation. Peppermint oil, when inhaled, can stimulate the trigeminal nerve, potentially reducing nausea. Employ a diffuser or apply a diluted solution to a cloth for inhalation during travel. Ensure the peppermint oil is of therapeutic grade and appropriately diluted.
Tip 4: Investigate Bioavailability-Enhanced Formulations. Look for herbal remedies formulated with liposomes, phytosomes, or other technologies designed to improve the absorption and bioavailability of active compounds. These advancements can lead to greater efficacy at lower doses.
Tip 5: Combine Herbs Synergistically. Certain herbal combinations may offer enhanced relief. For example, pairing ginger with chamomile or lavender could provide both anti-nausea and calming effects. Research validated synergistic combinations.
Tip 6: Time Herbal Administration Strategically. Administer herbal remedies proactively, ideally 30-60 minutes prior to travel. This allows sufficient time for the active compounds to be absorbed and exert their effects before motion stimulation begins.
Tip 7: Maintain Hydration. Dehydration can exacerbate motion sickness symptoms. Drink plenty of water or herbal teas throughout the journey to maintain adequate hydration levels.
Implementing these tips can offer a proactive and potentially more tolerable approach to managing motion-induced discomfort, minimizing reliance on conventional pharmaceuticals.
The subsequent section will explore the scientific rationale behind these recommendations, detailing the mechanisms of action and supporting research.
1. Targeted Delivery Systems
The integration of targeted delivery systems represents a pivotal advancement in the application of herbal remedies for motion sickness. These systems enhance the efficacy and bioavailability of herbal compounds, addressing the limitations of traditional oral administration.
- Liposomal Encapsulation
Liposomes, microscopic vesicles composed of lipid bilayers, encapsulate herbal extracts, protecting them from degradation in the gastrointestinal tract. This encapsulation allows for enhanced absorption through cell membranes, delivering a higher concentration of active compounds to the bloodstream. For instance, liposomal ginger formulations have demonstrated improved anti-nausea effects compared to standard ginger capsules.
- Nanoparticle Delivery
Nanoparticles, even smaller than liposomes, offer another avenue for targeted delivery. These particles can be engineered to target specific areas of the body, such as the vestibular system, which plays a key role in motion sickness. The precise targeting minimizes systemic exposure, potentially reducing side effects and maximizing therapeutic benefit.
- Transdermal Patches
While often associated with synthetic drugs, transdermal patches are being explored for herbal applications. These patches allow for the slow and controlled release of herbal extracts through the skin, providing a sustained therapeutic effect. This approach bypasses the digestive system, reducing the risk of gastrointestinal irritation and ensuring a consistent drug level in the bloodstream. For example, research is underway to develop ginger-based transdermal patches for motion sickness prevention.
- Sublingual Administration
Sublingual delivery, involving placing a tablet or liquid under the tongue, allows for direct absorption of herbal compounds into the bloodstream, bypassing the first-pass metabolism in the liver. This results in a faster onset of action and higher bioavailability compared to oral administration. Sublingual formulations are particularly useful for acute episodes of motion sickness, offering rapid relief.
These targeted delivery systems transform the landscape of herbal motion sickness management, moving beyond traditional preparations to offer more effective, efficient, and convenient solutions. The continued development and refinement of these technologies promise to unlock the full potential of herbal remedies for mitigating motion-induced discomfort.
2. Enhanced Bioavailability
Enhanced bioavailability forms a cornerstone of advanced herbal motion sickness treatments. Bioavailability, in essence, defines the degree and rate at which an active ingredient is absorbed from a drug product and becomes available at the site of action. For herbal remedies, which often face challenges related to poor absorption and rapid metabolism, enhancing bioavailability is paramount. This enhancement directly impacts the clinical effectiveness of the herbal intervention.
The connection between enhanced bioavailability and advanced herbal motion sickness solutions is causal: advancements in formulation techniques directly improve the absorption and utilization of key herbal compounds, leading to greater therapeutic benefit. For instance, curcumin, a potent anti-inflammatory compound from turmeric, exhibits limited bioavailability in its natural form. However, when formulated with phospholipids to create a phytosome, absorption increases significantly, resulting in improved anti-nausea and anti-inflammatory effects relevant to motion sickness. Similarly, quercetin formulated with galactomannans displays enhanced bioavailability, potentially amplifying its anti-vertigo properties. The practical significance lies in achieving therapeutic concentrations of the active compounds within the body, thereby maximizing the likelihood of symptom relief and preventing motion sickness episodes.
Without enhanced bioavailability, even the most promising herbal remedies may fail to deliver satisfactory results. This understanding underscores the necessity of prioritizing advanced formulations, such as liposomes, nanoparticles, and phospholipid complexes, in the development of effective herbal motion sickness treatments. These formulations address the inherent limitations of traditional herbal preparations, ensuring that patients receive the full benefits of botanical medicine. While challenges remain in optimizing these delivery systems and conducting rigorous clinical trials, the focus on enhancing bioavailability represents a critical step towards more reliable and potent herbal interventions for motion sickness.
3. Synergistic Herb Combinations
Synergistic herb combinations represent a sophisticated approach to managing motion sickness, constituting a crucial component of advanced herbal solutions. This principle posits that combining specific herbs can produce a therapeutic effect greater than the sum of their individual actions. The underlying mechanism involves multiple active compounds targeting different physiological pathways involved in the etiology of motion sickness, such as the vestibular system, gastrointestinal tract, and central nervous system. This multi-target approach enhances overall efficacy and minimizes the reliance on single-ingredient solutions, potentially reducing the risk of adverse effects.
A compelling example is the combination of ginger and peppermint. Ginger’s antiemetic properties, primarily attributed to gingerols and shogaols, help to suppress nausea and vomiting by modulating gastric motility and serotonin receptors. Peppermint, on the other hand, offers carminative and spasmolytic effects, relieving gastrointestinal discomfort often associated with motion sickness. Moreover, its menthol content may provide a calming effect, further contributing to symptom relief. The combined effect addresses both the nausea and the accompanying digestive distress, resulting in a more comprehensive therapeutic outcome. Similarly, a blend of chamomile and lavender, while individually known for their anxiolytic properties, can synergistically reduce anxiety and promote relaxation, which is particularly beneficial for individuals prone to motion sickness triggered by anxiety or fear. The practical significance of this synergistic effect lies in the optimization of therapeutic outcomes, potentially enabling lower dosages of individual herbs while achieving superior results.
However, developing effective synergistic herb combinations necessitates careful consideration of herb-herb interactions, potential contraindications, and individual patient factors. Rigorous scientific research, including preclinical and clinical studies, is essential to validate the efficacy and safety of these combinations. Furthermore, standardization of herbal extracts and precise dosage formulations are critical to ensure consistent therapeutic effects. Despite these challenges, the strategic combination of herbs holds significant promise for advancing the management of motion sickness, offering a more holistic and personalized approach compared to conventional single-agent pharmacotherapy. Future research should focus on identifying and validating novel synergistic combinations, optimizing their formulations, and elucidating the underlying mechanisms of action.
4. Individual Sensitivity Variations
The effectiveness of advanced herbal interventions for motion sickness is significantly modulated by individual sensitivity variations. These variations, stemming from genetic predispositions, physiological differences, and environmental factors, dictate how individuals respond to specific herbal compounds and formulations.
- Genetic Polymorphisms and Metabolic Capacity
Genetic variations in drug-metabolizing enzymes, such as cytochrome P450 (CYP) enzymes, can influence the rate at which herbal compounds are metabolized and cleared from the body. Individuals with certain CYP polymorphisms may experience either enhanced or diminished responses to specific herbs. For instance, individuals with reduced CYP2D6 activity may exhibit a prolonged effect from certain herbal antiemetics, potentially leading to adverse reactions.
- Physiological Factors and Vestibular Function
The sensitivity of the vestibular system, responsible for balance and spatial orientation, varies across individuals. This inherent variability influences susceptibility to motion sickness and, consequently, the effectiveness of herbal remedies targeting vestibular function. Some individuals may require higher doses or more potent formulations to achieve symptom relief, while others may experience adverse effects even at low doses.
- Prior Exposure and Sensitization
Previous exposure to herbal compounds can alter an individual’s sensitivity. Sensitization, a process by which repeated exposure to an allergen or irritant leads to an exaggerated response, can occur with certain herbs. This can manifest as allergic reactions or increased sensitivity to side effects. Conversely, long-term use of certain herbs may lead to tolerance, requiring higher doses to achieve the desired effect.
- Gut Microbiome Composition and Herbal Metabolism
The composition of the gut microbiome influences the metabolism of many herbal compounds. Certain gut bacteria can metabolize herbal constituents into more or less active metabolites, affecting their bioavailability and efficacy. Individuals with distinct gut microbiome profiles may exhibit varying responses to the same herbal intervention. Pre- or probiotic supplementation, aimed at modulating the gut microbiome, may influence the effectiveness of herbal motion sickness remedies.
These diverse facets of individual sensitivity underscore the importance of personalized approaches in utilizing advanced herbal therapies for motion sickness. Understanding these variations can guide clinicians in tailoring treatment plans, optimizing dosages, and minimizing the risk of adverse effects. Further research is warranted to identify specific biomarkers that predict individual responses to herbal interventions, enabling a more targeted and effective therapeutic strategy.
5. Proactive administration timing
Proactive administration timing is a critical determinant in the efficacy of advanced herbal interventions for motion sickness. The rationale stems from the need for herbal compounds to reach therapeutic concentrations in the body before the onset of motion-induced stimuli. Delaying administration until symptoms manifest often results in diminished effectiveness, as the body’s physiological response to motion sickness, including the release of emetic signals, is already underway. This timing constitutes a foundational element of the “advanced” approach, contrasting with reactive strategies often employed with conventional medications.
The relationship between proactive timing and the successful application of herbal remedies is exemplified by ginger. Ginger, known for its antiemetic properties, requires a period of absorption and distribution to exert its effects on the gastrointestinal tract and central nervous system. Administering ginger extracts or formulations (e.g., capsules, chews) approximately 30-60 minutes before travel allows active constituents like gingerols and shogaols to modulate gastric motility and serotonin receptors, thereby preempting the onset of nausea and vomiting. Similarly, for herbal combinations targeting anxiety associated with travel, such as lavender and chamomile, pre-emptive administration supports relaxation and mitigates the anticipatory anxiety that can exacerbate motion sickness. This proactive approach aligns the timing of peak herbal activity with the anticipated period of motion exposure, maximizing therapeutic impact.
Therefore, integrating proactive administration timing into herbal motion sickness management necessitates a shift from reactive symptom management to preventative strategies. While individual responses may vary, adhering to recommended pre-exposure dosing schedules significantly enhances the likelihood of successful symptom control. Challenges remain in educating patients on the importance of timing and ensuring adherence to prescribed regimens. Further research is needed to optimize dosing intervals and explore novel delivery methods that facilitate rapid absorption and prolonged therapeutic effects. By emphasizing proactive administration, the full potential of advanced herbal solutions for motion sickness can be realized.
6. Adjunctive Therapies Integration
The incorporation of adjunctive therapies represents a sophisticated and patient-centered approach to managing motion sickness, enhancing the efficacy of advanced herbal interventions. These therapies, employed alongside herbal remedies, address the multifactorial nature of kinetosis by targeting different aspects of the condition, promoting a more comprehensive and personalized treatment strategy.
- Acupressure and Acupuncture
Stimulation of specific acupoints, such as P6 (Neiguan) on the wrist, has demonstrated efficacy in reducing nausea and vomiting. Integrating acupressure or acupuncture with herbal remedies may amplify the antiemetic effect, offering synergistic relief. The proposed mechanism involves modulating the vagal nerve and influencing gastrointestinal motility. Clinical studies suggest that combining acupressure with ginger can significantly reduce motion sickness symptoms compared to either therapy alone.
- Behavioral and Cognitive Strategies
Cognitive behavioral therapy (CBT) and related techniques, such as relaxation exercises and guided imagery, can help manage anxiety and anticipatory nausea associated with motion sickness. Integrating these strategies with herbal interventions addresses the psychological component of the condition, improving overall well-being and treatment adherence. For instance, pairing mindfulness meditation with lavender aromatherapy may reduce anxiety-induced nausea.
- Vestibular Rehabilitation
Vestibular rehabilitation exercises, designed to improve balance and reduce sensitivity to motion, can complement herbal remedies targeting the vestibular system. These exercises promote habituation to motion stimuli, reducing the likelihood of motion sickness episodes. Integrating vestibular rehabilitation with herbs such as ginger or ginkgo biloba may enhance vestibular function and improve symptom control.
- Dietary Modifications
Specific dietary changes, such as avoiding heavy meals, spicy foods, and alcohol before and during travel, can mitigate gastrointestinal distress and reduce the likelihood of motion sickness. Integrating these dietary modifications with herbal interventions optimizes the body’s physiological response to motion stimuli. For example, consuming light, easily digestible snacks and herbal teas during travel can help stabilize blood sugar levels and reduce nausea.
These adjunctive therapies, when thoughtfully integrated with advanced herbal solutions, provide a holistic and individualized approach to managing motion sickness. This multifaceted strategy addresses not only the physiological but also the psychological and behavioral aspects of the condition, ultimately leading to improved patient outcomes and a better quality of life.
7. Long-term usage safety
Long-term usage safety is paramount when considering advanced herbal interventions for motion sickness. While botanicals are often perceived as inherently safe, chronic use can lead to unforeseen consequences, including adverse effects, herb-drug interactions, and the development of tolerance. The term “advanced” implies a refined understanding of these risks, necessitating rigorous evaluation and monitoring. The absence of robust long-term safety data for many herbal remedies presents a significant challenge, making continuous surveillance and careful patient management essential. Real-life examples highlight the importance of this consideration. For instance, prolonged use of certain anti-nausea herbs like ginger, while generally well-tolerated, may potentially interact with blood-thinning medications. Similarly, belladonna alkaloids, sometimes used in low doses for motion sickness, carry the risk of anticholinergic side effects with extended use, particularly in susceptible individuals such as the elderly. Understanding the potential for these long-term consequences is crucial for informed decision-making and responsible application of advanced herbal strategies.
Practical applications of this understanding necessitate a proactive approach. This includes thorough patient history-taking to identify pre-existing conditions and concurrent medication use, regular monitoring for potential side effects, and periodic assessment of treatment efficacy to minimize unnecessary long-term exposure. Dose adjustments based on individual responses and consideration of intermittent dosing schedules can further mitigate the risk of cumulative toxicity. Furthermore, rigorous quality control measures are essential to ensure the purity and standardization of herbal products, minimizing the potential for adulteration or contamination that could compromise long-term safety. Open communication between patients and healthcare providers is crucial for reporting any adverse events and adjusting treatment plans accordingly. The development of comprehensive databases documenting long-term safety data for herbal remedies remains a priority.
In summary, long-term usage safety is an indispensable component of advanced herbal motion sickness management. Addressing the challenges associated with limited long-term data requires a multifaceted approach encompassing careful patient selection, diligent monitoring, quality control measures, and ongoing research. By prioritizing safety and acknowledging the potential risks associated with chronic herbal use, healthcare professionals can ensure that patients receive the maximum benefit from these interventions while minimizing the likelihood of adverse outcomes. This commitment to safety is fundamental to advancing the responsible and sustainable application of herbal medicine for motion sickness.
Frequently Asked Questions
This section addresses common inquiries regarding the application of advanced herbal approaches to mitigate motion sickness. Information provided is intended to enhance understanding and inform decision-making.
Question 1: What constitutes “advanced” in the context of herbal motion sickness remedies?
The term “advanced” refers to formulations and delivery methods that enhance the bioavailability, efficacy, and targeted action of herbal compounds. This includes techniques such as liposomal encapsulation, nanoparticle delivery, and synergistic herb combinations.
Question 2: Are advanced herbal motion sickness remedies suitable for all individuals?
Suitability varies depending on individual factors such as age, medical history, concurrent medications, and specific sensitivities. Consultation with a qualified healthcare professional is recommended to determine appropriateness and ensure safety.
Question 3: How do advanced herbal remedies compare to conventional medications for motion sickness?
Advanced herbal remedies may offer a gentler alternative for some individuals, potentially with fewer side effects. However, the efficacy of herbal interventions can vary, and conventional medications may be more appropriate in certain cases. A balanced evaluation of potential benefits and risks is essential.
Question 4: What are some examples of synergistic herb combinations used in advanced motion sickness treatments?
Common examples include ginger combined with peppermint for nausea and digestive relief, and chamomile or lavender paired with antiemetic herbs to address anxiety-related symptoms. The specific combination should be tailored to individual needs and preferences.
Question 5: How can bioavailability be enhanced in herbal motion sickness formulations?
Bioavailability can be improved through various techniques, including liposomal encapsulation, phytosome complexation, and nanoparticle delivery. These methods protect herbal compounds from degradation and enhance their absorption into the bloodstream.
Question 6: Are there any potential risks associated with long-term use of advanced herbal motion sickness remedies?
Long-term use may pose risks such as herb-drug interactions, development of tolerance, and unforeseen adverse effects. Regular monitoring by a healthcare professional is essential to mitigate these risks.
The key takeaway is that advanced herbal motion sickness management requires a personalized and informed approach, incorporating advanced formulations, synergistic combinations, and careful consideration of individual factors. Consultation with a healthcare provider is essential for safe and effective implementation.
The following section will summarize the key findings and provide concluding remarks.
Advanced Herbal Motion Sickness
This exploration of advanced herbal motion sickness interventions has highlighted key aspects of botanical remedies. The integration of targeted delivery systems, enhanced bioavailability techniques, and strategic herb combinations represents a significant evolution in managing kinetosis. Individualized approaches, acknowledging varying sensitivities and incorporating adjunctive therapies, further optimize treatment outcomes. However, responsible application necessitates careful consideration of long-term usage safety and the potential for herb-drug interactions.
Continued research and rigorous clinical trials are crucial to validate the efficacy and safety of these advanced herbal strategies. As the scientific understanding of herbal medicine deepens, opportunities emerge for developing more precise and effective interventions for motion sickness and other related conditions. Further advancements in formulation technology and personalized medicine hold promise for maximizing the therapeutic potential of herbal remedies while minimizing potential risks, ultimately improving the quality of life for individuals susceptible to motion-induced discomfort.